Superchargers provide immediate boost by driving the compressor directly from the engine, ensuring instant power delivery without lag. Turbochargers rely on exhaust gases to spin the turbine, offering greater efficiency and higher peak power but often with a delayed throttle response. Choosing between a supercharger and turbocharger depends on whether priority is given to low-end torque or top-end performance and fuel economy.
Table of Comparison
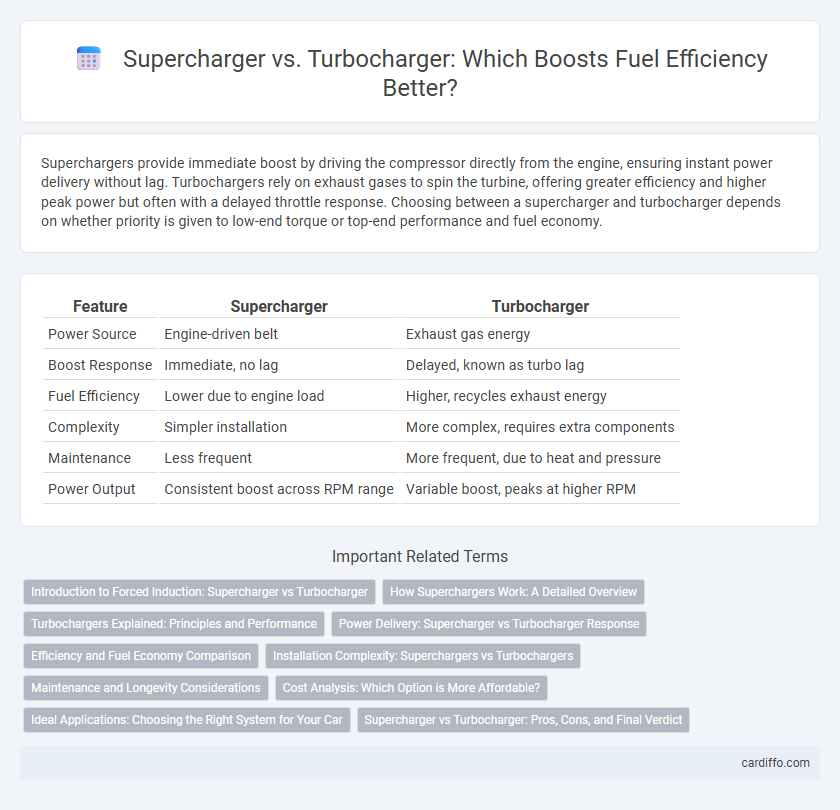
| Feature | Supercharger | Turbocharger |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Engine-driven belt | Exhaust gas energy |
| Boost Response | Immediate, no lag | Delayed, known as turbo lag |
| Fuel Efficiency | Lower due to engine load | Higher, recycles exhaust energy |
| Complexity | Simpler installation | More complex, requires extra components |
| Maintenance | Less frequent | More frequent, due to heat and pressure |
| Power Output | Consistent boost across RPM range | Variable boost, peaks at higher RPM |
Introduction to Forced Induction: Supercharger vs Turbocharger
Superchargers and turbochargers are both forced induction systems designed to increase engine power by compressing intake air, allowing more oxygen to enter the combustion chamber. Superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine's crankshaft, providing instant boost and improved throttle response, while turbochargers utilize exhaust gas energy to spin a turbine, maximizing efficiency and power output at higher RPMs. Understanding the differences in operation, response time, and energy sourcing is critical for optimizing performance and fuel efficiency in modern engines.
How Superchargers Work: A Detailed Overview
Superchargers operate by compressing air and delivering it directly to the engine's intake manifold, increasing the air density for enhanced combustion efficiency and greater power output. Powered mechanically through a belt connected to the engine's crankshaft, superchargers provide immediate boost without lag, improving throttle response at low and mid RPMs. This direct-drive mechanism differentiates superchargers from turbochargers, which rely on exhaust gases, making superchargers particularly effective for consistent power delivery in performance vehicles.
Turbochargers Explained: Principles and Performance
Turbochargers increase engine efficiency and power by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, using exhaust gas energy to spin a turbine connected to a compressor. This process boosts fuel combustion, resulting in higher horsepower and improved fuel economy without significantly increasing engine size. Compared to superchargers, turbochargers are typically more fuel-efficient and provide better performance at higher engine speeds due to their exhaust-driven operation.
Power Delivery: Supercharger vs Turbocharger Response
Superchargers provide immediate power delivery due to their direct mechanical connection to the engine, resulting in zero lag and consistent boost across the RPM range. Turbochargers rely on exhaust gases to spool up, causing a noticeable delay known as turbo lag before maximum power is achieved. This difference in response times significantly influences driving dynamics, with superchargers offering more linear acceleration and turbochargers delivering peak power at higher engine speeds.
Efficiency and Fuel Economy Comparison
Superchargers provide immediate boost by drawing power directly from the engine, often resulting in higher fuel consumption compared to turbochargers, which utilize exhaust gases to increase efficiency. Turbochargers improve fuel economy by recovering energy that would otherwise be wasted, enabling better air-fuel mixture and combustion. In terms of fuel efficiency, turbochargers generally outperform superchargers due to their ability to deliver boost without extra mechanical load on the engine.
Installation Complexity: Superchargers vs Turbochargers
Superchargers offer a more straightforward installation process as they are typically belt-driven and mounted directly to the engine, allowing for easier integration with existing components. Turbochargers require a more complex installation involving exhaust manifold modifications, additional piping for the intercooler, and precise tuning to manage boost pressure effectively. The increased complexity and need for heat management in turbochargers often result in longer installation times and higher labor costs compared to superchargers.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Superchargers typically demand more frequent maintenance due to their mechanical drive connection to the engine, which subjects them to greater wear and tear over time. Turbochargers, powered by exhaust gases, often have longer lifespans but require careful monitoring of oil quality and temperature to prevent premature failure. Understanding these maintenance and longevity factors helps optimize performance and reduces overall repair costs in fuel-boosting systems.
Cost Analysis: Which Option is More Affordable?
Superchargers typically have higher upfront costs due to their complex design and robust materials, while turbochargers tend to be more affordable initially as they utilize exhaust gases to increase engine power. Maintenance and repair expenses for superchargers can be greater over time because of the direct mechanical connection to the engine, whereas turbochargers often incur additional costs related to heat management and turbo lag issues. Overall, turbochargers offer a more cost-effective solution for budget-conscious drivers seeking efficient power boosts without significant fuel consumption increases.
Ideal Applications: Choosing the Right System for Your Car
Superchargers excel in low-RPM torque delivery, making them ideal for street-driven vehicles requiring immediate throttle response and enhanced acceleration. Turbochargers, driven by exhaust gases, provide greater efficiency and higher peak power, benefiting high-performance or racing cars that operate at higher RPMs. Selecting the right system depends on driving style, engine design, and performance goals to maximize fuel efficiency and power output.
Supercharger vs Turbocharger: Pros, Cons, and Final Verdict
Superchargers provide immediate power by mechanically driven boost, enhancing low-end torque but often reducing fuel efficiency compared to turbochargers, which utilize exhaust gases to improve engine output with better fuel economy but can suffer from turbo lag. Turbochargers excel in maximizing horsepower and fuel savings for high-performance and fuel-conscious drivers, while superchargers deliver consistent power gain without delay, making them ideal for applications demanding instant throttle response. The final verdict depends on use case: superchargers suit vehicles prioritizing quick power delivery and simplicity, whereas turbochargers favor efficiency and peak performance in modern engines.
Supercharger vs Turbocharger Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com