A standard fine is typically a fixed amount imposed for minor violations, providing a straightforward penalty without additional conditions. Enhanced fines escalate the financial consequences based on factors like repeated offenses or the severity of the violation, serving as a stronger deterrent. Choosing between standard and enhanced fines depends on the regulatory framework and the intent to discourage future non-compliance.
Table of Comparison
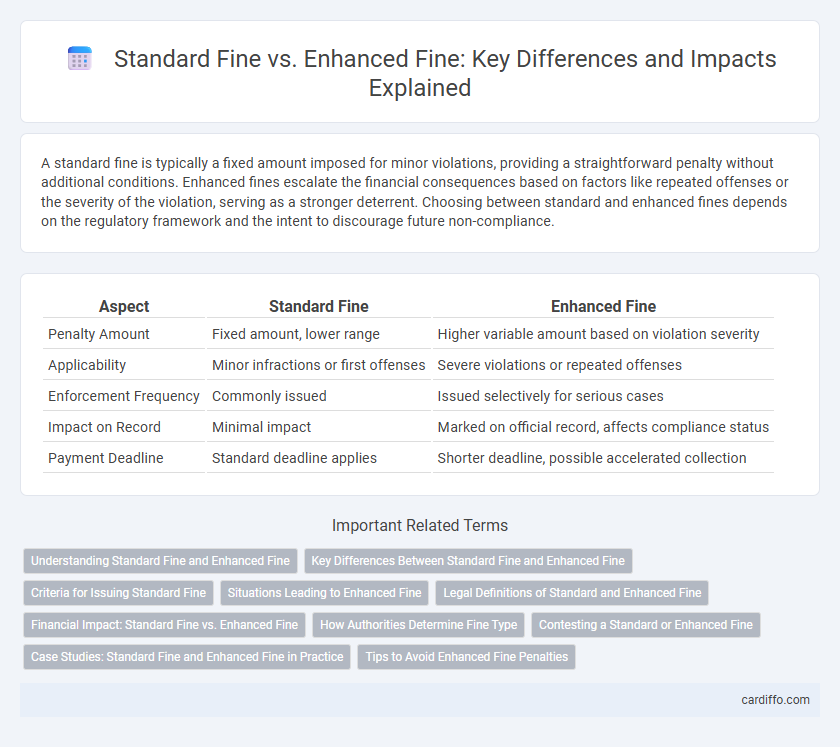
| Aspect | Standard Fine | Enhanced Fine |
|---|---|---|
| Penalty Amount | Fixed amount, lower range | Higher variable amount based on violation severity |
| Applicability | Minor infractions or first offenses | Severe violations or repeated offenses |
| Enforcement Frequency | Commonly issued | Issued selectively for serious cases |
| Impact on Record | Minimal impact | Marked on official record, affects compliance status |
| Payment Deadline | Standard deadline applies | Shorter deadline, possible accelerated collection |
Understanding Standard Fine and Enhanced Fine
Standard fines serve as the baseline penalty for regulatory violations, often determined by the severity and nature of the offense. Enhanced fines apply in cases involving aggravating factors such as repeated offenses, intentional misconduct, or failure to cooperate, resulting in significantly higher penalties. Understanding the distinction is crucial for compliance strategies, as enhanced fines can substantially increase financial liabilities beyond standard fine amounts.
Key Differences Between Standard Fine and Enhanced Fine
Standard fines typically apply to common offenses with fixed penalty amounts set by law, whereas enhanced fines involve higher financial penalties triggered by aggravating factors such as repeat violations or severity of the offense. Enhanced fines serve as a deterrent by imposing stricter economic consequences, often calculated as multiples of the standard fine. The key difference lies in the increased monetary impact and stricter applicability criteria of enhanced fines compared to the more predictable and uniform nature of standard fines.
Criteria for Issuing Standard Fine
Standard fines are issued based on clear criteria such as the nature and severity of the violation, the offender's compliance history, and the potential harm caused by the infraction. Regulatory bodies prioritize cases where the breach is minor, non-repetitive, and shows no intent to evade compliance, resulting in standard penalties. Enhanced fines apply when violations are deliberate, repeated, or cause significant damage, exceeding the thresholds set for standard fines.
Situations Leading to Enhanced Fine
Enhanced fines apply in situations where violations involve repeated offenses, significant harm, or intentional misconduct, exceeding the thresholds set for standard fines. Standard fines typically cover minor or first-time infractions with limited impact, while enhanced fines respond to aggravating factors such as fraud, negligence, or failure to comply with corrective measures. Regulatory agencies impose enhanced fines to deter severe violations and ensure compliance in high-risk environments.
Legal Definitions of Standard and Enhanced Fine
Standard fines are monetary penalties imposed for minor offenses defined under legal statutes without aggravating factors, typically capped by legislation to a fixed amount or range. Enhanced fines apply when specific aggravating circumstances are present, such as repeat offenses or actions causing significant harm, leading to higher maximum penalties authorized by law. Legal definitions distinguish standard fines as baseline penalties, while enhanced fines reflect escalated sanctions designed to deter severe or persistent violations.
Financial Impact: Standard Fine vs. Enhanced Fine
Standard fines impose fixed financial penalties that serve as straightforward deterrents for regulatory violations, typically based on the severity of the offense. Enhanced fines significantly increase the monetary penalties, often scaling with factors such as the size of the company, the duration of the violation, and the nature of the harm caused, resulting in a substantially higher financial impact. This escalation aims to reinforce compliance by imposing more substantial economic consequences that exceed the ordinary financial burden of standard fines.
How Authorities Determine Fine Type
Authorities determine the type of fine based on the severity and nature of the violation, with standard fines applied for minor infractions and enhanced fines reserved for repeat offenses or cases involving significant harm or negligence. Factors such as the extent of damage, intent, and compliance history influence whether a standard or enhanced fine is issued. Enhanced fines aim to deter serious breaches by imposing higher penalties that reflect the increased risk or impact associated with the violation.
Contesting a Standard or Enhanced Fine
Contesting a standard or enhanced fine requires understanding the specific grounds and evidence needed for each type. A standard fine typically involves lower penalties and can be challenged by demonstrating mitigating circumstances or procedural errors. Enhanced fines carry higher penalties and often demand more substantial proof, such as disproving deliberate violations or highlighting inconsistencies in enforcement to successfully contest the charge.
Case Studies: Standard Fine and Enhanced Fine in Practice
Case studies reveal that standard fines typically address minor infractions with fixed penalties, ensuring swift resolution and compliance reinforcement. Enhanced fines apply to severe or repeated violations, leveraging increased financial deterrents to promote corrective action in high-risk scenarios. Analysis of enforcement outcomes shows enhanced fines significantly reduce recidivism rates compared to standard penalties.
Tips to Avoid Enhanced Fine Penalties
To avoid enhanced fine penalties, ensure strict compliance with regulations by regularly updating safety protocols and conducting thorough employee training sessions. Implement comprehensive record-keeping practices to document adherence to standards and promptly address any identified violations. Regular internal audits help identify potential risks early, minimizing the chances of incurring costly enhanced fines compared to standard fines.
Standard fine vs enhanced fine Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com