Angled parking spaces optimize vehicle alignment by positioning cars at a specific angle to the curb, increasing ease of entry and exit while maximizing available parking spots in narrow areas. Straight parking, also known as perpendicular parking, allows vehicles to park at a 90-degree angle to the curb, providing more direct access but often requiring more space for maneuvering. Choosing between angled and straight parking depends on factors like traffic flow, space constraints, and the need for efficient use of parking areas.
Table of Comparison
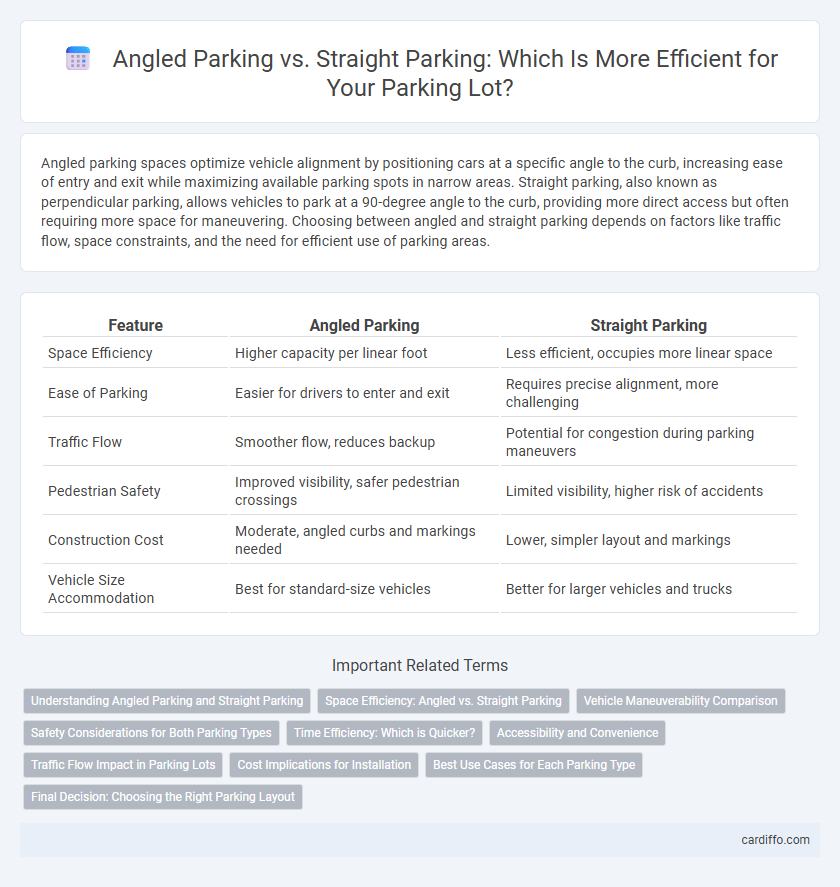
| Feature | Angled Parking | Straight Parking |
|---|---|---|
| Space Efficiency | Higher capacity per linear foot | Less efficient, occupies more linear space |
| Ease of Parking | Easier for drivers to enter and exit | Requires precise alignment, more challenging |
| Traffic Flow | Smoother flow, reduces backup | Potential for congestion during parking maneuvers |
| Pedestrian Safety | Improved visibility, safer pedestrian crossings | Limited visibility, higher risk of accidents |
| Construction Cost | Moderate, angled curbs and markings needed | Lower, simpler layout and markings |
| Vehicle Size Accommodation | Best for standard-size vehicles | Better for larger vehicles and trucks |
Understanding Angled Parking and Straight Parking
Angled parking spaces are designed at a slant, typically between 30 to 60 degrees, allowing easier entry and exit, especially in high-traffic areas. Straight parking, also known as perpendicular parking, has vehicles parked at a 90-degree angle to the curb, maximizing the number of spaces but requiring more maneuvering. Understanding the spatial efficiency and accessibility of angled versus straight parking aids in optimizing parking lot layouts for safety and capacity.
Space Efficiency: Angled vs. Straight Parking
Angled parking spaces maximize space efficiency by allowing more vehicles to fit into a given area compared to straight parking, due to the reduced width requirement per vehicle. The angled design facilitates easier entry and exit, reducing the need for wide aisles and enabling tighter parking layouts. Conversely, straight parking requires wider spaces and aisles to accommodate perpendicular maneuvering, often resulting in lower vehicle density per square foot.
Vehicle Maneuverability Comparison
Angled parking spaces typically allow easier vehicle maneuverability due to the reduced turning radius required for entry and exit, making them ideal for parking lots with limited space or high traffic. In contrast, straight parking demands more precise maneuvering and wider turning angles, which can increase the risk of collisions or difficulty, especially for larger vehicles. Vehicles in angled parking generally experience quicker and smoother parking maneuvers, enhancing overall parking efficiency and minimizing congestion.
Safety Considerations for Both Parking Types
Angled parking reduces the risk of collisions by requiring slower speeds when entering and exiting spaces, enhancing pedestrian visibility and vehicle maneuverability. Straight parking offers better space utilization and simpler alignment but can increase the likelihood of side-impact accidents due to limited driver visibility when reversing. Both parking types benefit from clear signage, well-marked spaces, and proper lighting to improve overall safety for drivers and pedestrians.
Time Efficiency: Which is Quicker?
Angled parking typically enables quicker maneuvers compared to straight parking due to its easier entry and exit angles, reducing the time needed to position a vehicle correctly. Studies show that angled parking spaces often decrease the average parking time by up to 30%, contributing to improved traffic flow in busy parking lots. However, straight parking can be more efficient in narrow spaces where reversed entry is faster than multiple adjustment attempts.
Accessibility and Convenience
Angled parking offers easier vehicle maneuverability and reduces the risk of collisions, enhancing accessibility for drivers with limited mobility or larger vehicles. Straight parking maximizes space efficiency in parking lots but often requires more precise reversing skills, potentially limiting convenience for some users. Accessibility improvements in angled parking benefit individuals with disabilities by providing wider aisles and better visibility, promoting safer and more user-friendly parking experiences.
Traffic Flow Impact in Parking Lots
Angled parking enhances traffic flow in parking lots by allowing easier entry and exit, reducing maneuvering time and vehicle conflicts compared to straight parking. This layout typically supports one-way traffic patterns, minimizing congestion and improving safety for both drivers and pedestrians. Parking lots designed with angled spaces often accommodate higher turnover rates, optimizing space utilization and overall efficiency.
Cost Implications for Installation
Angled parking requires more space per vehicle compared to straight parking, leading to higher land acquisition and paving costs. The design complexity of angled parking often demands additional signage and markings, increasing installation expenses. Straight parking maximizes lot capacity and minimizes construction costs, making it a more cost-effective option for large-scale parking areas.
Best Use Cases for Each Parking Type
Angled parking is ideal for locations with narrow aisles or one-way traffic flows, maximizing space efficiency and easing vehicle entry and exit. Straight parking suits areas with wider aisles or two-way traffic, providing simpler maneuverability and typically accommodating larger vehicle volumes. Both parking types optimize lot design when matched to specific traffic patterns and available space constraints.
Final Decision: Choosing the Right Parking Layout
Angled parking maximizes space efficiency and ease of access, suitable for areas with limited width or one-way traffic flow, while straight parking accommodates higher vehicle density in wider lots and supports two-way traffic movement. Decision-makers must assess factors such as traffic direction, lot dimensions, and user convenience to determine the optimal layout. Prioritizing safety, maneuverability, and space utilization ensures the chosen design effectively meets the specific demands of the parking environment.
Angled parking vs straight parking Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com