All-electronic tolling (AET) streamlines traffic flow by eliminating cash payments, reducing congestion and enhancing safety through automated license plate recognition or transponder technology. Hybrid tolling combines traditional cash lanes with electronic toll collection, offering flexibility for drivers without transponders while gradually transitioning toward full automation. Choosing between AET and hybrid tolling depends on traffic volume, infrastructure investment, and user adoption rates to balance efficiency and accessibility.
Table of Comparison
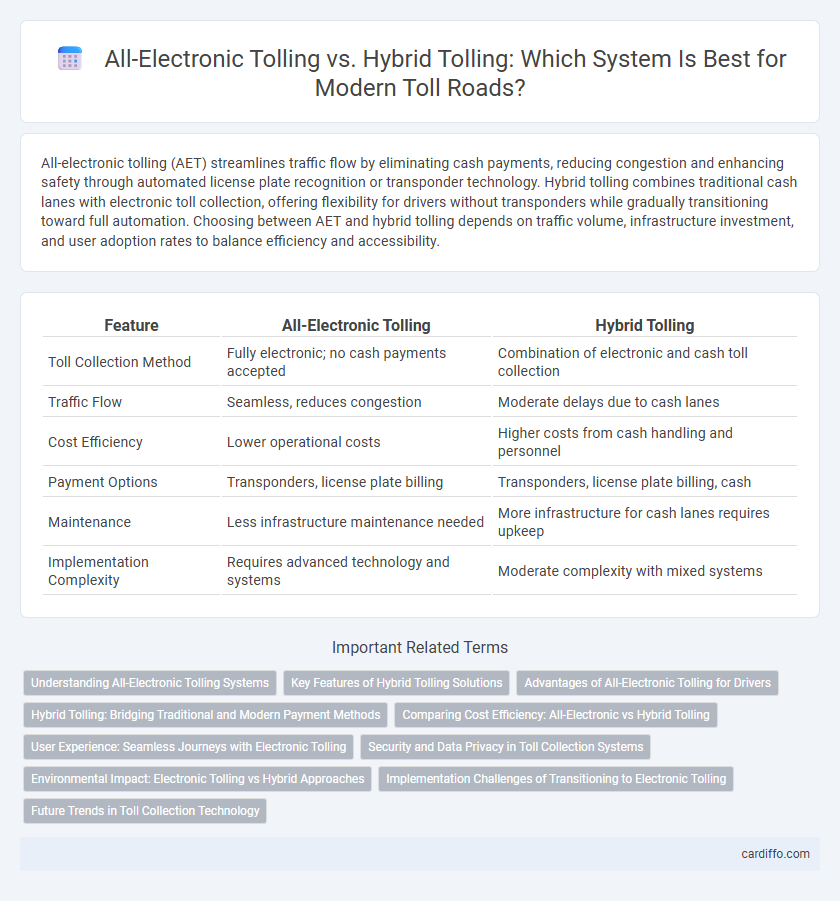
| Feature | All-Electronic Tolling | Hybrid Tolling |
|---|---|---|
| Toll Collection Method | Fully electronic; no cash payments accepted | Combination of electronic and cash toll collection |
| Traffic Flow | Seamless, reduces congestion | Moderate delays due to cash lanes |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs | Higher costs from cash handling and personnel |
| Payment Options | Transponders, license plate billing | Transponders, license plate billing, cash |
| Maintenance | Less infrastructure maintenance needed | More infrastructure for cash lanes requires upkeep |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires advanced technology and systems | Moderate complexity with mixed systems |
Understanding All-Electronic Tolling Systems
All-electronic tolling systems use electronic transponders and license plate recognition to collect tolls without requiring vehicles to stop, significantly reducing traffic congestion and emissions. These systems rely on advanced sensors and cameras to accurately capture vehicle data for seamless payment processing, increasing operational efficiency compared to hybrid tolling methods. Understanding the technology behind all-electronic tolling is crucial for transportation agencies aiming to enhance infrastructure and improve user experience across toll roads.
Key Features of Hybrid Tolling Solutions
Hybrid tolling solutions combine all-electronic tolling (AET) with traditional toll booth operations, enabling seamless transactions for both electronic transponder users and cash payers. Key features include interoperability with multiple payment methods, real-time data processing for dynamic toll calculations, and enhanced traffic flow management to reduce congestion. This system balances the efficiency of electronic tolling while accommodating drivers without transponders, optimizing overall toll collection revenue and user experience.
Advantages of All-Electronic Tolling for Drivers
All-electronic tolling eliminates the need for cash transactions, reducing congestion and wait times at toll plazas, which significantly enhances the driving experience. With seamless toll collection via transponders or license plate recognition, drivers benefit from continuous traffic flow and improved fuel efficiency due to fewer stops. This system also increases safety by minimizing lane changes and the risk of accidents in toll areas.
Hybrid Tolling: Bridging Traditional and Modern Payment Methods
Hybrid tolling systems integrate traditional cash or card payments with all-electronic tolling technologies, offering flexibility for drivers who prefer physical payment options alongside digital methods. This approach enables seamless traffic flow through electronic toll collection (ETC) lanes while maintaining barrier lanes for manual transactions, reducing congestion and improving user experience. By combining legacy toll infrastructure with state-of-the-art transponder and license plate recognition technology, hybrid tolling accommodates diverse driver preferences and accelerates the transition to fully electronic systems.
Comparing Cost Efficiency: All-Electronic vs Hybrid Tolling
All-electronic tolling (AET) significantly reduces operational costs by eliminating cash handling and manual toll collection, leading to lower labor expenses and increased traffic flow efficiency. Hybrid tolling systems incur higher costs due to maintaining both electronic and cash toll collection infrastructure, which results in more complex maintenance and staffing requirements. Studies show AET systems can reduce toll operation costs by up to 40% compared to hybrid tolling, making them more cost-efficient for large-scale implementations.
User Experience: Seamless Journeys with Electronic Tolling
All-electronic tolling enhances user experience by eliminating the need for cash payments and physical toll booths, enabling seamless journeys with uninterrupted traffic flow. Hybrid tolling, which combines electronic and manual toll collection, can cause delays and increases the likelihood of traffic congestion at toll plazas. Electronic tolling systems use automated license plate recognition and RFID transponders to provide efficient, contactless payment, improving convenience and reducing travel time for drivers.
Security and Data Privacy in Toll Collection Systems
All-electronic tolling systems enhance security by eliminating physical toll booths, reducing the risk of fraud and tampering with cash-based transactions. Hybrid tolling integrates electronic and manual methods, potentially increasing vulnerability due to the mixed handling of sensitive payment data. Advanced encryption protocols and secure data storage are critical in both systems to protect personal information from cyber threats and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
Environmental Impact: Electronic Tolling vs Hybrid Approaches
All-electronic tolling (AET) significantly reduces vehicle emissions by eliminating the need for vehicles to stop or slow down at toll plazas, decreasing idling times and improving traffic flow. Hybrid tolling systems, which combine electronic tolling with traditional toll booths, mitigate emissions to a lesser extent because some vehicles still experience delays and idling. Studies indicate that AET systems can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 30% compared to hybrid models, making them a more environmentally sustainable choice for toll operations.
Implementation Challenges of Transitioning to Electronic Tolling
Transitioning to all-electronic tolling poses challenges such as upgrading infrastructure to support high-speed vehicle detection and license plate recognition systems, ensuring interoperability across various toll agencies, and addressing privacy concerns related to continuous electronic monitoring. The integration of hybrid tolling systems can complicate traffic flow management, as both cash and electronic payment lanes require coordination and clear signage to minimize congestion. Effective implementation demands comprehensive public communication strategies and robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive customer data during the transition.
Future Trends in Toll Collection Technology
All-electronic tolling systems rely on advanced sensor networks and RFID technology to enable seamless, cashless toll collection, reducing congestion and operational costs. Hybrid tolling combines electronic methods with traditional cash or card payment options, facilitating a gradual transition for regions with diverse user preferences and infrastructure constraints. Future trends emphasize the expansion of all-electronic tolling powered by AI-based traffic analytics, dynamic pricing models, and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication to optimize traffic flow and enhance revenue collection.
All-electronic tolling vs hybrid tolling Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com