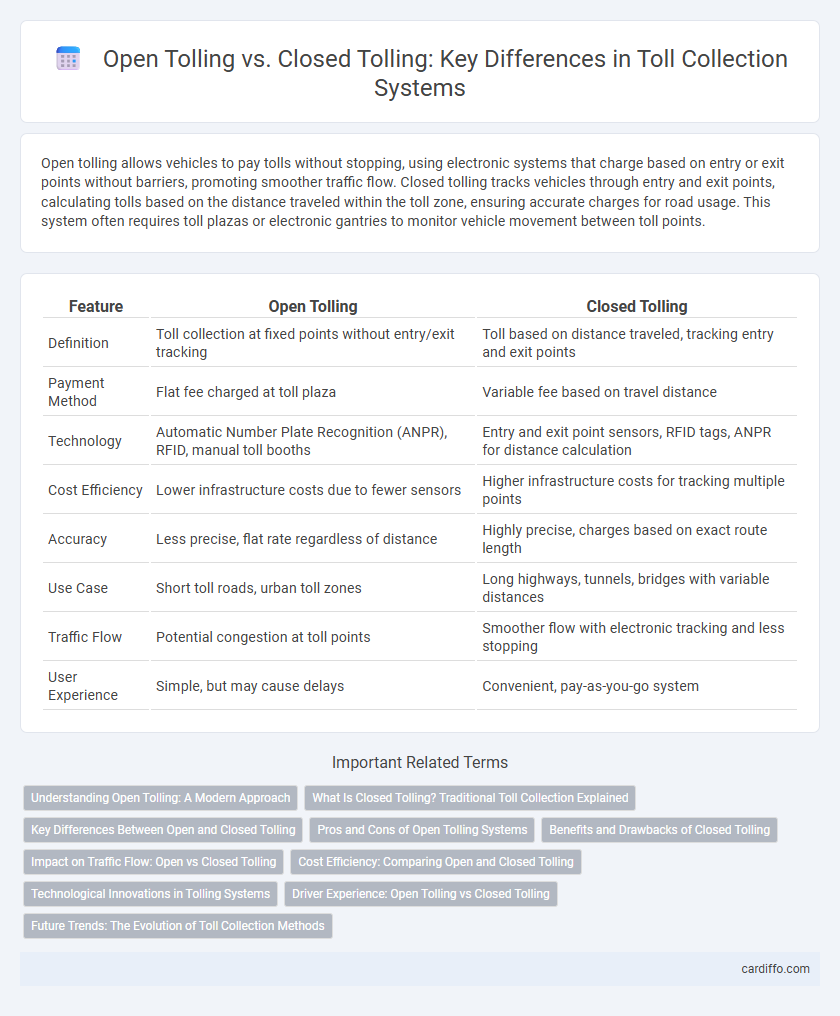
Open tolling allows vehicles to pay tolls without stopping, using electronic systems that charge based on entry or exit points without barriers, promoting smoother traffic flow. Closed tolling tracks vehicles through entry and exit points, calculating tolls based on the distance traveled within the toll zone, ensuring accurate charges for road usage. This system often requires toll plazas or electronic gantries to monitor vehicle movement between toll points.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Open Tolling | Closed Tolling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Toll collection at fixed points without entry/exit tracking | Toll based on distance traveled, tracking entry and exit points |
| Payment Method | Flat fee charged at toll plaza | Variable fee based on travel distance |
| Technology | Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR), RFID, manual toll booths | Entry and exit point sensors, RFID tags, ANPR for distance calculation |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower infrastructure costs due to fewer sensors | Higher infrastructure costs for tracking multiple points |
| Accuracy | Less precise, flat rate regardless of distance | Highly precise, charges based on exact route length |
| Use Case | Short toll roads, urban toll zones | Long highways, tunnels, bridges with variable distances |
| Traffic Flow | Potential congestion at toll points | Smoother flow with electronic tracking and less stopping |
| User Experience | Simple, but may cause delays | Convenient, pay-as-you-go system |
Understanding Open Tolling: A Modern Approach
Open Tolling represents a modern toll collection system where vehicles are charged without requiring them to stop or slow down at toll booths, using electronic methods such as RFID or license plate recognition. This approach reduces traffic congestion and improves travel efficiency by enabling seamless toll payments across multiple lanes. Enhanced with real-time data processing, Open Tolling supports dynamic pricing models and facilitates better traffic management on highways.
What Is Closed Tolling? Traditional Toll Collection Explained
Closed tolling collects fees by issuing a ticket upon entry to a toll road and calculating charges based on the distance traveled when the ticket is surrendered at the exit point. This traditional toll collection method requires toll plazas at both entry and exit points to record vehicle data and determine accurate toll amounts. Closed tolling systems reduce toll-related disputes by charging users precisely for the road segments they use, improving fairness compared to flat-rate open tolling.
Key Differences Between Open and Closed Tolling
Open tolling charges vehicles at specific toll points without requiring entry or exit data, enabling seamless travel but potentially causing revenue leakage. Closed tolling records entry and exit points, calculating tolls based on distance traveled, which promotes accurate fare collection but requires more infrastructure and data management. The choice between open and closed tolling impacts traffic flow, enforcement efficiency, and tolling system costs.
Pros and Cons of Open Tolling Systems
Open tolling systems eliminate the need for toll booths, reducing traffic congestion and operational costs by using electronic toll collection methods such as RFID or ANPR cameras. They enhance convenience for drivers by enabling seamless passage without stopping, but may face challenges with toll evasion and require robust enforcement mechanisms. Data accuracy and upfront infrastructure investment also influence the effectiveness and adoption of open tolling systems.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Closed Tolling
Closed tolling systems offer precise toll calculation based on actual distance traveled, enhancing fairness and revenue accuracy across highways. However, they require extensive infrastructure like entry and exit point sensors, leading to higher installation and maintenance costs compared to open tolling. The comprehensive data collection improves traffic management but raises privacy concerns among users due to detailed tracking.
Impact on Traffic Flow: Open vs Closed Tolling
Open tolling reduces congestion by enabling vehicles to maintain highway speeds without stopping at toll booths, resulting in smoother and faster traffic flow. Closed tolling requires vehicles to enter and exit toll zones, calculating tolls based on distance traveled, which can cause delays at entry and exit points, especially during peak hours. Overall, open tolling significantly enhances traffic throughput and decreases bottlenecks compared to closed toll systems.
Cost Efficiency: Comparing Open and Closed Tolling
Open tolling systems reduce infrastructure and operational costs by eliminating the need for toll booths and allowing free-flow traffic, which decreases congestion and maintenance expenses. Closed tolling requires more extensive infrastructure with entrance and exit toll points, leading to higher setup and maintenance costs but can provide more accurate toll collection based on distance traveled. Cost efficiency depends on traffic volume and geographic factors, with open tolling favoring high-density urban areas and closed tolling better suited for longer highway stretches.
Technological Innovations in Tolling Systems
Open tolling systems leverage advanced technologies such as RFID, ANPR (Automatic Number Plate Recognition), and mobile payment platforms to enable seamless vehicle detection without traditional toll booths, reducing congestion and operational costs. Closed tolling utilizes electronic sensors and cameras to track entry and exit points, calculating tolls based on distance traveled, enhancing accuracy in toll collection through real-time data processing and dynamic pricing algorithms. Innovations like AI-based analytics and cloud computing improve toll system efficiency, enabling adaptive traffic management and fraud detection in both open and closed tolling infrastructures.
Driver Experience: Open Tolling vs Closed Tolling
Open tolling enhances driver experience by eliminating the need to stop at toll booths, allowing seamless travel and reducing congestion on highways. Closed tolling requires drivers to collect a ticket upon entry and pay based on distance traveled at exit points, which can cause delays and increase travel time during peak hours. Open tolling systems use electronic toll collection technologies like RFID and ANPR, improving convenience and ensuring consistent vehicle flow without manual interactions.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Toll Collection Methods
Open tolling systems eliminate traditional toll booths by using electronic transponders and license plate recognition, enabling seamless traffic flow and reduced congestion. Closed tolling collects tolls based on entry and exit points, providing precise distance-based charges and improved revenue accuracy. Emerging trends emphasize integration of AI, blockchain technology, and real-time data analytics to enhance toll collection efficiency, security, and user experience.
Open Tolling vs Closed Tolling Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com