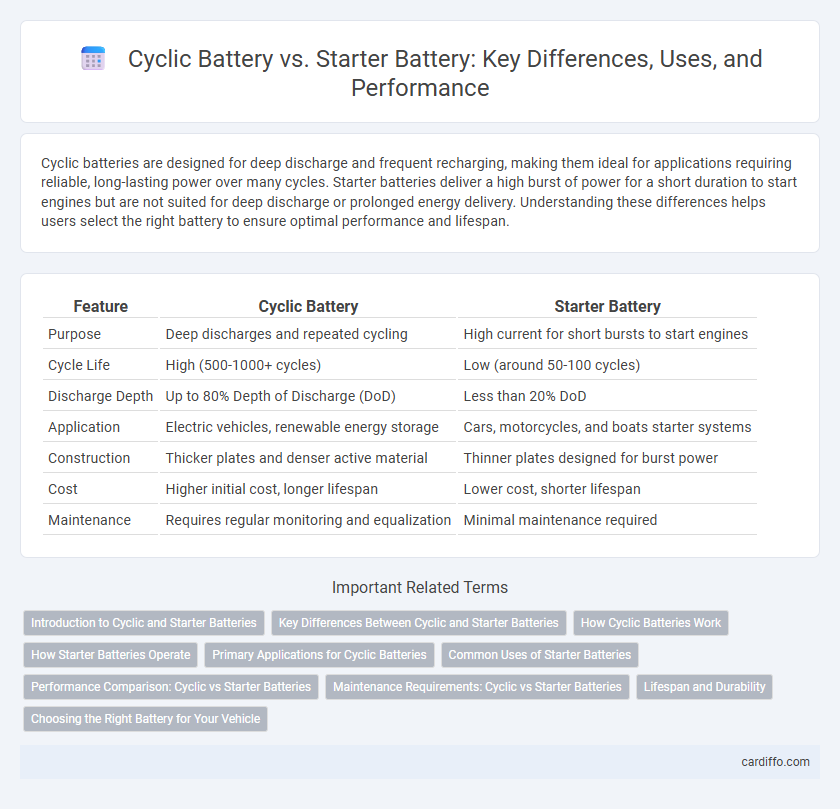
Cyclic batteries are designed for deep discharge and frequent recharging, making them ideal for applications requiring reliable, long-lasting power over many cycles. Starter batteries deliver a high burst of power for a short duration to start engines but are not suited for deep discharge or prolonged energy delivery. Understanding these differences helps users select the right battery to ensure optimal performance and lifespan.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cyclic Battery | Starter Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Deep discharges and repeated cycling | High current for short bursts to start engines |
| Cycle Life | High (500-1000+ cycles) | Low (around 50-100 cycles) |
| Discharge Depth | Up to 80% Depth of Discharge (DoD) | Less than 20% DoD |
| Application | Electric vehicles, renewable energy storage | Cars, motorcycles, and boats starter systems |
| Construction | Thicker plates and denser active material | Thinner plates designed for burst power |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, longer lifespan | Lower cost, shorter lifespan |
| Maintenance | Requires regular monitoring and equalization | Minimal maintenance required |
Introduction to Cyclic and Starter Batteries
Cyclic batteries are designed for deep discharges and repeated charge and discharge cycles, making them ideal for applications like solar energy storage and electric vehicles. Starter batteries provide high bursts of power for short durations to start engines, commonly used in automotive ignition systems. Understanding the distinct performance characteristics and typical uses of cyclic and starter batteries helps optimize energy solutions for specific needs.
Key Differences Between Cyclic and Starter Batteries
Cyclic batteries are designed for deep discharge and recharge cycles, delivering sustained power over extended periods, making them ideal for applications like solar energy systems and electric vehicles. Starter batteries provide short bursts of high current to start engines, with limited capacity for deep discharges and faster recharging suitable for automotive use. Key differences include cyclic batteries' higher cycle life and depth of discharge tolerance, whereas starter batteries prioritize delivering immediate, high cranking amps.
How Cyclic Batteries Work
Cyclic batteries operate by undergoing repeated deep discharge and recharge cycles, making them ideal for applications requiring sustained energy delivery over time, such as renewable energy storage and electric vehicles. These batteries utilize thicker plates and robust active materials to withstand frequent cycling without significant capacity loss. Their design enables efficient energy release and storage through chemical reactions that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa, optimizing longevity and performance.
How Starter Batteries Operate
Starter batteries operate by delivering a high burst of current for a short duration, enabling quick engine ignition in vehicles. These batteries utilize thin plates made of lead and lead oxide, optimizing them for rapid energy discharge rather than deep cycling. Unlike cyclic batteries, starter batteries are designed to provide maximum cranking power without sustaining long-term energy depletion, ensuring reliable engine starts.
Primary Applications for Cyclic Batteries
Cyclic batteries are primarily designed for deep discharge and recharge cycles, making them ideal for renewable energy storage, electric vehicles, and backup power systems where sustained energy output is critical. They excel in applications requiring frequent cycling and high capacity retention over time, unlike starter batteries that deliver short bursts of high current to initiate engine ignition. The robust construction and enhanced chemical stability of cyclic batteries ensure longevity and reliability in off-grid solar setups and marine or RV energy systems.
Common Uses of Starter Batteries
Starter batteries are primarily used in vehicles to deliver a high burst of power needed to start internal combustion engines. These batteries are designed to provide quick, high-current energy for a short duration, making them ideal for cars, motorcycles, and boats. Unlike cyclic batteries, which support deep discharge and multiple recharge cycles, starter batteries focus on reliable engine cranking performance.
Performance Comparison: Cyclic vs Starter Batteries
Cyclic batteries excel in deep discharge performance, maintaining capacity and lifespan during repeated charge-discharge cycles, making them ideal for applications like solar energy storage and electric vehicles. Starter batteries are optimized for delivering high burst currents needed to start engines but are not designed for frequent deep discharges, which can significantly reduce their lifespan. Performance metrics such as cycle life, depth of discharge (DoD), and reserve capacity distinctly favor cyclic batteries for prolonged use, while starter batteries prioritize cranking power and rapid recharge.
Maintenance Requirements: Cyclic vs Starter Batteries
Cyclic batteries require regular deep discharge and recharge cycles to maintain optimal performance and prevent capacity loss, often necessitating scheduled maintenance and careful monitoring of charge levels. Starter batteries demand minimal maintenance as they are designed to provide short, high-current bursts for engine starting and typically operate at a high state of charge without frequent deep discharges. Proper maintenance of cyclic batteries involves balancing electrolyte levels and ensuring accurate charging, while starter batteries mainly require corrosion checks and voltage testing to ensure reliability.
Lifespan and Durability
Cyclic batteries are designed for deep discharge and recharge cycles, offering a longer lifespan of up to 1,000 cycles due to their durable construction suited for sustained energy delivery. Starter batteries are optimized for short, high-current bursts to start engines but have a shorter lifespan, typically around 200 to 300 cycles, because they are not built to endure repeated deep discharges. The enhanced durability of cyclic batteries makes them ideal for applications requiring frequent use and reliable performance over time.
Choosing the Right Battery for Your Vehicle
Cyclic batteries are designed for deep discharge and recharge cycles, making them ideal for electric vehicles and recreational use where continuous power supply is necessary. Starter batteries, on the other hand, provide high bursts of energy to start internal combustion engines, suitable for cars, trucks, and motorcycles that require quick ignition. Selecting the right battery depends on your vehicle's power demands and usage patterns, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Cyclic Battery vs Starter Battery Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com