Idling fines target drivers who leave their engines running while parked to reduce pollution and conserve fuel, promoting environmental responsibility. Unnecessary honking fines penalize excessive or inappropriate use of the car horn to minimize noise pollution and disturbances in urban areas. Both fines encourage more considerate driving habits that benefit public health and community well-being.
Table of Comparison
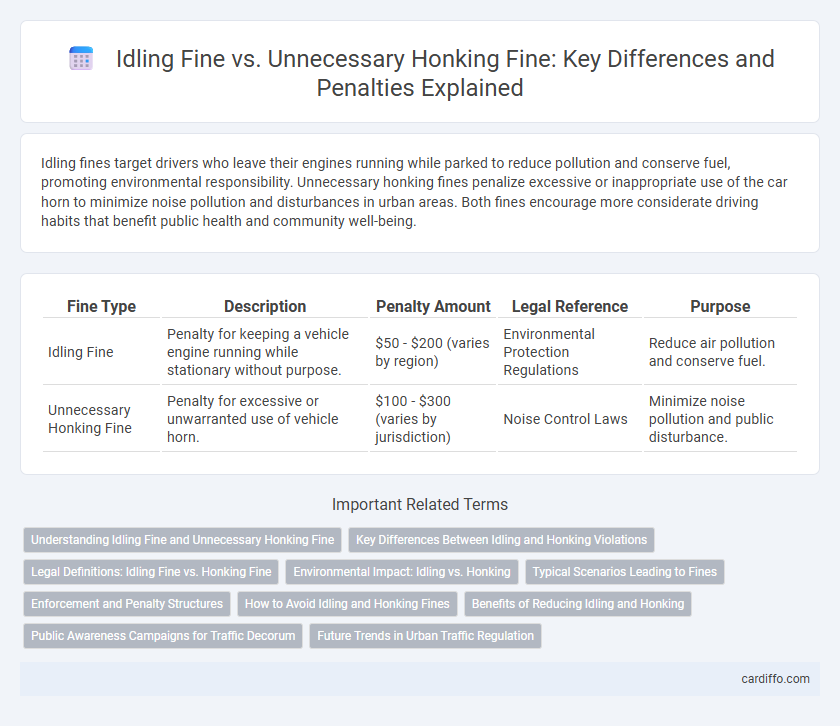
| Fine Type | Description | Penalty Amount | Legal Reference | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Idling Fine | Penalty for keeping a vehicle engine running while stationary without purpose. | $50 - $200 (varies by region) | Environmental Protection Regulations | Reduce air pollution and conserve fuel. |
| Unnecessary Honking Fine | Penalty for excessive or unwarranted use of vehicle horn. | $100 - $300 (varies by jurisdiction) | Noise Control Laws | Minimize noise pollution and public disturbance. |
Understanding Idling Fine and Unnecessary Honking Fine
Understanding idling fines involves recognizing penalties imposed for keeping a vehicle engine running while stationary, which helps reduce air pollution and conserve fuel. Unnecessary honking fines target excessive or inappropriate use of vehicle horns, aiming to minimize noise pollution and maintain public peace. Both fines serve as deterrents that promote responsible driving behavior and environmental awareness.
Key Differences Between Idling and Honking Violations
Idling fines target drivers who keep their vehicle engines running unnecessarily, contributing to environmental pollution and wasting fuel, with penalties often based on duration and local air quality regulations. Unnecessary honking fines address noise pollution caused by excessive or unwarranted use of the vehicle horn, aiming to maintain public peace and reduce auditory disturbance, typically enforced through fixed fines and repeat offense penalties. The key differences lie in the nature of the violation--engine inactivity versus noise emission--and the distinct environmental and social impacts each fine intends to mitigate.
Legal Definitions: Idling Fine vs. Honking Fine
Idling fines are penalties imposed for keeping a vehicle engine running while stationary for extended periods, typically defined by specific local environmental regulations aiming to reduce air pollution. Unnecessary honking fines address the prohibition of noise pollution caused by excessive or unjustified use of vehicle horns, with legal definitions varying by jurisdiction but often emphasizing the disturbance caused to public peace. Both fines are enforced through traffic laws designed to promote environmental protection and public tranquility, with clearly outlined criteria distinguishing idling from honking violations.
Environmental Impact: Idling vs. Honking
Idling vehicles emit significant amounts of carbon dioxide and pollutants, contributing directly to urban air pollution and climate change. Unnecessary honking, while primarily a noise pollution issue, can indirectly affect public health by increasing stress and reducing air quality through prolonged traffic congestion. Reducing idling helps decrease greenhouse gas emissions, whereas minimizing honking improves overall urban environmental conditions by lowering noise levels and promoting smoother traffic flow.
Typical Scenarios Leading to Fines
Idling fines commonly occur when drivers leave their engines running while parked or waiting for extended periods, such as outside schools or in residential neighborhoods. Unnecessary honking fines are often issued in urban areas where drivers use the horn excessively in traffic jams or near hospitals and quiet zones. Both fines aim to reduce noise pollution and environmental impact by targeting typical scenarios of careless vehicle use.
Enforcement and Penalty Structures
Enforcement of idling fines typically involves monitoring vehicle emissions and time limits at specific locations, with penalties ranging from $50 to $150 depending on jurisdiction and repeat offenses. Unnecessary honking fines are often imposed based on noise pollution regulations, carrying fines between $75 and $200, aimed at reducing urban noise disturbances. Both penalties are enforced by traffic authorities using surveillance cameras and officer assessments to ensure compliance and promote public environmental health.
How to Avoid Idling and Honking Fines
To avoid idling fines, turn off your engine when stationary for more than a few minutes, especially in restricted zones or congested urban areas where local regulations are strict. Minimize unnecessary honking by using it only for safety alerts and conforming to noise pollution laws often enforced with significant penalties. Familiarize yourself with specific municipal ordinances on idling and honking to ensure compliance and reduce the risk of fines.
Benefits of Reducing Idling and Honking
Reducing idling decreases fuel consumption and lowers harmful emissions, improving air quality and promoting public health. Minimizing unnecessary honking contributes to noise pollution reduction, enhancing community well-being and reducing stress-related health issues. Both measures support environmental sustainability and foster more peaceful urban environments.
Public Awareness Campaigns for Traffic Decorum
Public awareness campaigns targeting idling fines and unnecessary honking fines play a crucial role in promoting traffic decorum by educating drivers on the environmental and noise pollution impacts. These campaigns utilize multimedia channels to highlight legal repercussions and encourage behavioral changes that reduce emissions and noise disturbances. Engaging community participation and consistent messaging significantly improve compliance rates and foster a culture of responsible driving.
Future Trends in Urban Traffic Regulation
Future trends in urban traffic regulation emphasize stricter enforcement of idling fines to reduce air pollution and improve air quality. Unnecessary honking fines are expected to increase as cities adopt smart noise monitoring technologies to enhance urban soundscapes. Integration of AI-driven sensors and real-time data analytics will enable dynamic fine adjustments based on environmental impact assessments.
Idling fine vs unnecessary honking fine Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com