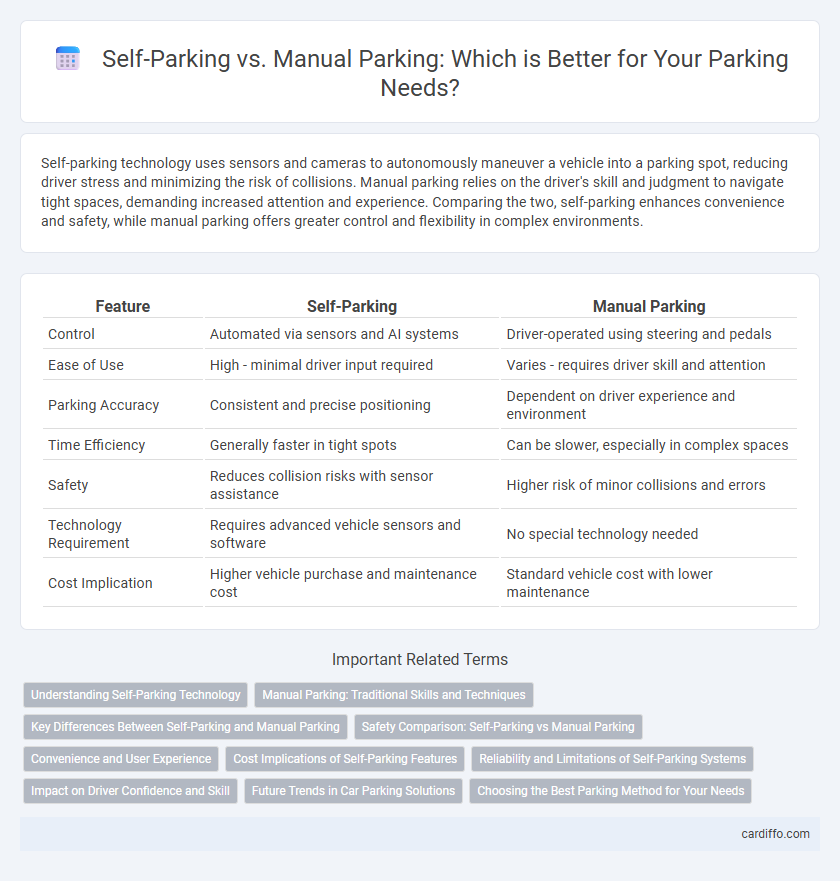
Self-parking technology uses sensors and cameras to autonomously maneuver a vehicle into a parking spot, reducing driver stress and minimizing the risk of collisions. Manual parking relies on the driver's skill and judgment to navigate tight spaces, demanding increased attention and experience. Comparing the two, self-parking enhances convenience and safety, while manual parking offers greater control and flexibility in complex environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Parking | Manual Parking |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Automated via sensors and AI systems | Driver-operated using steering and pedals |
| Ease of Use | High - minimal driver input required | Varies - requires driver skill and attention |
| Parking Accuracy | Consistent and precise positioning | Dependent on driver experience and environment |
| Time Efficiency | Generally faster in tight spots | Can be slower, especially in complex spaces |
| Safety | Reduces collision risks with sensor assistance | Higher risk of minor collisions and errors |
| Technology Requirement | Requires advanced vehicle sensors and software | No special technology needed |
| Cost Implication | Higher vehicle purchase and maintenance cost | Standard vehicle cost with lower maintenance |
Understanding Self-Parking Technology
Self-parking technology utilizes advanced sensors, cameras, and algorithms to identify suitable parking spaces and autonomously maneuver the vehicle into them with precision. This system enhances convenience and safety by reducing human error during parking in tight or complex spots. Understanding the integration of ultrasonic sensors, radar, and real-time object detection is essential for recognizing how self-parking compares to manual parking techniques.
Manual Parking: Traditional Skills and Techniques
Manual parking requires drivers to rely on traditional skills such as spatial awareness, precise steering control, and accurate judgment of distances to maneuver vehicles into tight spaces. Mastery of techniques like parallel parking, angle parking, and reverse parking remains essential for effective vehicle placement without automation. These foundational skills ensure safety and efficiency in diverse parking environments where self-parking technology is unavailable or impractical.
Key Differences Between Self-Parking and Manual Parking
Self-parking systems utilize sensors, cameras, and automated control to maneuver vehicles into parking spaces without driver input, enhancing convenience and reducing parking errors. Manual parking requires driver skill and attention to navigate tight spaces, relying solely on human judgment and control. Key differences include automation level, accuracy, time efficiency, and user involvement during the parking process.
Safety Comparison: Self-Parking vs Manual Parking
Self-parking systems use advanced sensors and cameras to detect obstacles, significantly reducing the risk of collisions compared to manual parking where human error is common. These autonomous features enhance safety by providing precise control in tight spaces and minimizing blind spots. Studies show that self-parking reduces minor fender benders by up to 30%, making it a safer option for urban and crowded parking environments.
Convenience and User Experience
Self-parking systems enhance convenience by automating the steering and maneuvering process, reducing driver stress and minimizing the risk of parking errors. Manual parking requires skill and attention, often leading to longer parking times and increased frustration, especially in tight or crowded spaces. Advanced self-parking technology integrates sensors and cameras to provide a seamless user experience, ensuring precision and safety while freeing drivers from complex parking tasks.
Cost Implications of Self-Parking Features
Self-parking systems typically increase vehicle costs by $1,000 to $2,500 depending on the technology and manufacturer, reflecting advanced sensors and software integration. Maintenance expenses also rise as specialized components require professional calibration and occasional software updates. While self-parking can reduce potential damage and insurance claims, the upfront price and service fees remain significant factors for budget-conscious buyers.
Reliability and Limitations of Self-Parking Systems
Self-parking systems offer convenience by autonomously maneuvering vehicles into parking spaces, yet their reliability can be impacted by sensor limitations and environmental factors such as poor lighting or tight spaces. These systems may struggle with complex parking scenarios, including irregularly shaped spots or crowded lots, where manual parking allows for nuanced human judgment and adaptation. While advancing technology enhances accuracy, drivers should remain vigilant and prepared to intervene to prevent potential errors and ensure safety.
Impact on Driver Confidence and Skill
Self-parking technology enhances driver confidence by reducing stress during tight parking maneuvers, allowing users to rely on automated systems for precision. However, excessive dependence on self-parking can diminish manual parking skills over time, potentially reducing overall driver proficiency in complex or unfamiliar environments. Balancing the use of self-parking features with regular manual practice helps maintain essential parking skills while benefiting from technological convenience.
Future Trends in Car Parking Solutions
Self-parking systems leverage advanced sensors and AI algorithms to enhance convenience and reduce parking time, signaling a shift toward fully automated parking solutions. Future trends in car parking emphasize integration with smart city infrastructure, enabling seamless vehicle-to-infrastructure communication for optimized space utilization. Manual parking remains valuable in complex environments but is increasingly supplemented by augmented reality and driver-assist technologies for improved safety and precision.
Choosing the Best Parking Method for Your Needs
Self-parking systems utilize advanced sensors and cameras to precisely maneuver vehicles into tight spaces, reducing the risk of minor accidents and saving time in crowded parking lots. Manual parking offers greater control and adaptability in complex or unconventional parking situations, allowing drivers to assess each environment uniquely. Evaluate the parking environment, vehicle capabilities, and personal comfort with technology to select the most effective parking method tailored to your needs.
Self-parking vs Manual parking Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com