Cash payment at toll booths offers immediate transaction processing without the need for electronic devices, ensuring accessibility for all drivers. Electronic payment systems, such as RFID or mobile apps, provide faster lane clearance and reduce congestion by enabling seamless, contactless toll collection. Choosing electronic payment enhances efficiency and convenience, while cash payment remains essential for those without access to digital payment methods.
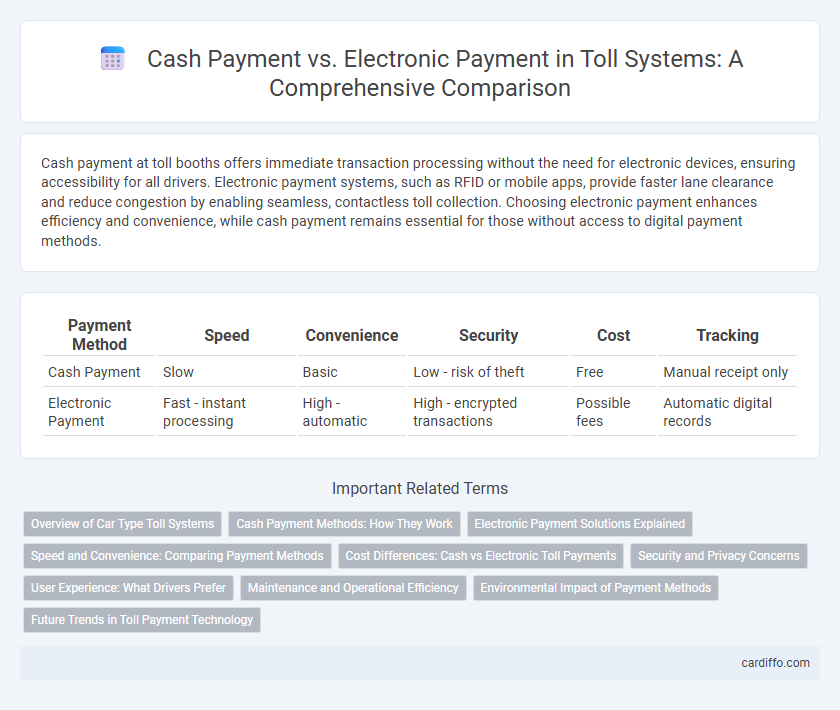
Table of Comparison
| Payment Method | Speed | Convenience | Security | Cost | Tracking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cash Payment | Slow | Basic | Low - risk of theft | Free | Manual receipt only |
| Electronic Payment | Fast - instant processing | High - automatic | High - encrypted transactions | Possible fees | Automatic digital records |
Overview of Car Type Toll Systems
Car type toll systems categorize vehicles based on size, weight, and axle count to determine toll fees accurately. Electronic payment systems leverage automatic vehicle identification technologies such as RFID and license plate recognition to enable seamless toll collection without stopping. Cash payment methods, while traditional, require manual transactions and often lead to congestion, making electronic toll collection more efficient and preferred on high-traffic highways.
Cash Payment Methods: How They Work
Cash payment methods at toll booths involve physically handing over currency or coins to a toll collector or inserting cash into automated machines, which register the transaction and grant access after confirmation. These methods operate on immediate payment principles, requiring drivers to stop and interact directly with the toll infrastructure. Cash transactions ensure anonymity and accessibility for users without electronic payment options but often lead to slower processing times compared to electronic toll collection systems.
Electronic Payment Solutions Explained
Electronic payment solutions at toll booths streamline transactions by enabling contactless methods such as RFID tags, mobile apps, and prepaid cards, which significantly reduce wait times and congestion. These systems enhance accuracy and security by minimizing cash handling and providing real-time transaction data for toll operators. Adopting electronic payments improves overall efficiency and supports integrated toll network management across multiple locations.
Speed and Convenience: Comparing Payment Methods
Electronic payment methods at toll booths significantly reduce transaction times, enabling faster vehicle throughput compared to cash payments. Contactless cards and mobile apps facilitate seamless toll collection without stopping, enhancing convenience and reducing congestion. Cash transactions require manual handling, causing delays and increasing wait times, which impact overall traffic flow efficiency.
Cost Differences: Cash vs Electronic Toll Payments
Cash toll payments incur higher operational costs due to the need for physical cash handling, personnel, and infrastructure maintenance, resulting in increased overhead for toll operators. Electronic toll payments significantly reduce expenses by automating transaction processing, minimizing labor, and enhancing traffic flow efficiency. Studies show that electronic systems can lower operational costs by up to 60% compared to cash-based toll collection methods.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Cash payments at tolls offer anonymity, reducing the risk of personal data exposure, but pose security risks such as theft or loss. Electronic payments provide convenience and faster processing while protecting transaction data through encryption, yet they may raise privacy concerns due to potential tracking and data sharing with third parties. Secure toll systems implement advanced encryption protocols and strict data governance policies to mitigate privacy risks and enhance payment security.
User Experience: What Drivers Prefer
Drivers consistently prefer electronic payment methods at toll booths due to faster transaction times and reduced congestion, enhancing overall travel efficiency. Cash payments often lead to longer wait times and increased stress, detracting from the user experience. Toll operators report higher satisfaction and smoother traffic flow when electronic options like RFID tags or mobile apps are utilized.
Maintenance and Operational Efficiency
Cash payment systems require frequent manual collection and reconciliation, increasing labor costs and the risk of errors that hinder maintenance efficiency. Electronic payment technologies streamline toll collection through automated processes, reducing downtime and enabling faster detection of system malfunctions. Enhanced operational efficiency from electronic payments lowers maintenance demands by minimizing physical infrastructure wear and improving transaction accuracy.
Environmental Impact of Payment Methods
Cash payments contribute to increased environmental impact due to the production, transportation, and disposal of physical currency, which consumes natural resources and generates waste. Electronic payments reduce carbon footprint by minimizing the need for paper money and coins, lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with cash handling and processing. Digital transactions also promote energy efficiency and decrease reliance on fossil fuels compared to traditional cash systems.
Future Trends in Toll Payment Technology
Future trends in toll payment technology emphasize a shift from cash payments to electronic systems, utilizing RFID tags, mobile apps, and license plate recognition for seamless transactions. These innovations reduce congestion and enhance toll collection efficiency by enabling real-time data processing and automated billing. Cloud-based platforms and AI-driven analytics are set to further optimize toll management and user experience in smart transportation networks.
Cash payment vs Electronic payment Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com