Track alignment focuses on optimizing your pet's movement for off-road and uneven terrain, ensuring better traction and stability on dirt trails and rugged paths. Street alignment, however, prioritizes smooth, balanced motion on pavement, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing wear during city walks or urban runs. Choosing the right alignment for your pet's activity level improves overall comfort and performance during their daily adventures.
Table of Comparison
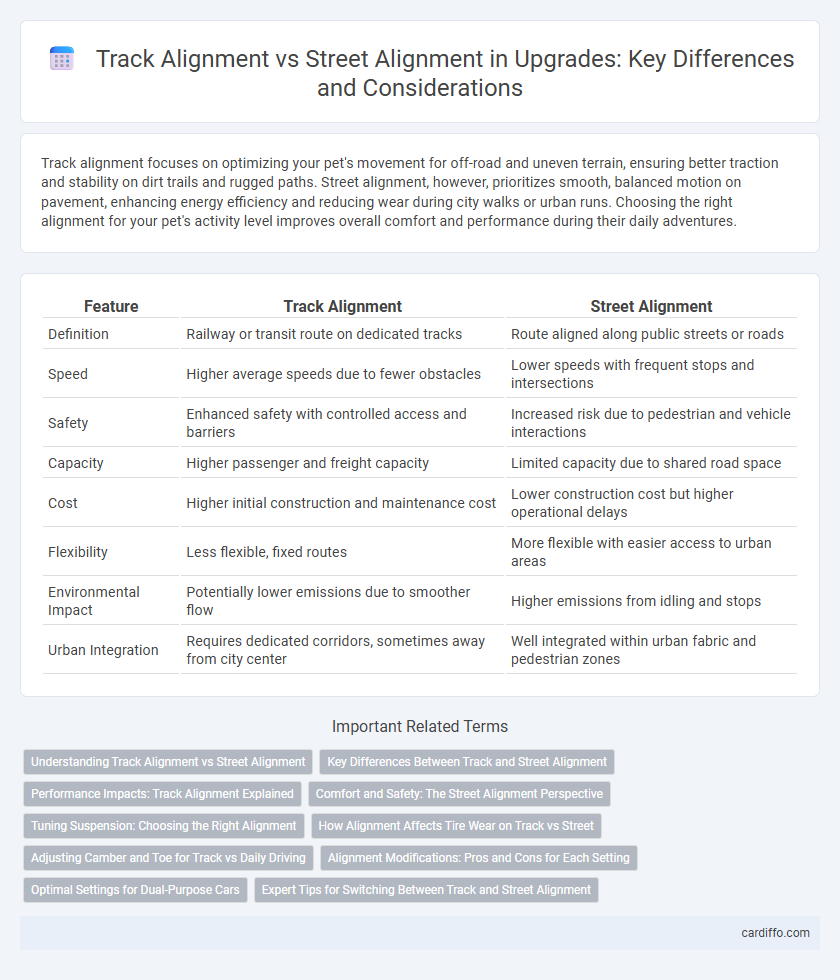
| Feature | Track Alignment | Street Alignment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Railway or transit route on dedicated tracks | Route aligned along public streets or roads |
| Speed | Higher average speeds due to fewer obstacles | Lower speeds with frequent stops and intersections |
| Safety | Enhanced safety with controlled access and barriers | Increased risk due to pedestrian and vehicle interactions |
| Capacity | Higher passenger and freight capacity | Limited capacity due to shared road space |
| Cost | Higher initial construction and maintenance cost | Lower construction cost but higher operational delays |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fixed routes | More flexible with easier access to urban areas |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially lower emissions due to smoother flow | Higher emissions from idling and stops |
| Urban Integration | Requires dedicated corridors, sometimes away from city center | Well integrated within urban fabric and pedestrian zones |
Understanding Track Alignment vs Street Alignment
Track alignment refers to the precise positioning of railway tracks ensuring smooth, safe train operations, while street alignment pertains to the layout and routing of roadways designed for vehicles and pedestrians. Understanding track alignment involves analyzing factors such as curvature, gradient, and cant to optimize train speed and stability. In contrast, street alignment focuses on traffic flow, pedestrian safety, and connectivity within urban planning constraints.
Key Differences Between Track and Street Alignment
Track alignment prioritizes smoother curves and consistent gradients to enhance train stability and speed, while street alignment focuses on integrating roadways with urban infrastructure, emphasizing accessibility and pedestrian safety. Track alignment requires precise engineering to minimize lateral forces and maintain efficient rail operations, contrasting with street alignment's flexibility to accommodate traffic signals, intersections, and mixed vehicle use. The key distinctions lie in design objectives: track alignment aims for optimized rail performance, whereas street alignment balances vehicle flow with urban planning constraints.
Performance Impacts: Track Alignment Explained
Track alignment directly influences vehicle stability and ride smoothness by maintaining consistent rail spacing and precise geometry, reducing wear on wheels and tracks. Street alignment, often designed for mixed traffic, compromises optimal rail positioning, leading to increased vibrations and decreased speed limits. Proper track alignment enhances overall performance, minimizing maintenance costs and maximizing operational efficiency in rail transit systems.
Comfort and Safety: The Street Alignment Perspective
Street alignment prioritizes comfort and safety by ensuring smoother transitions and minimizing abrupt changes in direction, which reduces the risk of derailments and enhances passenger stability. It is designed to accommodate varying traffic conditions and pedestrian interactions, improving overall accessibility and reducing potential hazards. The focus on gradual curves and consistent gradients in street alignment contributes significantly to a safer and more comfortable ride experience.
Tuning Suspension: Choosing the Right Alignment
Tuning suspension requires selecting the appropriate alignment to enhance vehicle handling and tire wear. Track alignment prioritizes camber and toe settings to improve cornering grip and stability during high-speed driving, while street alignment emphasizes comfort and tire longevity with balanced settings. Choosing the right alignment depends on driving conditions, with track alignment suited for performance and street alignment optimized for daily driving comfort.
How Alignment Affects Tire Wear on Track vs Street
Track alignment typically involves more aggressive camber and toe settings to enhance cornering grip, which can cause uneven tire wear, especially on the inner edges. Street alignment prioritizes balanced tire contact for longevity and comfort, resulting in more even tread wear patterns over time. The differing alignment objectives directly influence how tires degrade, with track setups accelerating wear due to increased lateral forces and heat buildup.
Adjusting Camber and Toe for Track vs Daily Driving
Adjusting camber and toe settings differs significantly between track alignment and street alignment to optimize vehicle performance. Track alignment typically features increased negative camber to maximize tire contact during aggressive cornering, while toe settings are fine-tuned for sharper response and stability at high speeds. In contrast, daily driving alignment prioritizes tire longevity and ride comfort, using minimal negative camber and a slight toe-in to enhance straight-line stability and reduce uneven tire wear.
Alignment Modifications: Pros and Cons for Each Setting
Track alignment modifications improve train stability and speed by precisely adjusting rail geometry, but they often require extensive infrastructure changes and can disrupt rail operations during implementation. Street alignment changes enhance traffic flow and pedestrian safety by optimizing road curvature and lane positioning, though they may impact adjacent properties and increase construction costs. Choosing between track and street alignment modifications depends on balancing operational efficiency with urban planning constraints and budget considerations.
Optimal Settings for Dual-Purpose Cars
Optimal settings for dual-purpose cars require precise calibration of both track alignment and street alignment to ensure smooth transitions and maximum performance. Track alignment optimizes wheel angles for rail guidance, minimizing wear and enhancing stability, while street alignment focuses on tire contact and steering responsiveness on pavement. Balancing these alignments ensures safety, reduces mechanical strain, and maintains efficient operation across both environments.
Expert Tips for Switching Between Track and Street Alignment
When switching between track alignment and street alignment, experts recommend precise measurement of track gauge and tire clearance to ensure optimal vehicle handling and safety. Adjustments to camber and toe angles tailored for track performance improve grip and cornering, while street alignment settings prioritize tire longevity and ride comfort. Regular inspections and alignment recalibrations are essential for maintaining performance across both driving environments.
track alignment vs street alignment Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com