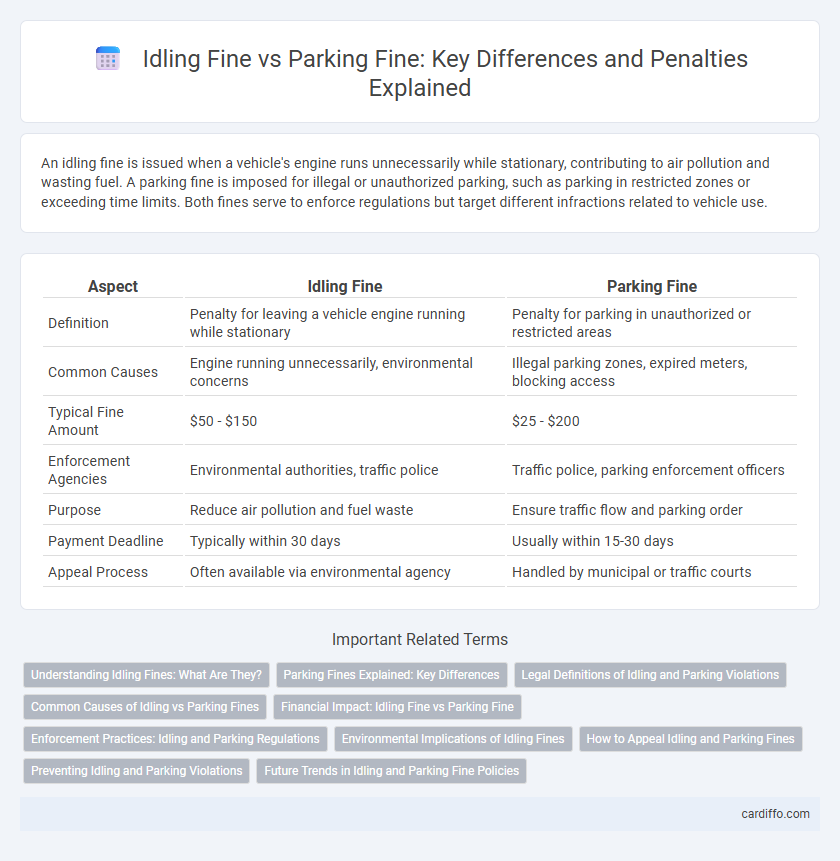
An idling fine is issued when a vehicle's engine runs unnecessarily while stationary, contributing to air pollution and wasting fuel. A parking fine is imposed for illegal or unauthorized parking, such as parking in restricted zones or exceeding time limits. Both fines serve to enforce regulations but target different infractions related to vehicle use.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Idling Fine | Parking Fine |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Penalty for leaving a vehicle engine running while stationary | Penalty for parking in unauthorized or restricted areas |
| Common Causes | Engine running unnecessarily, environmental concerns | Illegal parking zones, expired meters, blocking access |
| Typical Fine Amount | $50 - $150 | $25 - $200 |
| Enforcement Agencies | Environmental authorities, traffic police | Traffic police, parking enforcement officers |
| Purpose | Reduce air pollution and fuel waste | Ensure traffic flow and parking order |
| Payment Deadline | Typically within 30 days | Usually within 15-30 days |
| Appeal Process | Often available via environmental agency | Handled by municipal or traffic courts |
Understanding Idling Fines: What Are They?
Idling fines are penalties imposed for leaving a vehicle's engine running while stationary, often aimed at reducing air pollution and conserving fuel. These fines vary by jurisdiction but typically occur when a vehicle is idle beyond a permitted time limit, such as three to five minutes. Understanding idling fines helps drivers comply with local regulations and avoid unnecessary charges while promoting environmental responsibility.
Parking Fines Explained: Key Differences
Parking fines are penalties imposed for violations such as parking in unauthorized zones, exceeding allotted parking time, or failing to display a valid parking permit. Idling fines, by contrast, penalize drivers who leave their engine running while the vehicle is stationary, often to reduce emissions and improve air quality. Understanding these distinctions helps drivers avoid fines by adhering to specific regulations related to vehicle placement and engine use.
Legal Definitions of Idling and Parking Violations
Idling fines result from violations of laws that prohibit running a vehicle's engine while it is stationary, often defined in local environmental or traffic codes to reduce emissions and conserve fuel. Parking fines occur when a vehicle is left unattended in a location where parking is restricted by municipal regulations, including no-parking zones, time-limited spaces, or permit-only areas. Legal definitions distinguish idling violations by engine activity status, whereas parking violations focus on vehicle placement and time restrictions.
Common Causes of Idling vs Parking Fines
Idling fines often result from leaving a vehicle's engine running while stationary for extended periods, commonly in no-idle zones or environmentally sensitive areas. Parking fines typically arise from violations such as parking in restricted zones, expired meters, or obstructing traffic and pedestrian pathways. Understanding these distinctions helps drivers avoid penalties by adhering to specific regulations related to engine operation and authorized parking locations.
Financial Impact: Idling Fine vs Parking Fine
Idling fines typically impose lower financial costs compared to parking fines, with idling penalties ranging from $20 to $100, while parking fines can exceed $200 depending on the jurisdiction. The cumulative impact of repeated idling fines can add up but usually remains less burdensome than the lump-sum payment of a parking fine. Businesses and individuals should weigh the frequency of violations and potential total expenditures when evaluating the financial impact of idling fines versus parking fines.
Enforcement Practices: Idling and Parking Regulations
Enforcement practices for idling fines typically involve monitoring specific time limits during which engines may run while stationary to reduce pollution and conserve fuel. Parking fines are enforced through regular patrols and automated systems that detect unauthorized or time-exceeded parking, often supported by parking meters or digital apps. Both regulations rely on clearly posted signs and local government ordinances to inform and regulate public behavior effectively.
Environmental Implications of Idling Fines
Idling fines significantly reduce unnecessary vehicle emissions by discouraging drivers from leaving engines running when parked, thus lowering air pollution and greenhouse gas contributions. Unlike parking fines, which primarily regulate space usage, idling fines target environmental health by reducing particulate matter and nitrogen oxides released during idle periods. Municipalities adopting stringent idling regulations help improve urban air quality and promote sustainable transportation practices.
How to Appeal Idling and Parking Fines
To appeal idling fines, gather evidence such as photos or video showing compliance with local anti-idling regulations and submit a formal written objection referencing the specific ordinance. For parking fines, review the ticket details for errors, collect supporting documentation like receipts or permits, and file an appeal with the relevant parking authority or court within the designated timeframe. Providing clear evidence and citing applicable laws enhances the chances of successfully contesting both idling and parking penalties.
Preventing Idling and Parking Violations
Preventing idling and parking violations requires clear signage and strict enforcement to reduce traffic congestion and improve air quality. Implementing educational campaigns that highlight the environmental and legal consequences of idling and illegal parking can foster compliance. Utilizing technology such as automated sensors and cameras enhances monitoring and ensures timely issuance of fines to deter violations effectively.
Future Trends in Idling and Parking Fine Policies
Emerging trends indicate that idling fines will increasingly incorporate real-time monitoring technologies to reduce vehicle emissions and improve air quality in urban areas. Parking fine policies are predicted to evolve with smart city integrations, utilizing AI-powered sensors to optimize space usage and enhance enforcement efficiency. Both idling and parking fines are expected to reflect growing environmental concerns and urban mobility innovations.
Idling Fine vs Parking Fine Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com