Wet braking distance significantly exceeds dry braking distance due to reduced tire-road friction caused by water acting as a lubricant. This decreased traction requires more time and distance for vehicles to come to a complete stop on wet surfaces compared to dry conditions. Understanding this difference is crucial for maintaining safe driving speeds and following distances during adverse weather.
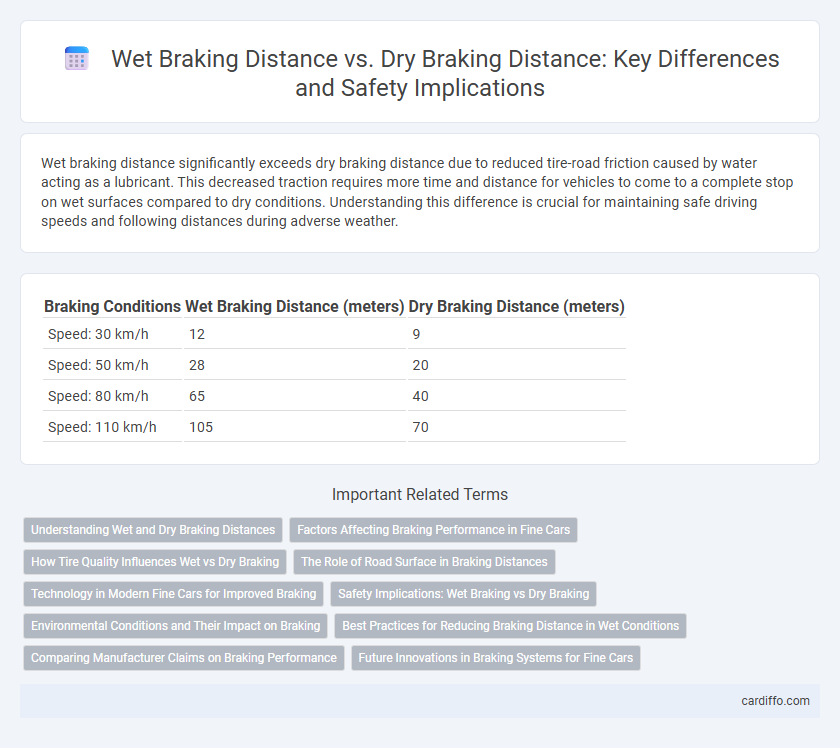
Table of Comparison
| Braking Conditions | Wet Braking Distance (meters) | Dry Braking Distance (meters) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed: 30 km/h | 12 | 9 |
| Speed: 50 km/h | 28 | 20 |
| Speed: 80 km/h | 65 | 40 |
| Speed: 110 km/h | 105 | 70 |
Understanding Wet and Dry Braking Distances
Wet braking distances significantly exceed dry braking distances due to reduced tire-road friction caused by water layers on the surface. Factors such as tire tread depth, water film thickness, and vehicle speed directly influence the increase in stopping distance during wet conditions. Understanding these variables is critical for improving vehicle safety and optimizing braking system performance in diverse weather scenarios.
Factors Affecting Braking Performance in Fine Cars
Wet braking distance in fine cars typically exceeds dry braking distance due to reduced tire-road friction and water film interference. Factors affecting braking performance include tire tread depth, brake system quality, and road surface texture, which influence grip and heat dissipation. Vehicle weight and electronic stability control systems also play crucial roles in optimizing braking efficiency under wet conditions.
How Tire Quality Influences Wet vs Dry Braking
High-quality tires with superior tread patterns and compounds significantly reduce both wet and dry braking distances by enhancing grip and water evacuation. In wet conditions, tires with advanced siping and deeper grooves maintain traction on slippery surfaces, shortening wet braking distances compared to lower-quality tires. On dry roads, premium tires with optimized rubber compounds offer increased friction, leading to more effective and shorter stopping distances.
The Role of Road Surface in Braking Distances
Road surface significantly influences wet and dry braking distances due to varying friction levels. Wet surfaces reduce tire-road traction, increasing braking distances by up to 50% compared to dry conditions. Pavement texture, water accumulation, and road material directly affect the coefficient of friction, impacting vehicle stopping performance.
Technology in Modern Fine Cars for Improved Braking
Modern fine cars utilize advanced technologies such as carbon-ceramic brakes and electronic brake-force distribution to significantly reduce wet braking distance compared to traditional systems. Anti-lock braking systems (ABS) combined with sophisticated sensor arrays optimize grip and stability by adjusting brake pressure dynamically under wet conditions. These innovations enhance safety by minimizing stopping distances on slippery surfaces, outperforming conventional dry braking performance.
Safety Implications: Wet Braking vs Dry Braking
Wet braking distance typically exceeds dry braking distance by 25-50%, significantly impacting vehicle stopping times during rain or wet road conditions. Reduced traction on wet surfaces increases the risk of hydroplaning and loss of control, emphasizing the need for increased following distances and cautious speed adjustment. Understanding these safety implications helps drivers prevent accidents caused by delayed stopping in adverse weather.
Environmental Conditions and Their Impact on Braking
Wet braking distance significantly exceeds dry braking distance due to reduced tire-road friction caused by water on the road surface. Environmental conditions such as rain, puddles, or wet asphalt decrease traction, leading to longer stopping times and increased risk of skidding. Temperature variations and surface contaminants like oil or mud further exacerbate the loss of grip, making wet braking distances unpredictable compared to dry conditions.
Best Practices for Reducing Braking Distance in Wet Conditions
Reducing braking distance in wet conditions requires optimizing tire traction through high-quality, properly inflated tires with deep tread patterns designed to channel water away effectively. Maintaining lower speeds and increasing following distances provide drivers with more reaction time and improved safety margins on slippery surfaces. Implementing advanced braking technologies such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and electronic stability control (ESC) enhances vehicle control and reduces stopping distances during wet road emergencies.
Comparing Manufacturer Claims on Braking Performance
Manufacturer claims on wet braking distance often show a 20% to 30% increase compared to dry braking due to reduced tire-road friction. Testing protocols reveal variability in reported distances, with some brands emphasizing advanced rubber compounds or tread designs to minimize wet stopping distances. Independent tests frequently highlight discrepancies between advertised performance and real-world results, underscoring the importance of third-party braking assessments.
Future Innovations in Braking Systems for Fine Cars
Emerging innovations in braking systems for fine cars emphasize reducing wet braking distances through advanced sensor integration and adaptive brake force distribution, enhancing safety on slippery surfaces. Brake-by-wire technology combined with AI-driven algorithms allows real-time assessment of road conditions, optimizing braking response more precisely than traditional hydraulic systems. Future developments will likely incorporate smart materials and enhanced regenerative braking capabilities to improve wet surface performance while maintaining efficiency on dry roads.
Wet Braking Distance vs Dry Braking Distance Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com