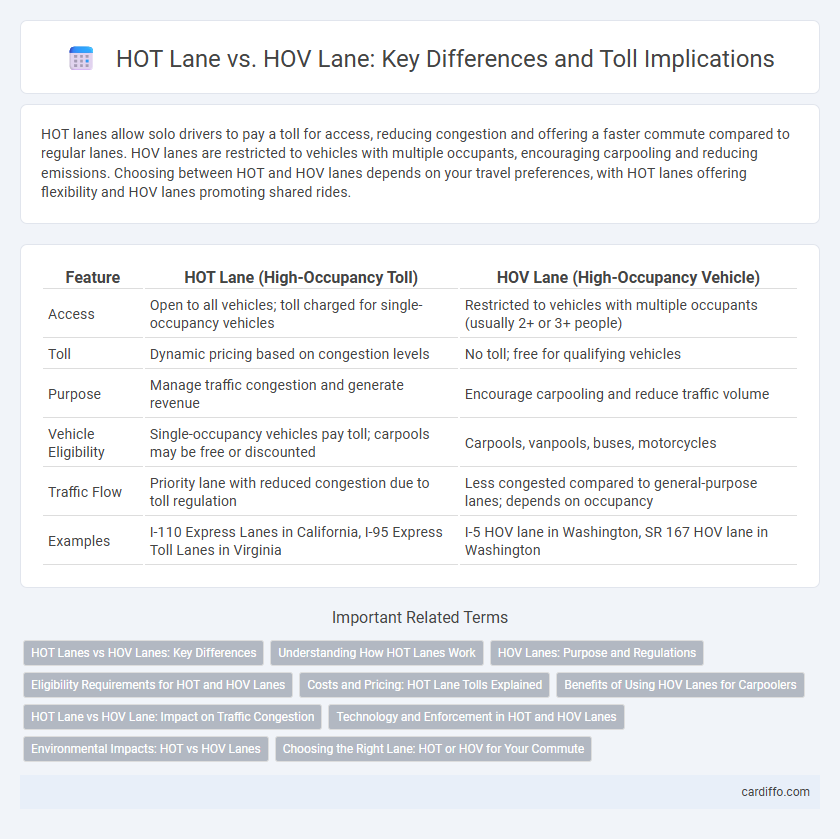
HOT lanes allow solo drivers to pay a toll for access, reducing congestion and offering a faster commute compared to regular lanes. HOV lanes are restricted to vehicles with multiple occupants, encouraging carpooling and reducing emissions. Choosing between HOT and HOV lanes depends on your travel preferences, with HOT lanes offering flexibility and HOV lanes promoting shared rides.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | HOT Lane (High-Occupancy Toll) | HOV Lane (High-Occupancy Vehicle) |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Open to all vehicles; toll charged for single-occupancy vehicles | Restricted to vehicles with multiple occupants (usually 2+ or 3+ people) |
| Toll | Dynamic pricing based on congestion levels | No toll; free for qualifying vehicles |
| Purpose | Manage traffic congestion and generate revenue | Encourage carpooling and reduce traffic volume |
| Vehicle Eligibility | Single-occupancy vehicles pay toll; carpools may be free or discounted | Carpools, vanpools, buses, motorcycles |
| Traffic Flow | Priority lane with reduced congestion due to toll regulation | Less congested compared to general-purpose lanes; depends on occupancy |
| Examples | I-110 Express Lanes in California, I-95 Express Toll Lanes in Virginia | I-5 HOV lane in Washington, SR 167 HOV lane in Washington |
HOT Lanes vs HOV Lanes: Key Differences
HOT lanes allow both high-occupancy vehicles and solo drivers willing to pay a toll, optimizing traffic flow while generating revenue, unlike HOV lanes restricted solely to vehicles with multiple passengers. HOT lanes use dynamic pricing strategies based on congestion levels to maintain optimal speeds, whereas HOV lanes are free but underutilized during off-peak hours. The main difference lies in accessibility and efficiency, with HOT lanes balancing demand management and revenue generation compared to HOV lanes' purely occupancy-based restrictions.
Understanding How HOT Lanes Work
HOT lanes, or High-Occupancy Toll lanes, are traffic lanes that allow solo drivers to pay a toll for access while high-occupancy vehicles (HOV) with multiple passengers can use the lanes for free or at a reduced cost. Toll rates in HOT lanes dynamically adjust based on real-time traffic conditions to manage congestion and maintain optimal traffic flow. This pricing strategy encourages carpooling and reduces overall traffic by offering faster travel options for toll-paying drivers and qualified HOV vehicles.
HOV Lanes: Purpose and Regulations
HOV lanes, or High-Occupancy Vehicle lanes, are designed to encourage carpooling and reduce traffic congestion by allowing vehicles with a minimum number of passengers, typically two or more, to use these lanes during peak hours. Regulations for HOV lanes strictly require compliance with occupancy rules, and enforcement often includes fines for solo drivers using the lane illegally. The purpose of HOV lanes is to promote efficient road usage, decrease emissions, and improve travel times for commuters in metropolitan areas.
Eligibility Requirements for HOT and HOV Lanes
HOT lanes require drivers to pay a toll unless they meet specific eligibility criteria such as driving a low-emission vehicle or carpooling with multiple passengers, usually two or more. HOV lanes are reserved exclusively for vehicles carrying a minimum number of occupants, commonly two or three, to encourage carpooling and reduce traffic congestion. Eligibility for HOT lanes is more flexible, allowing single-occupant vehicles to use the lane by paying a variable toll, whereas HOV lanes strictly enforce passenger count without toll exemptions.
Costs and Pricing: HOT Lane Tolls Explained
HOT lanes charge dynamic tolls based on real-time traffic conditions, allowing solo drivers to use these lanes by paying variable fees that increase during peak hours to manage congestion. In contrast, HOV lanes are typically toll-free and reserved for vehicles with multiple passengers, promoting carpooling but offering no direct cost to users. HOT lane pricing uses electronic tolling systems to optimize traffic flow and generate revenue, while HOV lanes rely on occupancy rules without direct charges.
Benefits of Using HOV Lanes for Carpoolers
HOV lanes significantly reduce commute times by allowing carpoolers to bypass congested traffic, enhancing travel efficiency and reducing fuel consumption. These lanes support environmental sustainability by lowering vehicle emissions through decreased single-occupancy trips, contributing to improved air quality. Carpoolers benefit from cost savings on tolls and fuel, making HOV lanes economically advantageous compared to HOT lanes that charge dynamic toll rates.
HOT Lane vs HOV Lane: Impact on Traffic Congestion
HOT lanes allow solo drivers to pay tolls for access, which helps manage traffic by regulating demand and reducing congestion during peak hours. HOV lanes prioritize vehicles with multiple occupants, promoting carpooling and lowering the total number of vehicles on the road, which decreases overall traffic volume. Compared to HOV lanes, HOT lanes provide more flexible road usage while maintaining smoother traffic flow by balancing occupancy incentives with dynamic pricing.
Technology and Enforcement in HOT and HOV Lanes
HOT lanes utilize dynamic electronic tolling technology with transponders and real-time traffic sensors to manage lane access and congestion pricing, enabling enforcement through automated license plate recognition and toll violation detection systems. HOV lanes rely primarily on occupancy sensors, visual enforcement by officers, and manual observation to ensure compliance with carpool or high-occupancy vehicle rules, often lacking automated toll collection. Advances in electronic toll collection and integrated camera systems in HOT lanes improve enforcement efficiency and reduce violations compared to traditional HOV lane monitoring methods.
Environmental Impacts: HOT vs HOV Lanes
HOT lanes enable solo drivers to pay tolls for access, potentially reducing overall congestion and vehicle emissions by promoting carpooling incentives and efficient traffic flow. HOV lanes restrict usage to vehicles with multiple passengers, directly encouraging carpooling and decreasing the number of single-occupancy vehicles, which leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality. Studies indicate HOT lanes can balance environmental benefits with traffic management, but their effectiveness depends on pricing strategies and enforcement compared to the strictly regulated HOV lanes.
Choosing the Right Lane: HOT or HOV for Your Commute
Choosing the right lane for your commute depends on your vehicle occupancy and willingness to pay tolls. High-Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lanes are reserved for vehicles with multiple passengers, offering toll-free travel to encourage carpooling and reduce congestion. High-Occupancy Toll (HOT) lanes allow single-occupancy vehicles to pay a variable toll for faster travel, providing flexibility for solo drivers who want to save time during peak hours.
HOT Lane vs HOV Lane Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com