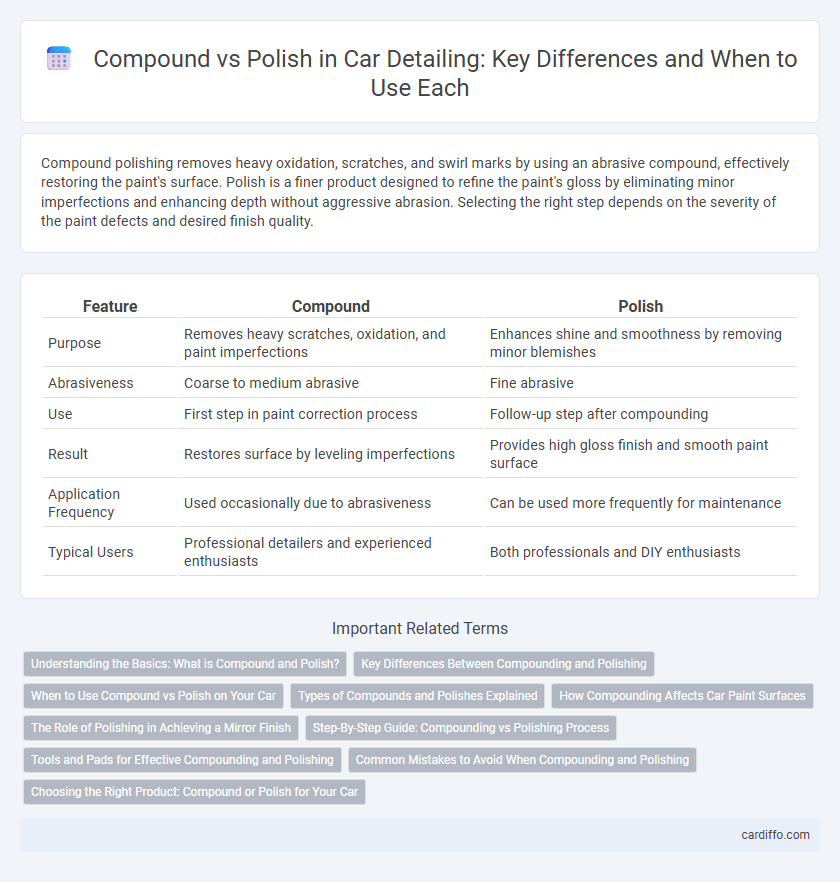
Compound polishing removes heavy oxidation, scratches, and swirl marks by using an abrasive compound, effectively restoring the paint's surface. Polish is a finer product designed to refine the paint's gloss by eliminating minor imperfections and enhancing depth without aggressive abrasion. Selecting the right step depends on the severity of the paint defects and desired finish quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Compound | Polish |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Removes heavy scratches, oxidation, and paint imperfections | Enhances shine and smoothness by removing minor blemishes |
| Abrasiveness | Coarse to medium abrasive | Fine abrasive |
| Use | First step in paint correction process | Follow-up step after compounding |
| Result | Restores surface by leveling imperfections | Provides high gloss finish and smooth paint surface |
| Application Frequency | Used occasionally due to abrasiveness | Can be used more frequently for maintenance |
| Typical Users | Professional detailers and experienced enthusiasts | Both professionals and DIY enthusiasts |
Understanding the Basics: What is Compound and Polish?
Compound is an abrasive detailing product designed to remove surface imperfections like scratches, oxidation, and swirl marks by cutting through the clear coat on a vehicle's paint. Polish is a finer abrasive that refines the paint surface after compounding, enhancing gloss and smoothness by removing minor imperfections and haze. Both processes restore the paint's clarity but serve different roles: compound for significant correction and polish for finishing refinement.
Key Differences Between Compounding and Polishing
Compounding involves using abrasive compounds to remove deeper scratches, oxidation, and surface defects, effectively restoring the paint's smoothness and color. Polishing, on the other hand, refines the paint surface after compounding by using finer abrasives to eliminate minor imperfections and enhance gloss and shine. The key difference lies in their purpose: compounding is more aggressive for paint correction, while polishing focuses on smoothening and boosting the finish's clarity.
When to Use Compound vs Polish on Your Car
Use compound to remove heavy scratches, oxidation, and surface imperfections on your car's paint, restoring its clarity through aggressive abrasion. Polish is best for refining the paint after compounding, enhancing gloss and smoothness by eliminating minor swirl marks and haze. Choose compound when the paint is heavily damaged, and polish when the surface appears dull but free from deep defects.
Types of Compounds and Polishes Explained
Compounds contain abrasive particles designed to remove heavy scratches, oxidation, and paint imperfections, typically available in coarse, medium, and fine varieties depending on the level of correction needed. Polishes, which have a finer abrasive content, refine the surface by eliminating minor swirls and haze, enhancing gloss and preparing the paint for wax or sealant application. Understanding the difference in abrasiveness between compounds and polishes is crucial for selecting the right product to achieve a smooth, high-gloss finish without damaging the paintwork.
How Compounding Affects Car Paint Surfaces
Compounding removes deep scratches and oxidation by using abrasive particles that cut through the clear coat, restoring car paint surfaces to a smoother finish. The process can diminish the clear coat if done excessively, potentially exposing base paint or primer, which risks premature paint failure. Proper compounding balances paint correction with preserving the integrity of the clear coat for long-lasting vehicle aesthetics.
The Role of Polishing in Achieving a Mirror Finish
Polishing plays a critical role in achieving a mirror finish by refining the surface smoothness after compounding has removed major imperfections. While compounding eliminates scratches and oxidation, polishing enhances gloss and depth by minimizing micro-scratches and restoring clarity to the paint. High-quality polishing compounds and pads create a reflective, glass-like surface crucial for a flawless mirror finish in automotive detailing.
Step-By-Step Guide: Compounding vs Polishing Process
The compounding process removes deep scratches, oxidation, and heavy swirl marks using abrasive compounds applied with a rotary polisher, restoring the paint's surface by leveling out imperfections. Polishing follows compounding and targets minor imperfections and fine swirl marks, enhancing paint clarity and gloss through finer abrasives and dual-action polishers. Completing compounding before polishing ensures optimal paint correction and a smooth, reflective finish.
Tools and Pads for Effective Compounding and Polishing
Effective compounding requires the use of cutting pads made from foam or microfiber, designed to remove oxidation and heavy scratches by abrading the clear coat surface. Polishing employs softer polishing pads, typically made of foam or wool, to refine the paint finish, enhance gloss, and eliminate minor imperfections without aggressive abrasion. Using the correct combination of tools, including dual-action or rotary polishers paired with appropriately matched pads, ensures optimal paint correction results and surface smoothness.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Compounding and Polishing
Common mistakes in compounding include using overly abrasive products that damage clear coat and ignoring surface preparation, leading to uneven results. Polishing errors often involve applying excessive pressure or skipping buffing pads, which causes swirl marks or holograms. Consistently using the wrong pad type or neglecting to clean the surface between steps reduces the effectiveness of both compounding and polishing stages.
Choosing the Right Product: Compound or Polish for Your Car
Selecting the right product between compound and polish depends on your car's paint condition; compounds remove deeper scratches and oxidation through abrasive action, while polishes refine the surface and enhance gloss by eliminating minor imperfections. Use a compound when the paint shows clear signs of wear and heavy defects, then follow with a polish to restore shine and smoothness. Proper evaluation of the paintwork ensures the correct balance between correction and protection, maximizing both appearance and finish durability.
Compound vs Polish Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com