RFID tags and transponders are essential for efficient toll collection, enabling automatic vehicle identification and seamless payment processing. RFID tags typically operate using passive technology, relying on radio waves from the reader to transmit data, while transponders often incorporate active components with internal power sources for extended range and functionality. Choosing between RFID tags and transponders depends on factors like system range, cost, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal tolling performance.
Table of Comparison
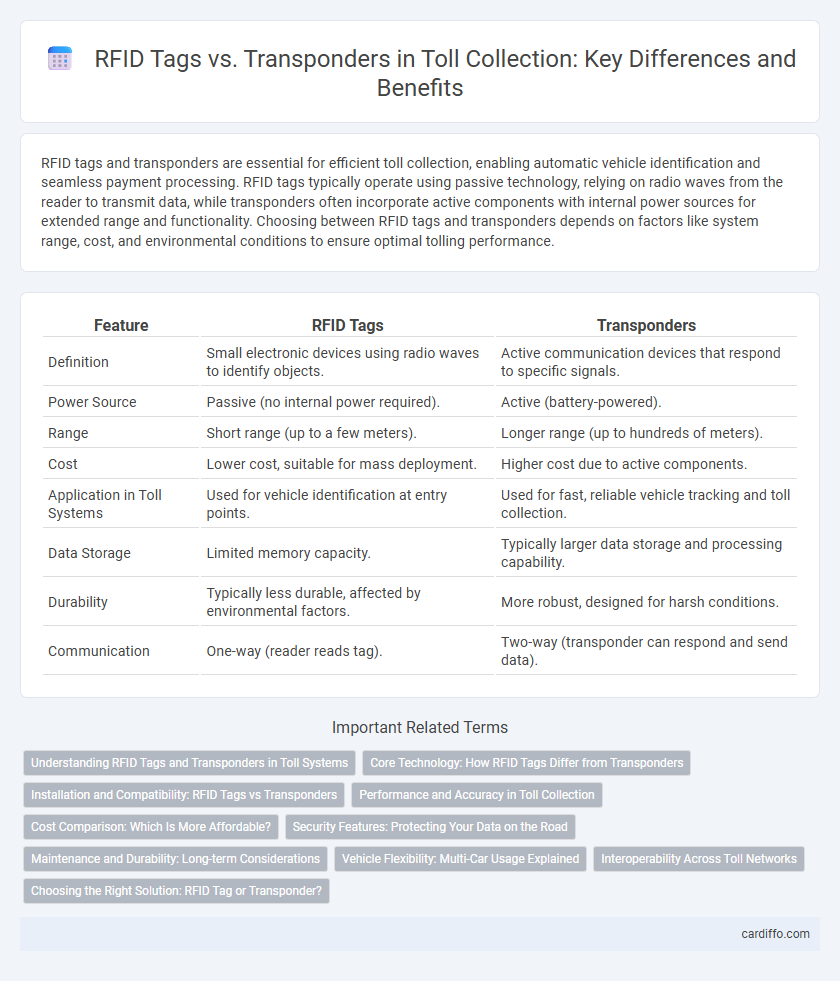
| Feature | RFID Tags | Transponders |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small electronic devices using radio waves to identify objects. | Active communication devices that respond to specific signals. |
| Power Source | Passive (no internal power required). | Active (battery-powered). |
| Range | Short range (up to a few meters). | Longer range (up to hundreds of meters). |
| Cost | Lower cost, suitable for mass deployment. | Higher cost due to active components. |
| Application in Toll Systems | Used for vehicle identification at entry points. | Used for fast, reliable vehicle tracking and toll collection. |
| Data Storage | Limited memory capacity. | Typically larger data storage and processing capability. |
| Durability | Typically less durable, affected by environmental factors. | More robust, designed for harsh conditions. |
| Communication | One-way (reader reads tag). | Two-way (transponder can respond and send data). |
Understanding RFID Tags and Transponders in Toll Systems
RFID tags and transponders play crucial roles in toll collection systems by enabling automatic vehicle identification and seamless payment processing. RFID tags, typically passive devices, use radio frequency to communicate with toll readers, while transponders are active devices that transmit signals for faster and more reliable detection. Understanding the differences in functionality and signal range between RFID tags and transponders helps optimize toll system efficiency and reduce traffic congestion.
Core Technology: How RFID Tags Differ from Transponders
RFID tags utilize passive or active radio frequency identification technology, relying on electromagnetic fields to transmit data without requiring a power source for passive tags, whereas transponders are active devices that both receive and transmit signals with their own power supply. The core technology difference lies in RFID tags often being simpler, smaller, and used for identification and tracking, while transponders perform more complex communication functions with longer ranges. In toll systems, RFID tags enable quick vehicle identification with minimal infrastructure, whereas transponders facilitate two-way communication for enhanced data exchange and secure transactions.
Installation and Compatibility: RFID Tags vs Transponders
RFID tags generally offer easier installation due to their compact, adhesive design that can be quickly affixed to vehicles or assets without specialized equipment. Transponders, often requiring mounting brackets and precise alignment with toll readers, involve more complex installation procedures but provide enhanced durability for long-term use. Compatibility varies as RFID tags are widely supported across different toll systems and vehicle types, whereas transponders are typically compatible only with specific toll network protocols, limiting their universal application.
Performance and Accuracy in Toll Collection
RFID tags offer high-speed vehicle identification with a read accuracy rate exceeding 99%, making them ideal for seamless toll collection at high traffic volumes. Transponders provide robust signal transmission and maintain consistent performance even in adverse weather conditions, ensuring reliable data capture. Both technologies enhance transaction speed, but RFID tags excel in multi-lane free-flow environments due to precise vehicle detection and minimal read errors.
Cost Comparison: Which Is More Affordable?
RFID tags generally offer a more affordable option compared to transponders due to lower manufacturing and deployment costs, making them suitable for large-scale toll systems. Transponders, featuring advanced signal processing and enhanced range capabilities, tend to be pricier but provide reliable performance in complex environments. Choosing between RFID tags and transponders hinges on balancing upfront expenses against long-term operational efficiency in toll collection systems.
Security Features: Protecting Your Data on the Road
RFID tags used in toll systems often offer basic encryption to protect vehicle and payment data, whereas transponders incorporate advanced security protocols such as mutual authentication and rolling codes to prevent cloning and unauthorized access. These enhanced security features in transponders ensure higher protection against data interception and fraud during toll transactions. Choosing transponders over standard RFID tags significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and maintains the integrity of road usage records.
Maintenance and Durability: Long-term Considerations
RFID tags generally require less maintenance due to their passive nature and lack of internal power sources, which reduces the risk of failure over time in toll systems. Transponders, often active devices with batteries, may need regular service or replacement to maintain reliability and durability, especially under harsh environmental conditions. Long-term toll operations benefit from RFID tags' extended lifespan and minimal upkeep, contributing to lower overall maintenance costs.
Vehicle Flexibility: Multi-Car Usage Explained
RFID tags offer greater vehicle flexibility compared to traditional transponders, as they can be easily transferred between different cars, making them ideal for multi-car households or fleets. Unlike transponders that are often fixed to a single vehicle, RFID tags adhere to the windshield or license plate and do not require electronic pairing, enabling seamless toll payments across multiple vehicles. This multi-car usage advantage reduces the need for multiple accounts or devices, streamlining toll management and lowering overall costs for users.
Interoperability Across Toll Networks
RFID tags offer broad interoperability across diverse toll networks by utilizing standardized frequency bands and communication protocols, enabling seamless vehicle identification and payment processing. Transponders, while often more specialized and sometimes limited to proprietary systems, can provide enhanced security features but may face compatibility issues when used outside specific toll operator networks. Choosing RFID technology significantly improves cross-network tolling efficiency, reducing the need for multiple devices and simplifying toll management for frequent travelers.
Choosing the Right Solution: RFID Tag or Transponder?
Selecting the right toll solution depends on factors such as range, data capacity, and environmental conditions. RFID tags offer cost-effective, short-range identification ideal for simple vehicle classification, while transponders provide longer range and greater data storage for advanced toll management systems. Evaluating traffic volume, infrastructure investment, and required accuracy ensures the optimal choice between RFID tags and transponders for toll collection efficiency.
RFID tags vs transponders Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com