Stage 1 tuning typically involves basic modifications such as air intake, exhaust systems, and ECU remapping to optimize engine performance without requiring hardware changes. Stage 2 tuning goes further by incorporating upgraded components like high-flow intercoolers, turbochargers, or exhaust headers to significantly increase power output and engine efficiency. Choosing between Stage 1 and Stage 2 depends on the desired performance goals and the vehicle's capacity to handle increased stress.
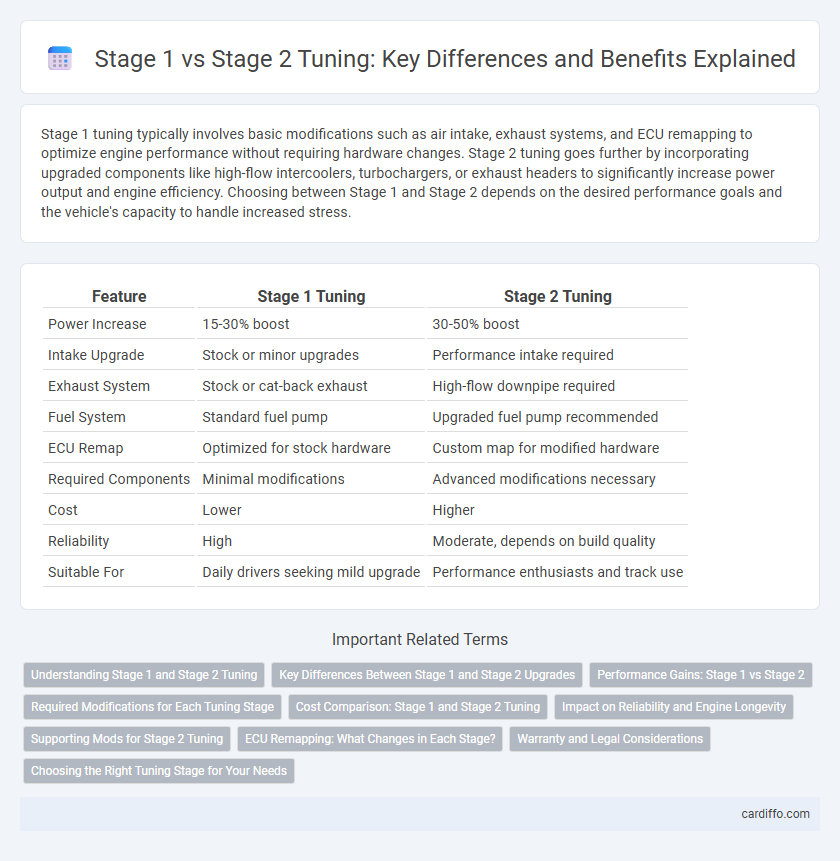
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stage 1 Tuning | Stage 2 Tuning |
|---|---|---|
| Power Increase | 15-30% boost | 30-50% boost |
| Intake Upgrade | Stock or minor upgrades | Performance intake required |
| Exhaust System | Stock or cat-back exhaust | High-flow downpipe required |
| Fuel System | Standard fuel pump | Upgraded fuel pump recommended |
| ECU Remap | Optimized for stock hardware | Custom map for modified hardware |
| Required Components | Minimal modifications | Advanced modifications necessary |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Reliability | High | Moderate, depends on build quality |
| Suitable For | Daily drivers seeking mild upgrade | Performance enthusiasts and track use |
Understanding Stage 1 and Stage 2 Tuning
Stage 1 tuning primarily focuses on optimizing basic engine parameters such as air-fuel ratio and ignition timing to enhance performance while maintaining factory components. Stage 2 tuning involves more extensive modifications, including upgraded hardware like intake, exhaust, and intercoolers, allowing for higher power gains and improved efficiency. Understanding the distinctions between Stage 1 and Stage 2 tuning helps in selecting the appropriate level of upgrade based on vehicle modifications and desired performance outcomes.
Key Differences Between Stage 1 and Stage 2 Upgrades
Stage 1 tuning primarily involves software modifications such as ECU remapping to optimize engine performance without altering hardware components, resulting in moderate gains in horsepower and torque while maintaining factory reliability and emissions standards. In contrast, Stage 2 upgrades combine ECU tuning with hardware enhancements like upgraded intake, exhaust systems, or turbochargers, delivering significantly higher power output and improved throttle response but often requiring enhanced cooling and fuel delivery systems. The key differences lie in the complexity, cost, and performance potential, with Stage 2 offering a more aggressive setup that demands careful calibration for long-term durability.
Performance Gains: Stage 1 vs Stage 2
Stage 1 tuning primarily enhances basic engine parameters such as air-fuel ratio and ignition timing, resulting in moderate performance gains typically around 15-20% horsepower increase. Stage 2 tuning builds on Stage 1 by incorporating hardware modifications like upgraded exhaust systems and turbochargers, delivering substantially higher power boosts often reaching 30-40%. The performance gap between Stage 1 and Stage 2 is significant, with Stage 2 offering improved throttle response, torque curve enhancement, and optimized boost pressure for advanced driving dynamics.
Required Modifications for Each Tuning Stage
Stage 1 tuning typically requires basic modifications such as an upgraded intake system, a high-flow air filter, and a performance exhaust to improve airflow and engine efficiency. Stage 2 tuning demands more extensive changes including a larger turbocharger or supercharger, upgraded fuel injectors, and an enhanced intercooler to handle increased power output and maintain engine reliability. Each stage's required modifications directly correspond to the achieved horsepower gains and overall vehicle performance improvements.
Cost Comparison: Stage 1 and Stage 2 Tuning
Stage 1 tuning generally costs between $300 and $600, offering basic performance enhancements by optimizing factory parameters without major hardware changes. Stage 2 tuning, priced from $700 to $1,200, involves more extensive modifications such as upgraded exhaust or intake systems, resulting in higher costs but significantly increased horsepower and torque. Evaluating the cost difference alongside performance gains is crucial for drivers seeking the best value upgrade for their vehicle.
Impact on Reliability and Engine Longevity
Stage 1 tuning offers moderate performance enhancements with minimal impact on engine reliability and longevity, maintaining factory safety margins. In contrast, Stage 2 tuning pushes the engine closer to its limits by increasing boost and fuel delivery, which can accelerate wear and reduce lifespan if not properly managed. Proper cooling and regular maintenance are critical to mitigate the risks associated with Stage 2 upgrades.
Supporting Mods for Stage 2 Tuning
Stage 2 tuning requires supporting mods such as high-flow downpipes, upgraded intercoolers, and performance exhaust systems to maximize turbo efficiency and engine output. These modifications improve airflow, reduce heat buildup, and enhance overall durability, enabling the ECU to safely increase boost pressure and fuel delivery. Proper supporting mods ensure reliable power gains and prevent potential engine damage during aggressive tuning stages.
ECU Remapping: What Changes in Each Stage?
Stage 1 ECU remapping primarily targets the engine control unit's software to enhance fuel delivery and ignition timing, optimizing performance without requiring hardware modifications. Stage 2 tuning builds on Stage 1 by incorporating adjustments for upgraded components like a high-flow exhaust or intake, boosting power output further through refined air-fuel ratios and advanced torque management. Each stage modifies engine parameters to maximize efficiency and power within the constraints of existing or enhanced hardware setups.
Warranty and Legal Considerations
Stage 1 tuning typically maintains the vehicle's factory warranty and complies with legal emission standards by using manufacturer-approved software updates and minimally invasive modifications. Stage 2 tuning often includes more extensive hardware changes that may void the factory warranty and risk non-compliance with local emission regulations, potentially leading to legal penalties. Vehicle owners must carefully evaluate warranty terms and local laws before opting for Stage 2 upgrades to avoid unforeseen costs and legal issues.
Choosing the Right Tuning Stage for Your Needs
Stage 1 tuning offers a basic upgrade by optimizing the engine control unit (ECU) parameters for improved power and fuel efficiency without requiring hardware modifications. Stage 2 tuning involves both ECU adjustments and supporting hardware enhancements like upgraded intakes and exhausts, delivering significant performance gains suitable for enthusiasts seeking more aggressive driving dynamics. Selecting the right tuning stage depends on your vehicle's current setup, performance goals, and budget, ensuring the upgrade aligns with your driving needs and reliability expectations.
Stage 1 vs Stage 2 tuning Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com