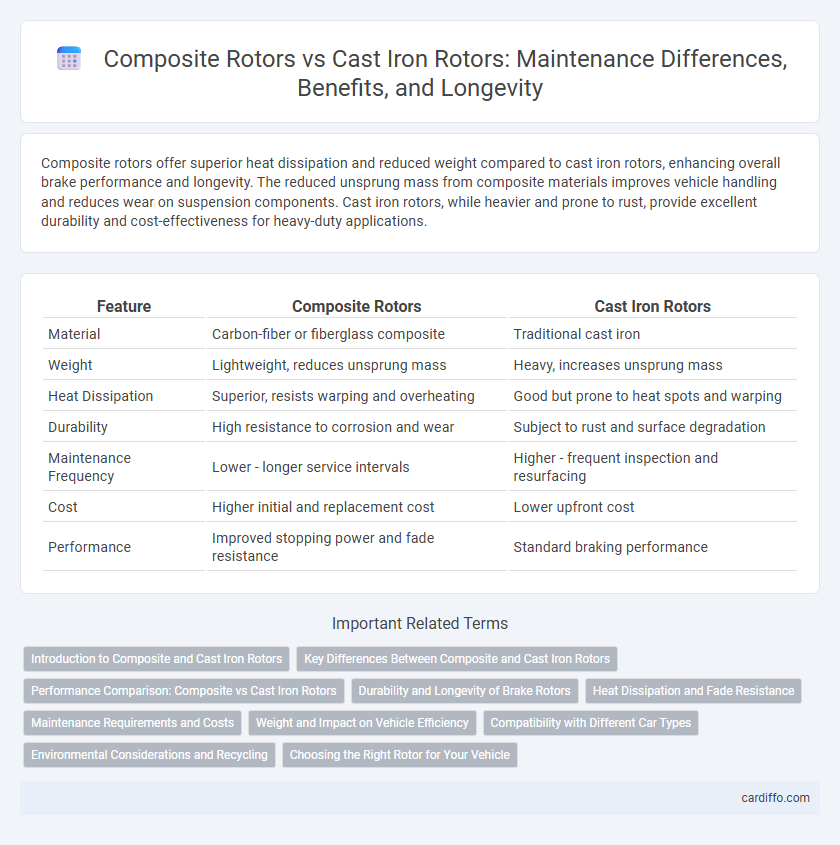
Composite rotors offer superior heat dissipation and reduced weight compared to cast iron rotors, enhancing overall brake performance and longevity. The reduced unsprung mass from composite materials improves vehicle handling and reduces wear on suspension components. Cast iron rotors, while heavier and prone to rust, provide excellent durability and cost-effectiveness for heavy-duty applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Composite Rotors | Cast Iron Rotors |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Carbon-fiber or fiberglass composite | Traditional cast iron |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces unsprung mass | Heavy, increases unsprung mass |
| Heat Dissipation | Superior, resists warping and overheating | Good but prone to heat spots and warping |
| Durability | High resistance to corrosion and wear | Subject to rust and surface degradation |
| Maintenance Frequency | Lower - longer service intervals | Higher - frequent inspection and resurfacing |
| Cost | Higher initial and replacement cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Performance | Improved stopping power and fade resistance | Standard braking performance |
Introduction to Composite and Cast Iron Rotors
Composite rotors, made from advanced materials such as carbon fiber and reinforced polymers, offer superior heat dissipation and reduced weight compared to traditional cast iron rotors. Cast iron rotors, known for their durability and high thermal mass, provide consistent braking performance but are heavier and more prone to rust. Maintenance considerations for composite rotors include monitoring for delamination and material fatigue, whereas cast iron rotors require regular inspection for corrosion and surface wear.
Key Differences Between Composite and Cast Iron Rotors
Composite rotors offer superior heat dissipation and reduced weight compared to cast iron rotors, resulting in improved braking performance and fuel efficiency. Cast iron rotors provide durability and cost-effectiveness but are prone to warping under high heat, leading to maintenance challenges. The choice between composite and cast iron rotors involves balancing performance benefits against longevity and expense in brake system maintenance.
Performance Comparison: Composite vs Cast Iron Rotors
Composite rotors offer enhanced heat dissipation and reduced weight compared to cast iron rotors, resulting in improved braking performance and quicker vehicle response. Cast iron rotors provide excellent durability and cost-effectiveness but generate higher thermal mass, which can lead to increased brake fade during intense or prolonged braking. The superior thermal conductivity and lower unsprung mass of composite rotors contribute to better overall driving dynamics and longer component lifespan under demanding maintenance conditions.
Durability and Longevity of Brake Rotors
Composite rotors, made from a blend of carbon fibers and resin, offer superior durability and longevity compared to traditional cast iron rotors due to their enhanced heat dissipation and resistance to warping. Cast iron rotors, while cost-effective, are prone to faster wear and surface deformation under high-stress braking conditions, reducing their lifespan significantly. Maintenance schedules for composite rotors can be extended as their structural integrity remains stable over time, making them a preferred choice for high-performance and heavy-duty applications.
Heat Dissipation and Fade Resistance
Composite rotors offer superior heat dissipation compared to cast iron rotors due to their lightweight materials and ventilated design, which helps maintain optimal braking performance during prolonged use. Their enhanced fade resistance reduces the risk of brake fade under extreme conditions, ensuring consistent stopping power and increased safety. Cast iron rotors, while durable, absorb and retain more heat, leading to quicker fade and reduced efficiency in high-stress applications.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Composite rotors demand less frequent maintenance due to their resistance to corrosion and lower susceptibility to warping compared to cast iron rotors. Cast iron rotors often require more frequent inspections, resurfacing, and replacement due to rust and uneven wear, increasing overall maintenance costs. The initial cost of composite rotors is higher, but their durability and reduced maintenance needs typically result in lower long-term expenses.
Weight and Impact on Vehicle Efficiency
Composite rotors are significantly lighter than cast iron rotors, reducing unsprung weight and improving vehicle handling and fuel efficiency. The lower weight of composite rotors decreases rotational inertia, allowing for quicker acceleration and deceleration, which enhances overall braking performance and energy efficiency. Cast iron rotors, while durable, add more mass, leading to increased fuel consumption and reduced responsiveness in vehicle dynamics.
Compatibility with Different Car Types
Composite rotors offer enhanced compatibility with a wider range of car types due to their lightweight design and superior heat dissipation, making them ideal for modern performance and electric vehicles. Cast iron rotors, while durable and cost-effective, are best suited for traditional gasoline-powered cars with standard braking needs. Selecting the appropriate rotor material ensures optimal braking performance and longevity tailored to the vehicle's specific requirements.
Environmental Considerations and Recycling
Composite rotors offer significant environmental advantages over cast iron rotors due to their lighter weight, which reduces vehicle fuel consumption and emissions. Unlike cast iron, composite materials can be more challenging to recycle, but advancements in recycling technologies are improving the recovery of fibers and resins, minimizing landfill waste. Cast iron rotors are fully recyclable through traditional metal recycling processes, but their heavier mass contributes to higher carbon footprints during transportation and manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Rotor for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right rotor for your vehicle involves comparing composite rotors and cast iron rotors based on durability, heat dissipation, and maintenance needs. Composite rotors offer superior resistance to heat and reduced weight, enhancing braking performance and fuel efficiency, while cast iron rotors provide excellent wear resistance and affordability but can be heavier and prone to rust. For vehicles frequently exposed to heavy braking or high-performance conditions, composite rotors are ideal, whereas cast iron rotors suit everyday driving with lower maintenance costs.
Composite Rotors vs Cast Iron Rotors Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com