The caster angle influences the steering stability and cornering performance by tilting the steering axis, promoting self-centering of the wheels. Camber angle affects tire contact with the road, optimizing grip and handling during turns by angling the wheels inward or outward. Proper adjustment of both angles ensures balanced alignment, enhancing vehicle control and tire wear.
Table of Comparison
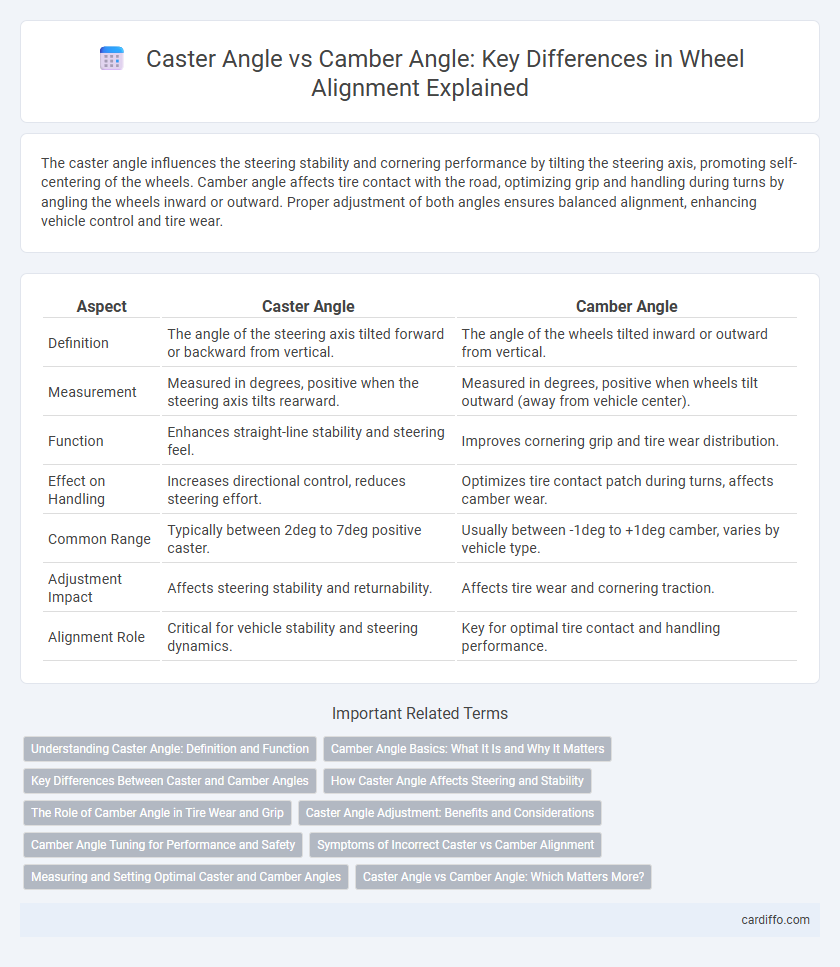
| Aspect | Caster Angle | Camber Angle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The angle of the steering axis tilted forward or backward from vertical. | The angle of the wheels tilted inward or outward from vertical. |
| Measurement | Measured in degrees, positive when the steering axis tilts rearward. | Measured in degrees, positive when wheels tilt outward (away from vehicle center). |
| Function | Enhances straight-line stability and steering feel. | Improves cornering grip and tire wear distribution. |
| Effect on Handling | Increases directional control, reduces steering effort. | Optimizes tire contact patch during turns, affects camber wear. |
| Common Range | Typically between 2deg to 7deg positive caster. | Usually between -1deg to +1deg camber, varies by vehicle type. |
| Adjustment Impact | Affects steering stability and returnability. | Affects tire wear and cornering traction. |
| Alignment Role | Critical for vehicle stability and steering dynamics. | Key for optimal tire contact and handling performance. |
Understanding Caster Angle: Definition and Function
Caster angle refers to the angle formed by the steering axis when viewed from the side of the vehicle, influencing directional stability and steering effort. It plays a crucial role in self-centering behavior of the wheels, enhancing straight-line tracking and cornering stability. Unlike camber angle, which affects tire contact and cornering grip, caster primarily impacts steering feel and returnability.
Camber Angle Basics: What It Is and Why It Matters
Camber angle refers to the tilt of the wheels in relation to the vertical axis when viewed from the front or rear of a vehicle, crucial for tire contact and handling stability. Proper camber angle ensures optimal tire grip during cornering, reducing uneven tire wear and improving overall vehicle performance. Unlike caster angle, which affects steering return and stability, camber primarily influences lateral traction and tire longevity.
Key Differences Between Caster and Camber Angles
Caster angle refers to the tilt of the steering axis in relation to the vertical axis when viewed from the side of the vehicle, primarily influencing steering stability and cornering performance. Camber angle, on the other hand, measures the tilt of the wheel relative to the vertical axis when viewed from the front, directly affecting tire contact patch and wear. Key differences include their impact on vehicle handling, with caster enhancing directional control and camber optimizing grip and tire longevity.
How Caster Angle Affects Steering and Stability
Caster angle significantly influences steering effort and directional stability by affecting the self-centering behavior of the steering wheel during driving. A positive caster angle enhances straight-line stability and improves high-speed cornering by increasing the trail, which helps the wheels return to a neutral position after turning. Excessive caster, however, may lead to heavier steering feel and increased tire wear, making balanced adjustment crucial for optimal handling performance.
The Role of Camber Angle in Tire Wear and Grip
Camber angle directly influences tire wear by affecting the distribution of load across the tire's contact patch, with excessive positive or negative camber causing uneven wear on the inner or outer edges. Optimal camber improves grip during cornering by maximizing the tire's contact surface and enhancing lateral stability. Proper adjustment of camber angle balances traction and tire longevity, reducing premature tread degradation and improving overall vehicle handling performance.
Caster Angle Adjustment: Benefits and Considerations
Caster angle adjustment enhances vehicle stability and steering feel by optimizing the directional control during driving, directly impacting handling performance and wheel returnability. Proper caster angle settings reduce driver fatigue by improving straight-line tracking and cornering response, especially on uneven surfaces. However, excessive caster adjustment can increase steering effort and cause uneven tire wear, making precise calibration critical for balanced alignment and safety.
Camber Angle Tuning for Performance and Safety
Camber angle tuning is critical for optimizing tire contact with the road, directly impacting vehicle handling and safety during cornering. Negative camber improves grip by maximizing the tire patch area under lateral loads, enhancing performance in high-speed turns and reducing understeer. Precise adjustment of camber angles ensures even tire wear, maintaining traction and stability essential for both everyday driving and competitive racing scenarios.
Symptoms of Incorrect Caster vs Camber Alignment
Incorrect caster alignment often causes steering pull, poor straight-line stability, and increased steering effort, leading to driver fatigue and reduced control. Misaligned camber angle results in uneven tire wear, typically excessive wear on one edge of the tire, compromising traction and handling performance. Both caster and camber misalignments can cause vibrations, irregular tire wear patterns, and negatively impact overall vehicle safety and ride quality.
Measuring and Setting Optimal Caster and Camber Angles
Measuring optimal caster and camber angles requires precise tools such as a digital alignment machine or caster-camber gauge, ensuring accurate suspension geometry assessment. Setting the caster angle between 3 to 5 degrees improves straight-line stability, while camber angles between -1 to -2 degrees enhance tire contact and cornering grip. Accurate alignment adjustments based on vehicle specifications prevent uneven tire wear and maintain handling performance.
Caster Angle vs Camber Angle: Which Matters More?
Caster angle influences steering stability and cornering performance by controlling the self-centering effect of the wheels, essential for straight-line tracking and smooth steering response. Camber angle primarily affects tire contact patch and grip during cornering, directly impacting tire wear and lateral traction. While both angles are critical for optimal alignment, caster angle matters more for steering precision and vehicle stability, whereas camber angle is more significant for maximizing cornering grip and tire longevity.
Caster angle vs Camber angle Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com