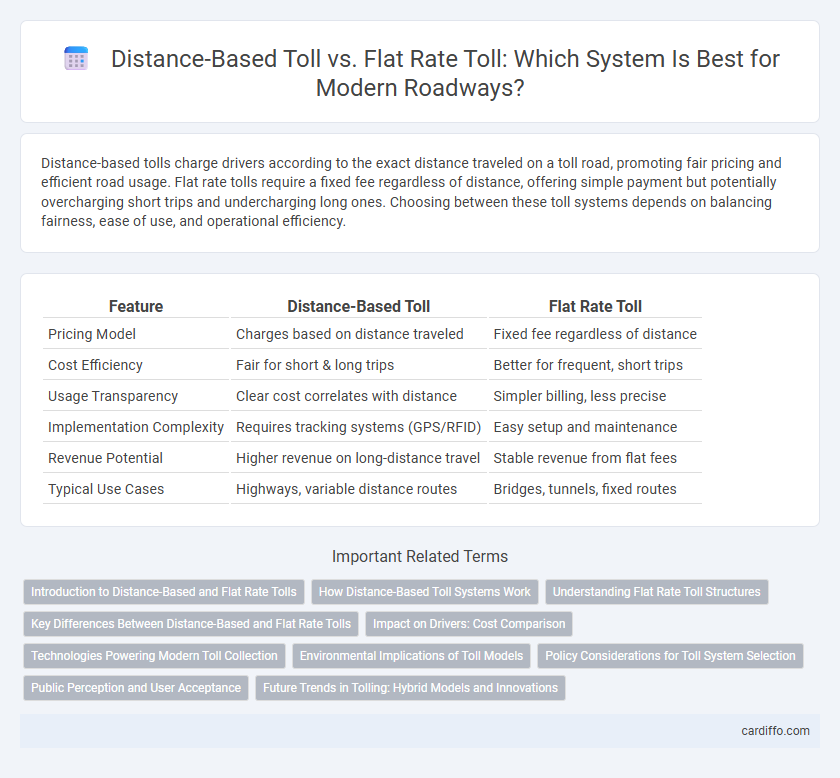
Distance-based tolls charge drivers according to the exact distance traveled on a toll road, promoting fair pricing and efficient road usage. Flat rate tolls require a fixed fee regardless of distance, offering simple payment but potentially overcharging short trips and undercharging long ones. Choosing between these toll systems depends on balancing fairness, ease of use, and operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Distance-Based Toll | Flat Rate Toll |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Charges based on distance traveled | Fixed fee regardless of distance |
| Cost Efficiency | Fair for short & long trips | Better for frequent, short trips |
| Usage Transparency | Clear cost correlates with distance | Simpler billing, less precise |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires tracking systems (GPS/RFID) | Easy setup and maintenance |
| Revenue Potential | Higher revenue on long-distance travel | Stable revenue from flat fees |
| Typical Use Cases | Highways, variable distance routes | Bridges, tunnels, fixed routes |
Introduction to Distance-Based and Flat Rate Tolls
Distance-based tolls charge drivers according to the exact miles traveled on a toll road, promoting fairness by linking fees directly to road usage. Flat rate tolls require a fixed fee regardless of distance, simplifying payment but potentially leading to inequity for short or long trips. Understanding these tolling methods helps in assessing cost efficiency and traffic management strategies on toll roads.
How Distance-Based Toll Systems Work
Distance-based toll systems calculate charges according to the exact distance a vehicle travels on toll roads, using technologies like GPS, RFID tags, or electronic toll collection points to track entry and exit locations. These systems enable precise tolling based on mileage, promoting fairness and encouraging efficient road usage. Unlike flat rate tolls, distance-based tolls dynamically adjust fees, potentially reducing congestion and lowering emissions by incentivizing shorter trips.
Understanding Flat Rate Toll Structures
Flat rate toll structures charge a fixed fee regardless of the distance traveled, simplifying payment processes and providing predictability for motorists. These tolls are commonly applied on bridges, tunnels, or specific road segments where administrative efficiency and ease of use are prioritized over distance-based fairness. Understanding flat rate tolls helps drivers anticipate exact costs, aiding in budgeting and route planning without concern for varying toll amounts based on mileage.
Key Differences Between Distance-Based and Flat Rate Tolls
Distance-based tolls charge drivers based on the exact mileage traveled on a toll road, providing a fair pricing model that correlates with road usage and vehicle impact. Flat rate tolls require a fixed fee regardless of distance, offering simplicity but potentially leading to inequities for short or long trips. The fundamental difference lies in cost calculation--distance-based tolls use GPS or sensor data for dynamic pricing, whereas flat rate tolls apply a uniform charge regardless of travel length.
Impact on Drivers: Cost Comparison
Distance-based tolls charge drivers according to the exact miles traveled, resulting in fairer expenses that correlate with road usage and promoting efficient route choices. Flat rate tolls impose a fixed fee regardless of distance, often disadvantaging short-distance travelers by making trips more expensive relative to actual road use. Cost comparison reveals that distance-based systems encourage cost savings for infrequent or local drivers while flat rate tolls simplify payment but may discourage short trips due to higher proportional costs.
Technologies Powering Modern Toll Collection
Distance-based toll systems utilize GPS and RFID technologies to accurately measure the exact distance traveled by vehicles, ensuring fair and usage-based charges. Flat rate toll collection primarily relies on traditional electronic toll collection (ETC) systems like transponders and license plate recognition for fixed fee processing. Advanced technologies such as Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR), mobile payment integration, and cloud-based data analytics enhance the efficiency and scalability of both toll collection methods.
Environmental Implications of Toll Models
Distance-based tolls encourage reduced vehicle miles traveled, lowering greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution by incentivizing drivers to choose shorter routes or alternative transportation modes. Flat rate tolls do not vary with distance, potentially leading to unchanged or increased vehicle mileage and higher environmental impact due to a lack of incentives for eco-friendly travel behavior. Implementing distance-based tolling aligns with sustainable transportation goals by promoting efficient road usage and decreasing overall carbon footprints.
Policy Considerations for Toll System Selection
Distance-based toll systems promote equitable revenue generation by charging drivers according to the actual distance traveled, encouraging efficient road use and reducing congestion. Flat rate tolls simplify administration and provide predictable revenue streams, but may disproportionately burden short-distance travelers and fail to incentivize reduced road use. Policy considerations must balance equity, administrative feasibility, traffic management goals, and revenue stability when selecting between distance-based and flat rate tolling systems.
Public Perception and User Acceptance
Distance-based toll systems are generally perceived as fairer by users because charges correspond directly to the traveled distance, enhancing acceptance among frequent and long-distance drivers. Flat rate tolls, while simpler and predictable, often face criticism for penalizing short-distance travelers and may lead to lower overall user satisfaction. Public perception strongly favors transparency and equity, making distance-based tolls more acceptable in diverse driving populations.
Future Trends in Tolling: Hybrid Models and Innovations
Future trends in tolling emphasize hybrid models that combine distance-based tolling with flat rate systems to optimize revenue and traffic flow. Advanced technologies such as GPS tracking and dynamic pricing enable more accurate distance measurement and flexible toll rates tailored to congestion levels and vehicle type. Innovations in electronic toll collection and data analytics support seamless integration of hybrid models, enhancing efficiency and user experience on toll roads.
Distance-Based Toll vs Flat Rate Toll Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com