Warranty pet plans distinguish between mechanical failure and electrical failure coverage, ensuring specific protection tailored to each type of issue. Mechanical failure typically includes problems related to the pet's physical parts such as joints or muscles, while electrical failure covers issues involving implanted devices or electronic components like pacemakers or hearing aids. Understanding the difference helps pet owners select a warranty that offers comprehensive care for both mechanical and electrical problems.
Table of Comparison
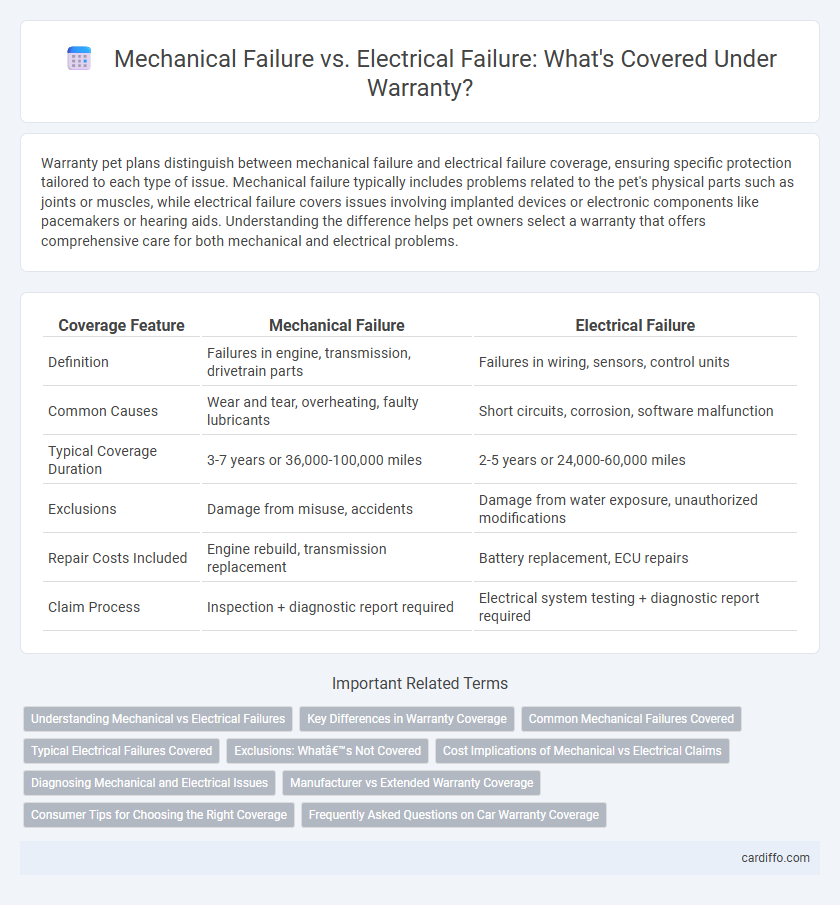
| Coverage Feature | Mechanical Failure | Electrical Failure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Failures in engine, transmission, drivetrain parts | Failures in wiring, sensors, control units |
| Common Causes | Wear and tear, overheating, faulty lubricants | Short circuits, corrosion, software malfunction |
| Typical Coverage Duration | 3-7 years or 36,000-100,000 miles | 2-5 years or 24,000-60,000 miles |
| Exclusions | Damage from misuse, accidents | Damage from water exposure, unauthorized modifications |
| Repair Costs Included | Engine rebuild, transmission replacement | Battery replacement, ECU repairs |
| Claim Process | Inspection + diagnostic report required | Electrical system testing + diagnostic report required |
Understanding Mechanical vs Electrical Failures
Mechanical failure coverage typically addresses issues related to physical components such as engines, transmissions, and suspension systems, which can wear out due to friction, stress, or material fatigue. Electrical failure coverage protects against malfunctions in wiring, sensors, control modules, and electronic components essential for vehicle operation. Understanding the distinction between mechanical and electrical failures is crucial for selecting a warranty plan that adequately covers potential repair costs and minimizes out-of-pocket expenses.
Key Differences in Warranty Coverage
Mechanical failure coverage typically includes issues related to engine, transmission, and drivetrain components, while electrical failure coverage addresses problems with wiring, sensors, and electronic control units. Mechanical warranties often cover wear and tear from regular use, whereas electrical warranties may be limited to defects and short circuits. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers choose comprehensive protection aligned with their vehicle's specific risks and technology.
Common Mechanical Failures Covered
Common mechanical failures covered under warranty typically include issues such as engine malfunctions, transmission problems, and suspension defects. These warranties often protect against wear and tear of mechanical components like timing belts, water pumps, and fuel pumps. Understanding the distinction between mechanical failure and electrical failure coverage helps ensure appropriate claims for repairs and replacements.
Typical Electrical Failures Covered
Typical electrical failures covered under warranty include issues such as battery degradation, alternator malfunctions, starter motor failures, wiring harness damage, and faulty sensors. Coverage often extends to problems related to the vehicle's electrical system components like power windows, lighting, and control modules. Mechanical failures generally cover engine and transmission problems, but distinguishing electrical failure coverage ensures specific protection against common faults in the vehicle's electronic systems.
Exclusions: What’s Not Covered
Mechanical failure coverage excludes damage caused by normal wear and tear, misuse, or lack of regular maintenance, ensuring that repairs related to internal engine or transmission breakdowns are typically covered. Electrical failure coverage does not cover issues arising from battery deterioration, wiring corrosion, or aftermarket modifications, focusing instead on factory-installed electrical components. Both warranties generally exclude damages resulting from accidents, environmental factors, and unauthorized repairs to prevent coverage abuse.
Cost Implications of Mechanical vs Electrical Claims
Mechanical failure claims typically result in higher repair costs due to the complexity and labor-intensive nature of engine or transmission repairs. Electrical failure claims often involve less expensive diagnostic procedures but can escalate costs when dealing with advanced electronic control modules and sensors. Insurers adjust premiums based on the frequency and average payout of mechanical versus electrical claims to balance risk and coverage affordability.
Diagnosing Mechanical and Electrical Issues
Diagnosing mechanical and electrical issues requires specialized techniques tailored to each system's complexity and function. Mechanical failure coverage typically addresses problems like engine wear, transmission faults, and drivetrain defects, while electrical failure coverage focuses on diagnosing circuitry, battery faults, and sensor malfunctions. Accurate diagnosis ensures appropriate repair approvals under warranty, minimizing unexpected costs and downtime.
Manufacturer vs Extended Warranty Coverage
Manufacturer warranties typically cover mechanical failures arising from defects in materials or workmanship for a limited period, ensuring repairs or replacements without additional cost. Extended warranties often broaden coverage to include electrical failures, offering protection against issues like wiring faults or electronic component breakdowns beyond the manufacturer's timeframe. Consumers benefit from extended warranties by safeguarding expensive repairs related to electrical systems that are not covered under standard manufacturer warranties.
Consumer Tips for Choosing the Right Coverage
Consumers should assess the likelihood of mechanical failures such as engine or transmission issues versus electrical failures involving components like wiring or sensors when selecting warranty coverage. Understanding the vehicle's age, make, and model can help determine which coverage--mechanical or electrical--provides better protection and value. Reviewing repair cost trends and manufacturer reliability ratings can guide consumers in choosing a warranty plan tailored to their specific risks.
Frequently Asked Questions on Car Warranty Coverage
Mechanical failure coverage typically includes engine, transmission, and drivetrain components, protecting against issues caused by wear and tear. Electrical failure coverage involves systems like the battery, alternator, wiring, and sensors, addressing faults in the vehicle's electrical or electronic components. Car warranty FAQs often clarify that these coverages differ in scope, with mechanical failures usually covered under powertrain warranties, while electrical failures may require specialized or extended coverage plans.
Mechanical Failure vs Electrical Failure Coverage Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com