Thrust angle and setback are crucial parameters in vehicle alignment that directly affect handling and tire wear. Thrust angle refers to the direction the rear wheels point relative to the vehicle's centerline, influencing straight-line stability. Setback measures the difference in the positioning of rear wheels on each side, which can cause pulling or uneven tire wear if not properly adjusted.
Table of Comparison
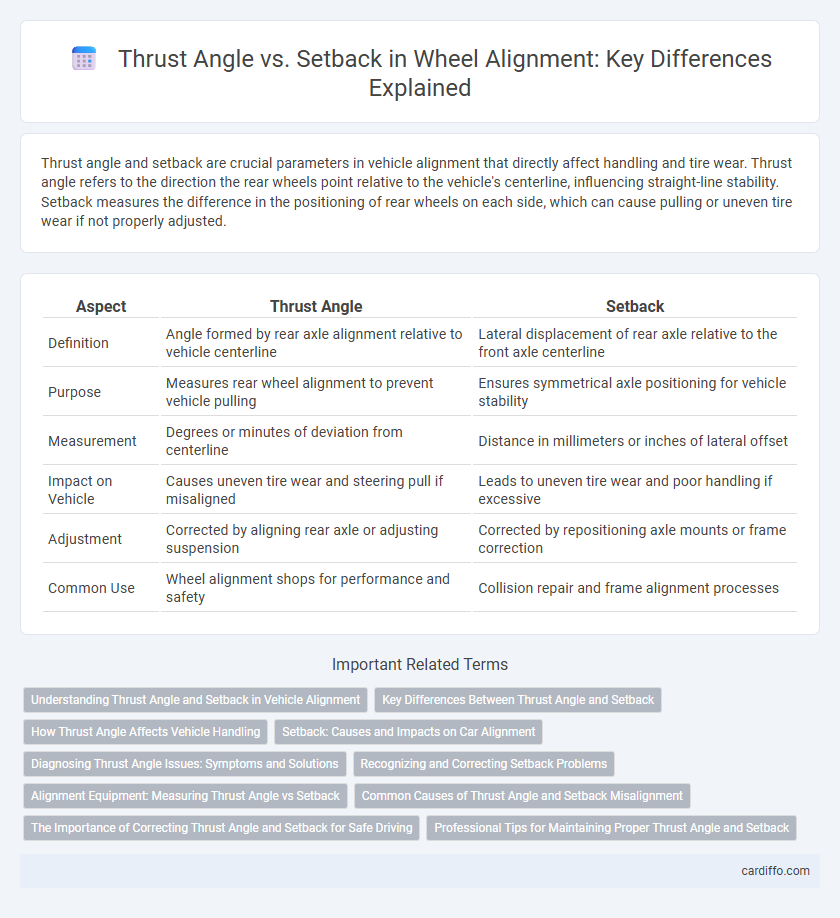
| Aspect | Thrust Angle | Setback |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Angle formed by rear axle alignment relative to vehicle centerline | Lateral displacement of rear axle relative to the front axle centerline |
| Purpose | Measures rear wheel alignment to prevent vehicle pulling | Ensures symmetrical axle positioning for vehicle stability |
| Measurement | Degrees or minutes of deviation from centerline | Distance in millimeters or inches of lateral offset |
| Impact on Vehicle | Causes uneven tire wear and steering pull if misaligned | Leads to uneven tire wear and poor handling if excessive |
| Adjustment | Corrected by aligning rear axle or adjusting suspension | Corrected by repositioning axle mounts or frame correction |
| Common Use | Wheel alignment shops for performance and safety | Collision repair and frame alignment processes |
Understanding Thrust Angle and Setback in Vehicle Alignment
Thrust angle measures the direction that the rear wheels push the vehicle relative to its centerline, affecting straight-line stability and tire wear. Setback refers to the difference in the front wheel positions on the left and right sides, influencing steering precision and vehicle tracking. Proper alignment requires correcting both thrust angle and setback to ensure balanced handling and optimal tire performance.
Key Differences Between Thrust Angle and Setback
Thrust Angle measures the deviation between the vehicle's rear axle alignment and the centerline, indicating how the rear wheels are positioned relative to the front wheels, while Setback refers to the difference in the front wheel positions from side to side, showing asymmetry in axle placement. Thrust Angle affects vehicle tracking and tire wear by causing the vehicle to pull to one side, whereas Setback primarily impacts steering effort and can cause uneven tire wear due to misaligned wheelbase lengths. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for precise wheel alignment and vehicle stability.
How Thrust Angle Affects Vehicle Handling
Thrust angle misalignment causes a vehicle to pull to one side, leading to uneven tire wear and reduced straight-line stability. When the rear axle is not aligned correctly with the centerline, the vehicle's steering efforts increase, compromising handling precision and responsiveness. Proper adjustment of thrust angle ensures balanced tire contact with the road, enhancing overall control and driving safety.
Setback: Causes and Impacts on Car Alignment
Setback refers to the difference in the position of one front wheel compared to the other when measured from the centerline of the car, often caused by manufacturing variances or collision damage. This misalignment can lead to uneven tire wear, steering pull to one side, and compromised vehicle handling. Correcting setback is crucial for precise wheel alignment to ensure consistent tire contact with the road and maintain optimal driving stability.
Diagnosing Thrust Angle Issues: Symptoms and Solutions
Thrust angle issues manifest through symptoms such as uneven tire wear, vehicle pulling to one side, and misaligned steering wheels, indicating misalignment between the rear axle and the vehicle's centerline. Diagnosing thrust angle problems involves measuring the angle with precision tools to detect deviations from manufacturer specifications, often caused by suspension damage or incorrect axle positioning. Corrective solutions include adjusting or replacing suspension components and realigning the rear axle to restore proper thrust angle, ensuring balanced handling and tire longevity.
Recognizing and Correcting Setback Problems
Thrust angle measures the direction your rear wheels point relative to the vehicle's centerline, while setback refers to the difference in the front or rear wheel positions on either side of the chassis. Recognizing setback problems involves inspecting for uneven gaps between tires and body panels or uneven tire wear patterns, which can indicate misalignment or structural damage. Correcting setback requires precise realignment of the suspension components or frame straightening to restore optimal vehicle handling and tire performance.
Alignment Equipment: Measuring Thrust Angle vs Setback
Thrust angle and setback are critical measurements in vehicle alignment that ensure proper tire and suspension positioning. Alignment equipment such as laser alignment systems and computerized wheel aligners provide precise data on thrust angle, which indicates the direction the rear wheels are pointing relative to the vehicle's centerline, while also measuring setback, the difference in distance between the front tires on each side. Accurate measurement of both thrust angle and setback is essential for optimizing handling, tire wear, and vehicle stability.
Common Causes of Thrust Angle and Setback Misalignment
Thrust angle and setback misalignment often result from uneven tire wear, suspension damage, or improper vehicle loading. Worn or damaged control arms and bushings can cause the rear axle to shift laterally, creating thrust angle deviations. Additionally, frame damage from collisions or off-road impacts frequently leads to setbacks, disrupting the rear wheels' alignment with the vehicle's centerline.
The Importance of Correcting Thrust Angle and Setback for Safe Driving
Correcting thrust angle and setback is crucial for maintaining proper vehicle alignment, which directly affects tire wear and steering precision. Misalignment in thrust angle causes the rear wheels to be improperly angled, leading to uneven tire wear and compromised handling stability. Addressing setback prevents the rear axle from being off-center, ensuring balanced vehicle dynamics and safer driving conditions.
Professional Tips for Maintaining Proper Thrust Angle and Setback
Maintaining proper thrust angle and setback requires precise measurements using alignment tools such as laser alignment systems or computerized wheel aligners. Regularly inspect suspension components, control arm bushings, and frame integrity to prevent deviations caused by wear or damage. Professional technicians should perform routine checks during tire rotations and major services to ensure vehicle stability and even tire wear.
Thrust Angle vs Setback Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com