Ceramic coating provides a durable, hydrophobic layer that protects paint from scratches, UV rays, and chemical stains, enhancing gloss and ease of cleaning. Graphene coating offers similar protection but excels in thermal conductivity, reducing water spot formation and delivering better heat dissipation. Both coatings extend vehicle appearance longevity, but graphene's advanced properties offer improved resistance to contaminants and enhanced durability.
Table of Comparison
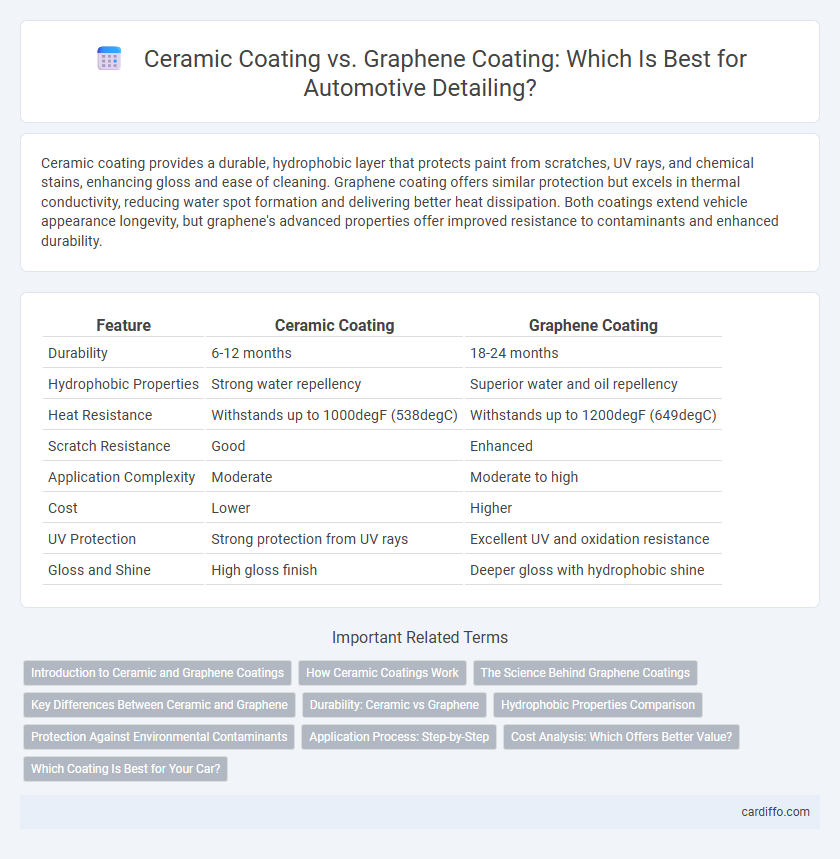
| Feature | Ceramic Coating | Graphene Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | 6-12 months | 18-24 months |
| Hydrophobic Properties | Strong water repellency | Superior water and oil repellency |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands up to 1000degF (538degC) | Withstands up to 1200degF (649degC) |
| Scratch Resistance | Good | Enhanced |
| Application Complexity | Moderate | Moderate to high |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| UV Protection | Strong protection from UV rays | Excellent UV and oxidation resistance |
| Gloss and Shine | High gloss finish | Deeper gloss with hydrophobic shine |
Introduction to Ceramic and Graphene Coatings
Ceramic coating, composed primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2) derived from silica, provides a durable, hydrophobic layer that protects automotive paint from contaminants and UV damage. Graphene coating utilizes a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, offering superior chemical resistance, heat dissipation, and enhanced scratch protection compared to traditional ceramic coatings. Both coatings create a protective barrier, but graphene's advanced molecular structure results in longer-lasting durability and improved surface gloss.
How Ceramic Coatings Work
Ceramic coatings create a durable, hydrophobic layer by bonding silica dioxide (SiO2) molecules to the vehicle's paint surface through a chemical reaction called cross-linking. This nanotechnology forms a hard, protective shield that resists UV damage, oxidation, and chemical stains while enhancing gloss and ease of cleaning. Compared to graphene coatings, ceramic coatings primarily rely on SiO2 for protection, delivering excellent hardness and water repellency but lacking the enhanced thermal conductivity and flexibility found in graphene formulations.
The Science Behind Graphene Coatings
Graphene coatings utilize a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, offering exceptional strength, conductivity, and hydrophobic properties that surpass traditional ceramic coatings. This molecular structure creates a dense, impermeable barrier that resists oxidation, UV damage, and chemical contaminants more effectively than silicon dioxide-based ceramic coatings. The superior thermal conductivity and flexibility of graphene coatings enhance their durability and self-cleaning abilities, making them a breakthrough in automotive detailing technology.
Key Differences Between Ceramic and Graphene
Ceramic coating offers superior hardness and chemical resistance, forming a durable layer that protects automotive paint from scratches, UV rays, and contaminants. Graphene coating excels in thermal conductivity and hydrophobic properties, reducing water spotting and enhancing heat dissipation for better paint longevity. Both coatings provide strong protection, but graphene's molecular structure allows for improved flexibility and easier maintenance compared to traditional ceramic options.
Durability: Ceramic vs Graphene
Ceramic coatings typically offer durability ranging from two to five years, providing excellent resistance to scratches, UV rays, and chemical stains. Graphene coatings extend this protection further, lasting up to seven years with superior hydrophobic properties and enhanced resistance to heat and contaminants. The molecular structure of graphene enables it to bond more effectively to surfaces, resulting in longer-lasting protection compared to traditional ceramic coatings.
Hydrophobic Properties Comparison
Ceramic coatings provide strong hydrophobic properties by creating a dense layer that repels water effectively, causing water to bead and slide off surfaces quickly. Graphene coatings enhance hydrophobicity through a thin, uniform layer of carbon atoms that offer superior water resistance and durability compared to traditional ceramic coatings. Studies show graphene coatings maintain hydrophobic performance longer under harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for sustained protection in automotive detailing.
Protection Against Environmental Contaminants
Ceramic coating provides a strong protective layer that resists water, dirt, and UV damage, effectively shielding the vehicle's paint from environmental contaminants. Graphene coating offers enhanced hydrophobic properties and superior heat dispersion, reducing water spotting and chemical etching caused by acid rain or bird droppings. Both coatings protect against oxidation and corrosion, but graphene's molecular structure delivers longer-lasting defense under harsh environmental conditions.
Application Process: Step-by-Step
The ceramic coating application process begins with thorough surface preparation, including washing, claying, and paint correction to remove contaminants and imperfections. After prepping, the coating is applied in small panels using a microfiber applicator, followed by a curing period of 24-48 hours to ensure chemical bonding with the paint. Graphene coating application mirrors ceramic processes but may require fewer layers and offers faster curing times, enhancing durability and heat dissipation.
Cost Analysis: Which Offers Better Value?
Ceramic coating typically costs between $500 and $1,000 depending on the vehicle size and quality, offering strong durability and resistance to chemicals and UV damage. Graphene coating, priced higher at $800 to $1,200, provides enhanced scratch resistance, heat dissipation, and longevity, potentially reducing maintenance expenses over time. Evaluating cost versus performance, graphene coatings deliver better long-term value for owners seeking advanced protection despite the initial premium.
Which Coating Is Best for Your Car?
Ceramic coating offers excellent durability and hydrophobic properties, providing long-lasting protection against dirt, UV rays, and minor scratches. Graphene coating enhances heat dissipation and reduces water spotting, making it ideal for harsher environments and extended gloss retention. Choosing the best coating depends on your car's usage and exposure, with ceramic favored for ease of maintenance and graphene preferred for advanced protection and durability.
Ceramic Coating vs Graphene Coating Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com