Turbocharging uses exhaust gases to spin a turbine and compress air into the engine, improving fuel efficiency and power without significantly increasing weight. Supercharging relies on a belt-driven compressor connected directly to the engine, delivering immediate power boost but often increasing fuel consumption. Turbochargers are preferred for fuel economy, while superchargers excel in providing instant throttle response.
Table of Comparison
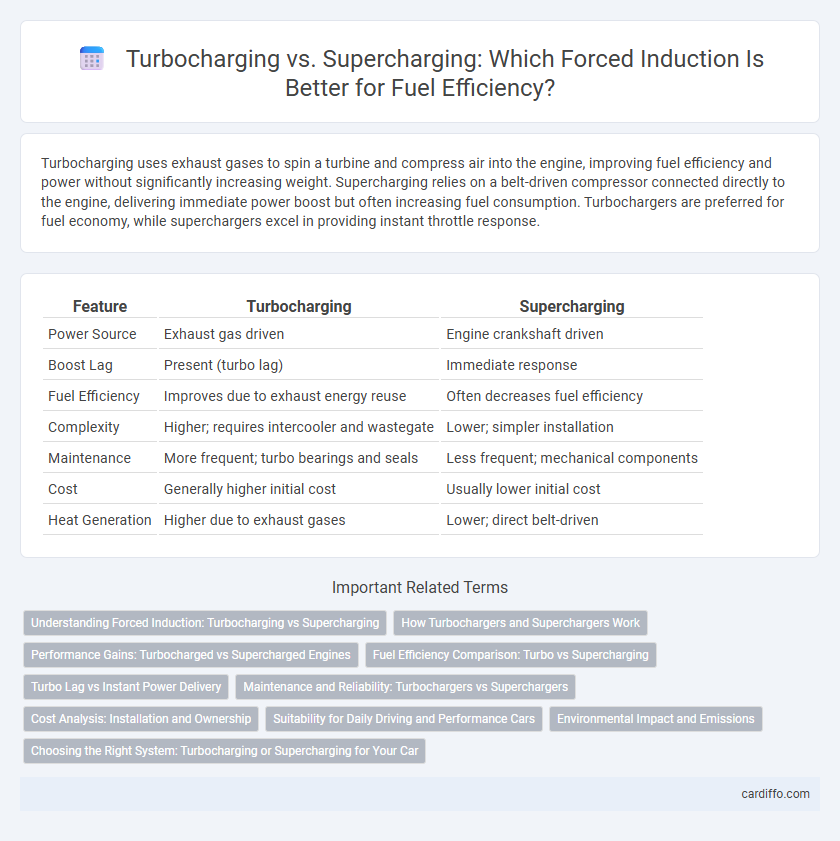
| Feature | Turbocharging | Supercharging |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Exhaust gas driven | Engine crankshaft driven |
| Boost Lag | Present (turbo lag) | Immediate response |
| Fuel Efficiency | Improves due to exhaust energy reuse | Often decreases fuel efficiency |
| Complexity | Higher; requires intercooler and wastegate | Lower; simpler installation |
| Maintenance | More frequent; turbo bearings and seals | Less frequent; mechanical components |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Usually lower initial cost |
| Heat Generation | Higher due to exhaust gases | Lower; direct belt-driven |
Understanding Forced Induction: Turbocharging vs Supercharging
Turbocharging and supercharging are two primary methods of forced induction used to increase an engine's power by compressing air into the combustion chamber. Turbochargers utilize exhaust gases to spin a turbine, improving fuel efficiency and power without mechanical drag, whereas superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine's crankshaft, providing instant boost but often at the cost of higher fuel consumption. Both systems enhance engine performance by increasing air density, but turbochargers excel in efficiency while superchargers deliver more immediate throttle response.
How Turbochargers and Superchargers Work
Turbochargers work by using exhaust gas energy to spin a turbine connected to a compressor, which forces more air into the engine's combustion chamber, increasing air density and engine efficiency. Superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine's crankshaft through a belt or gear system, directly compressing the intake air to boost power output instantly without relying on exhaust gases. Both systems enhance engine performance by increasing oxygen intake, but turbochargers depend on exhaust flow while superchargers provide immediate boost through mechanical linkage.
Performance Gains: Turbocharged vs Supercharged Engines
Turbocharged engines achieve superior performance gains by utilizing exhaust gases to spin the turbine, resulting in increased air intake and higher combustion efficiency, which boosts horsepower and torque without significantly increasing engine weight. Supercharged engines deliver immediate power increases through a belt-driven compressor, providing consistent boost but with a parasitic loss that slightly reduces overall efficiency compared to turbochargers. In terms of fuel economy, turbocharged systems offer better efficiency and performance balance, making them ideal for maximizing power output in modern fuel-conscious vehicles.
Fuel Efficiency Comparison: Turbo vs Supercharging
Turbocharging improves fuel efficiency by using exhaust gas to compress intake air, resulting in better combustion and lower fuel consumption. Supercharging, powered directly by the engine, tends to consume more fuel because it draws energy from the crankshaft, reducing overall efficiency. Studies indicate turbocharged engines typically achieve 10-20% better fuel economy compared to supercharged counterparts under similar driving conditions.
Turbo Lag vs Instant Power Delivery
Turbocharging enhances engine efficiency by using exhaust gases to spin a turbine, resulting in turbo lag due to the delay in reaching optimal boost pressure. Supercharging provides instant power delivery by mechanically driven compression, eliminating lag and offering immediate throttle response. The choice between turbocharging and supercharging impacts fuel performance, with superchargers favoring rapid acceleration and turbochargers excelling in fuel economy at higher RPMs.
Maintenance and Reliability: Turbochargers vs Superchargers
Turbochargers require meticulous maintenance due to their high operating temperatures and reliance on exhaust gases, necessitating frequent oil changes and careful monitoring of turbo lag-related wear. Superchargers, driven directly by the engine belt, offer more immediate power delivery and generally boast greater reliability with less intensive upkeep but may impose additional strain on the engine and consume more fuel. Understanding these differences in maintenance demands and durability helps optimize performance and longevity in forced induction systems.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Ownership
Turbocharging generally offers a more cost-effective installation compared to supercharging due to its utilization of exhaust gases, reducing the need for additional components. Ownership expenses for turbocharged systems tend to be lower since they improve fuel efficiency and require less frequent maintenance than superchargers. However, superchargers provide a more straightforward installation and immediate power delivery, which can result in higher upfront costs and potential long-term maintenance fees.
Suitability for Daily Driving and Performance Cars
Turbocharging offers improved fuel efficiency and enhanced engine performance by utilizing exhaust gases to increase air intake, making it ideal for both daily driving and performance cars seeking a balance between power and economy. Supercharging provides immediate power delivery with less lag due to its direct belt-driven mechanism, favored in high-performance vehicles that require consistent and linear boost throughout the RPM range. Daily drivers benefit from turbochargers' efficiency, while superchargers better suit performance cars needing instant throttle response and maximum horsepower.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Turbocharging improves fuel efficiency by utilizing exhaust gases to increase engine power without extra fuel consumption, resulting in lower CO2 emissions compared to naturally aspirated engines. Supercharging, driven mechanically by the engine, increases fuel consumption and often leads to higher emissions due to less efficient energy use. Environmental impact studies show turbocharged engines typically produce fewer pollutants, making them a greener option in modern automotive design.
Choosing the Right System: Turbocharging or Supercharging for Your Car
Turbocharging offers improved fuel efficiency and higher power gains by utilizing exhaust gases to spin the turbine, making it ideal for daily drivers seeking better mileage and performance. Supercharging provides immediate throttle response and consistent power delivery through a belt-driven mechanism, preferred in racing or high-performance applications where instant boost is critical. Selecting the right forced induction system depends on driving style, engine design, and desired power characteristics, balancing fuel economy against acceleration needs.
Turbocharging vs Supercharging Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com