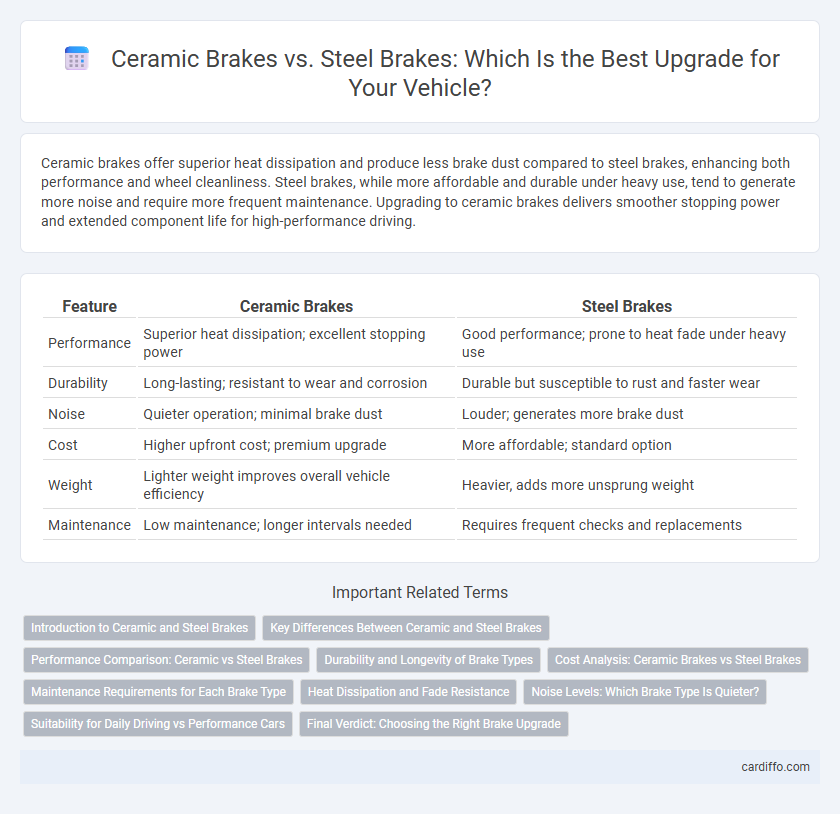
Ceramic brakes offer superior heat dissipation and produce less brake dust compared to steel brakes, enhancing both performance and wheel cleanliness. Steel brakes, while more affordable and durable under heavy use, tend to generate more noise and require more frequent maintenance. Upgrading to ceramic brakes delivers smoother stopping power and extended component life for high-performance driving.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Brakes | Steel Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Superior heat dissipation; excellent stopping power | Good performance; prone to heat fade under heavy use |
| Durability | Long-lasting; resistant to wear and corrosion | Durable but susceptible to rust and faster wear |
| Noise | Quieter operation; minimal brake dust | Louder; generates more brake dust |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost; premium upgrade | More affordable; standard option |
| Weight | Lighter weight improves overall vehicle efficiency | Heavier, adds more unsprung weight |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; longer intervals needed | Requires frequent checks and replacements |
Introduction to Ceramic and Steel Brakes
Ceramic brakes utilize ceramic compounds combined with copper fibers for enhanced heat dissipation, reduced noise, and longer lifespan compared to traditional steel brakes. Steel brakes, commonly made from cast iron or steel alloys, offer strong braking power and durability but tend to generate more heat and noise. Choosing between ceramic and steel brakes depends on factors like driving style, vehicle type, and performance requirements.
Key Differences Between Ceramic and Steel Brakes
Ceramic brakes offer superior heat dissipation and produce less brake dust compared to steel brakes, enhancing both performance and cleanliness. Steel brakes provide higher initial friction and durability under extreme conditions but generate more noise and wear faster on rotors. The key differences lie in material composition, heat management, longevity, and maintenance requirements, making ceramic brakes ideal for high-performance and daily driving, while steel brakes suit heavy-duty and budget-conscious applications.
Performance Comparison: Ceramic vs Steel Brakes
Ceramic brakes offer superior heat dissipation and reduced brake fade compared to steel brakes, making them ideal for high-performance driving and track use. Steel brakes provide consistent stopping power and durability at a lower cost, suitable for everyday driving conditions. The enhanced performance of ceramic brakes results in quieter operation, longer lifespan, and less brake dust, while steel brakes remain a reliable, budget-friendly option.
Durability and Longevity of Brake Types
Ceramic brakes offer superior durability compared to steel brakes, resisting wear and heat damage more effectively. Their longer lifespan results from advanced materials that reduce brake dust and maintain consistent performance under high temperatures. Steel brakes, while more affordable, tend to wear out faster and require more frequent replacements due to their susceptibility to corrosion and thermal degradation.
Cost Analysis: Ceramic Brakes vs Steel Brakes
Ceramic brakes typically have a higher initial cost, ranging from $1,200 to $2,500 per set, compared to steel brakes, which usually cost between $300 and $700 per set. Despite the upfront expense, ceramic brakes offer longer lifespan and reduced brake dust, leading to lower maintenance and replacement costs over time. Steel brakes are more affordable initially but require more frequent replacements due to faster wear, increasing long-term expenses.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Brake Type
Ceramic brakes require less frequent maintenance due to their enhanced resistance to wear and heat, resulting in longer brake pad life and reduced dust production. Steel brakes often demand more regular inspections and replacements because of their susceptibility to corrosion, wear, and heat-induced warping. Choosing ceramic brakes can significantly decrease maintenance intervals and overall upkeep costs compared to traditional steel brake systems.
Heat Dissipation and Fade Resistance
Ceramic brakes offer superior heat dissipation compared to steel brakes, significantly reducing the risk of brake fade during high-performance driving or heavy braking conditions. Their advanced material composition allows them to withstand higher temperatures without losing effectiveness, ensuring consistent stopping power and enhanced safety. Steel brakes, while generally more affordable, tend to retain heat longer, increasing the likelihood of fade and reduced braking performance under intense use.
Noise Levels: Which Brake Type Is Quieter?
Ceramic brakes produce significantly less noise compared to steel brakes due to their specialized composite material that reduces vibrations and squealing during braking. Steel brakes often generate more audible noise because of metal-on-metal contact and higher friction levels. For drivers prioritizing quieter braking performance, ceramic brakes offer a superior upgrade.
Suitability for Daily Driving vs Performance Cars
Ceramic brakes offer superior heat resistance, reduced brake fade, and longer lifespan, making them ideal for high-performance cars that demand consistent stopping power during aggressive driving. Steel brakes provide reliable performance and cost-effectiveness, suited for daily driving where moderate braking stress and durability under regular conditions are essential. Choosing ceramic brakes enhances performance and longevity in sports cars, while steel brakes balance efficiency and affordability for everyday commuting.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Brake Upgrade
Ceramic brakes offer superior heat dissipation, reduced brake fade, and longer lifespan, making them ideal for high-performance and daily driving applications. Steel brakes provide cost-effective durability and strong stopping power but tend to wear faster and produce more brake dust. Choosing the right brake upgrade depends on balancing budget, driving style, and performance needs, with ceramic brakes favored for enhanced longevity and efficiency.
Ceramic Brakes vs Steel Brakes Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com