Conventional brakes rely on friction to slow down a vehicle, generating heat and wearing down brake pads over time, which requires regular maintenance. Regenerative brakes convert kinetic energy into electrical energy during deceleration, improving energy efficiency and extending the lifespan of brake components. Service pets benefit from smoother rides provided by regenerative braking systems, ensuring comfort and stability during transportation.
Table of Comparison
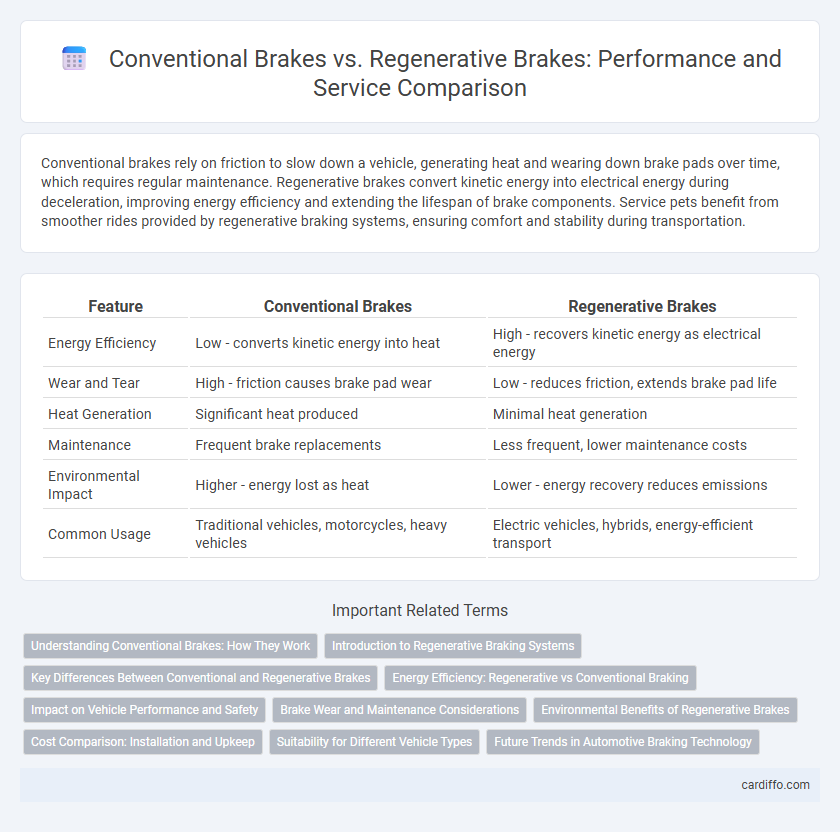
| Feature | Conventional Brakes | Regenerative Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Low - converts kinetic energy into heat | High - recovers kinetic energy as electrical energy |
| Wear and Tear | High - friction causes brake pad wear | Low - reduces friction, extends brake pad life |
| Heat Generation | Significant heat produced | Minimal heat generation |
| Maintenance | Frequent brake replacements | Less frequent, lower maintenance costs |
| Environmental Impact | Higher - energy lost as heat | Lower - energy recovery reduces emissions |
| Common Usage | Traditional vehicles, motorcycles, heavy vehicles | Electric vehicles, hybrids, energy-efficient transport |
Understanding Conventional Brakes: How They Work
Conventional brakes operate by using friction to slow down or stop a vehicle, where brake pads press against a rotor or drum to convert kinetic energy into heat. The braking system relies on hydraulic pressure to engage the pads, making it a straightforward and reliable mechanism. Despite being effective, this process dissipates energy as heat rather than capturing it for reuse.
Introduction to Regenerative Braking Systems
Regenerative braking systems capture kinetic energy during deceleration and convert it into electrical energy, enhancing vehicle efficiency and reducing wear on conventional brake components. Unlike traditional friction-based brakes that dissipate energy as heat, regenerative brakes channel energy back to the battery, extending electric vehicle range and improving overall sustainability. This technology is integral to hybrid and electric vehicles, providing a seamless blend of energy recovery and braking performance.
Key Differences Between Conventional and Regenerative Brakes
Conventional brakes rely on friction pads pressing against rotors to slow a vehicle, converting kinetic energy into heat, which is lost. Regenerative brakes capture and convert kinetic energy into electrical energy, storing it in the vehicle's battery for later use, enhancing energy efficiency. The primary difference lies in energy recovery, with regenerative systems contributing to improved fuel economy and reduced wear on brake components.
Energy Efficiency: Regenerative vs Conventional Braking
Regenerative braking systems capture kinetic energy during deceleration, converting it into electrical energy to recharge the vehicle's battery, significantly improving overall energy efficiency. Conventional brakes dissipate kinetic energy as heat, resulting in energy loss and reduced fuel economy. This energy recovery process in regenerative brakes enhances driving range and decreases reliance on fuel or grid electricity.
Impact on Vehicle Performance and Safety
Conventional brakes rely on friction to slow the vehicle, which can lead to heat buildup and faster wear, potentially affecting braking reliability and requiring frequent maintenance. Regenerative brakes convert kinetic energy into electrical energy, improving energy efficiency and reducing brake wear, which helps maintain consistent brake performance and enhances vehicle safety over time. The integration of regenerative braking systems often results in smoother deceleration and better control, contributing positively to overall driving stability and passenger safety.
Brake Wear and Maintenance Considerations
Conventional brakes rely on friction pads that wear down over time, requiring regular replacement and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and safety. Regenerative brakes reduce wear on traditional brake components by converting kinetic energy into electrical energy during deceleration, significantly extending the lifespan of brake pads and lowering maintenance costs. Vehicles equipped with regenerative braking systems benefit from less frequent servicing, resulting in reduced downtime and overall maintenance expenses.
Environmental Benefits of Regenerative Brakes
Regenerative brakes significantly reduce carbon emissions by converting kinetic energy into electrical energy, which recharges the vehicle's battery and decreases reliance on fossil fuels. Unlike conventional brakes that dissipate energy as heat, regenerative braking improves overall energy efficiency, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions in electric and hybrid vehicles. This technology also extends brake component lifespan, minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact from maintenance and manufacturing.
Cost Comparison: Installation and Upkeep
Conventional brakes typically have lower upfront installation costs compared to regenerative braking systems, which require specialized components and electronics. Over time, regenerative brakes reduce maintenance expenses due to less wear on brake pads and rotors, leading to longer service intervals and savings on replacement parts. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals regenerative brakes offer financial benefits despite higher initial investment.
Suitability for Different Vehicle Types
Conventional brakes are highly suitable for heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks and buses because they provide consistent stopping power and durability under high loads. Regenerative brakes excel in electric and hybrid vehicles by recovering energy during braking to improve battery efficiency and extend driving range. Passenger cars benefit from a combination of both systems to balance braking performance with energy conservation.
Future Trends in Automotive Braking Technology
Future trends in automotive braking technology emphasize the integration of regenerative braking systems to enhance energy efficiency and extend electric vehicle range. Conventional hydraulic brakes remain essential for safety and backup but are increasingly supplemented by advanced electronic control units that optimize brake force distribution. Innovations in brake-by-wire technology and smart sensors are driving a shift towards more responsive, energy-recovering, and predictive braking systems in next-generation vehicles.
Conventional Brakes vs Regenerative Brakes Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com