Plug welding involves filling a hole in one metal piece with weld material to join it to another surface, offering strong, localized bonding ideal for sheet metal. Stitch welding consists of a series of intermittent welds along the joint, reducing heat distortion while maintaining structural integrity. Choosing between plug welding and stitch welding depends on factors like load requirements, material thickness, and the need to control warping.
Table of Comparison
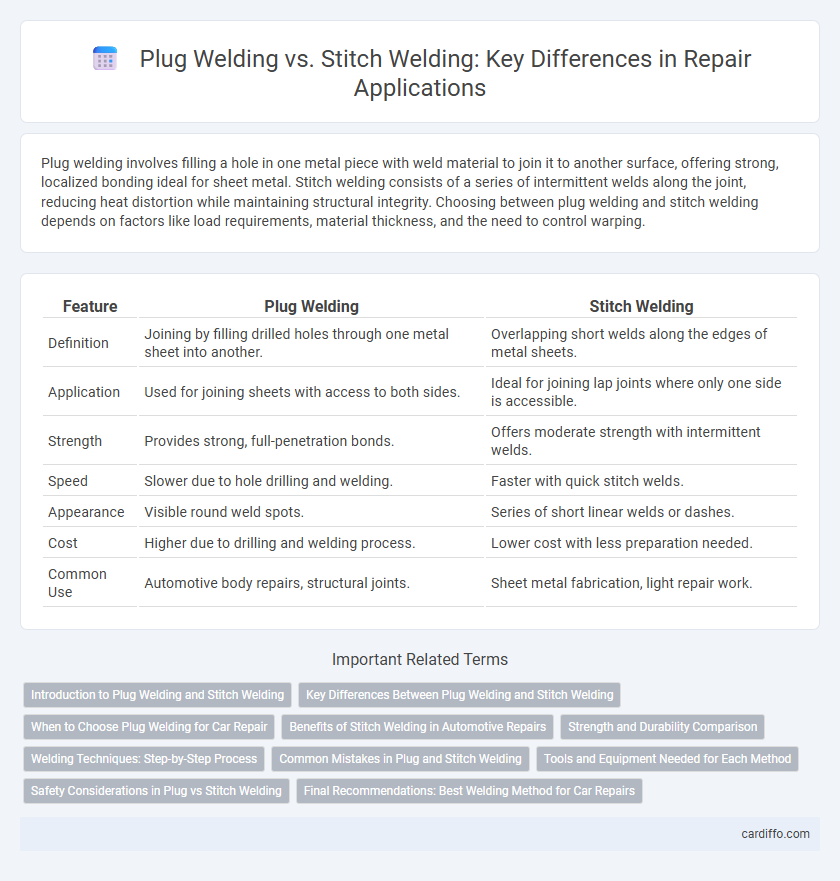
| Feature | Plug Welding | Stitch Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Joining by filling drilled holes through one metal sheet into another. | Overlapping short welds along the edges of metal sheets. |
| Application | Used for joining sheets with access to both sides. | Ideal for joining lap joints where only one side is accessible. |
| Strength | Provides strong, full-penetration bonds. | Offers moderate strength with intermittent welds. |
| Speed | Slower due to hole drilling and welding. | Faster with quick stitch welds. |
| Appearance | Visible round weld spots. | Series of short linear welds or dashes. |
| Cost | Higher due to drilling and welding process. | Lower cost with less preparation needed. |
| Common Use | Automotive body repairs, structural joints. | Sheet metal fabrication, light repair work. |
Introduction to Plug Welding and Stitch Welding
Plug welding involves filling a drilled hole in one metal piece with weld to join it to another, commonly used for lap joints in automotive repair. Stitch welding consists of a series of intermittent welds along the joint, providing strength while reducing heat distortion and material warping. Both techniques offer efficient metal joining solutions tailored for specific repair applications, balancing strength and thermal impact.
Key Differences Between Plug Welding and Stitch Welding
Plug welding involves filling a single hole in one metal piece to join it with another, providing strong, concentrated weld points ideal for load-bearing applications. Stitch welding uses a series of intermittent welds along a joint, balancing strength and heat input, reducing distortion in thinner materials. The key differences center on weld pattern, heat distribution, and suitability for varying metal thicknesses and structural demands.
When to Choose Plug Welding for Car Repair
Plug welding is ideal for joining overlapping metal panels where access is limited to one side, making it suitable for automotive body repairs involving frame rails or unibody structures. This technique ensures strong, localized welds that restore structural integrity without warping thin automotive sheets. Choose plug welding when precise, penetration welds are needed to fill holes or attach components without compromising surrounding metal.
Benefits of Stitch Welding in Automotive Repairs
Stitch welding offers improved control over heat distortion compared to plug welding, making it ideal for delicate automotive panels prone to warping. The smaller, intermittent welds enhance structural integrity while minimizing metal fatigue, contributing to longer-lasting repairs. This technique also reduces filler material usage and allows for faster cooling times, increasing overall repair efficiency in automotive applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Plug welding provides superior strength by creating solid, continuous welds that fully penetrate the joined materials, making it ideal for heavy-duty repairs requiring high durability. Stitch welding consists of shorter, intermittent welds that offer moderate strength but excel in reducing heat distortion and maintaining material integrity in lighter applications. When comparing durability, plug welds resist fatigue and shear forces better, while stitch welds are more suitable for flexible joints where thermal management is crucial.
Welding Techniques: Step-by-Step Process
Plug welding involves drilling holes through overlapping metal sheets, then filling the holes with weld material to join the layers, ensuring a solid bond and minimal distortion. Stitch welding uses intermittent welds placed at intervals along the joint, reducing heat input and warping while maintaining adequate strength. Both techniques require precise alignment, clean surfaces, and proper welding parameters to achieve optimal results in repair projects.
Common Mistakes in Plug and Stitch Welding
Common mistakes in plug and stitch welding include improper hole preparation, such as incorrect hole diameter or insufficient cleaning, leading to weak welds and poor penetration. Another frequent error is excessive welding current, which causes burn-through or distortion around the weld area, compromising structural integrity. Inadequate weld spacing and inconsistent weld size often result in uneven load distribution and reduced joint strength, increasing the risk of failure during service.
Tools and Equipment Needed for Each Method
Plug welding requires specialized tools such as a plug weld cutter or drill to create holes in the base metal, and a MIG or TIG welder to fill the holes with weld material. Stitch welding primarily uses a MIG or TIG welder set to intermittent weld mode, allowing for controlled, spaced welds without the need for hole preparation tools. Both methods demand appropriate safety equipment including welding helmets, gloves, and protective clothing to ensure operator safety during the repair process.
Safety Considerations in Plug vs Stitch Welding
Plug welding offers enhanced safety by minimizing the risk of weld cracking and ensuring stronger joint integrity, which reduces the likelihood of structural failure during repairs. Stitch welding, while faster, may generate more heat input and residual stresses, increasing the risk of distortion and burn-through, especially on thinner materials. Proper ventilation and protective gear remain crucial in both methods to mitigate exposure to fumes and UV radiation during the welding process.
Final Recommendations: Best Welding Method for Car Repairs
Plug welding is ideal for repairing car panels as it offers stronger joints and better resistance to stress and vibrations common in automotive use, while stitch welding is more suitable for temporary fixes or less critical areas due to its quicker application but weaker bond. For long-lasting and structurally sound car repairs, plug welding ensures superior durability and alignment of body parts, making it the preferred choice for professional automotive technicians. Selecting plug welding enhances the safety and longevity of vehicle repairs by providing consistent weld penetration and minimizing metal distortion.
Plug Welding vs Stitch Welding Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com