Directional tires have a specific tread pattern designed to rotate in one direction, improving water evacuation and enhancing wet traction for pets that enjoy off-road adventures. Non-directional tires feature symmetrical tread patterns that allow for rotation in multiple directions, providing even wear and extended tire life ideal for everyday driving with pets. Choosing between directional and non-directional tires depends on driving conditions and pet safety preferences.
Table of Comparison
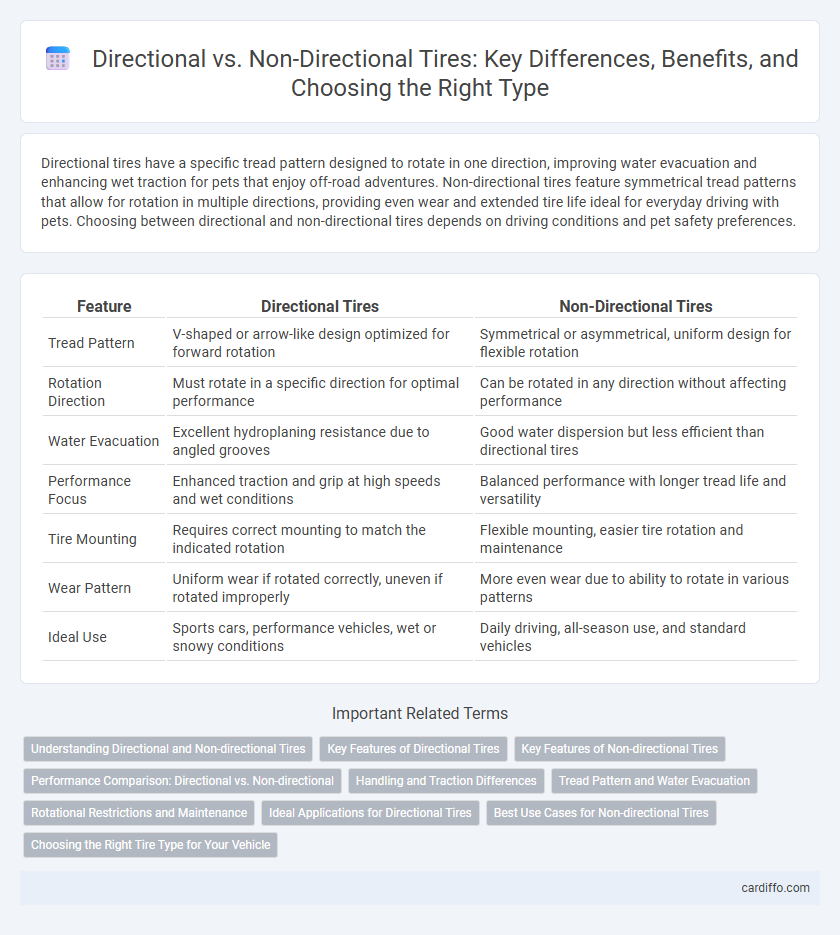
| Feature | Directional Tires | Non-Directional Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Tread Pattern | V-shaped or arrow-like design optimized for forward rotation | Symmetrical or asymmetrical, uniform design for flexible rotation |
| Rotation Direction | Must rotate in a specific direction for optimal performance | Can be rotated in any direction without affecting performance |
| Water Evacuation | Excellent hydroplaning resistance due to angled grooves | Good water dispersion but less efficient than directional tires |
| Performance Focus | Enhanced traction and grip at high speeds and wet conditions | Balanced performance with longer tread life and versatility |
| Tire Mounting | Requires correct mounting to match the indicated rotation | Flexible mounting, easier tire rotation and maintenance |
| Wear Pattern | Uniform wear if rotated correctly, uneven if rotated improperly | More even wear due to ability to rotate in various patterns |
| Ideal Use | Sports cars, performance vehicles, wet or snowy conditions | Daily driving, all-season use, and standard vehicles |
Understanding Directional and Non-directional Tires
Directional tires feature a tread pattern designed to rotate in one direction for optimized water evacuation and enhanced traction on wet surfaces. Non-directional tires offer versatile mounting options with symmetrical tread patterns, allowing for easier tire rotation and even wear. Understanding the differences helps drivers select the best tire type for performance, safety, and maintenance preferences.
Key Features of Directional Tires
Directional tires feature a tread pattern designed to channel water away efficiently, enhancing wet traction and reducing hydroplaning risk. Their V-shaped or arrow-like grooves optimize grip and stability at high speeds, making them ideal for performance vehicles. These tires require correct mounting to maintain their directional properties and ensure safety.
Key Features of Non-directional Tires
Non-directional tires feature a symmetrical tread pattern that allows mounting on any wheel position, enhancing flexibility in tire rotation and ensuring even wear. Their key benefits include improved longevity, consistent traction in various driving conditions, and simplified maintenance. These tires are ideal for drivers seeking cost-effective performance without the constraint of directional installation.
Performance Comparison: Directional vs. Non-directional
Directional tires offer superior wet traction and enhanced cornering stability due to their tread pattern designed to channel water efficiently, reducing hydroplaning risk. Non-directional tires provide more uniform wear and ease of rotation, contributing to longer tire life and balanced performance on dry surfaces. Performance comparison shows directional tires excel in high-speed handling and wet conditions, while non-directional tires deliver consistent performance and cost-effectiveness for everyday driving.
Handling and Traction Differences
Directional tires feature a tread pattern designed to rotate in one direction, enhancing water evacuation and improving wet traction, which results in better handling and stability at high speeds. Non-directional tires have a symmetrical tread pattern that allows for flexible rotation options, providing balanced traction and consistent handling across various conditions but typically less optimized for channeling water. Choosing between the two impacts cornering precision and grip, with directional tires excelling in aggressive driving scenarios and non-directional tires offering versatility and ease of tire rotation for extended tread life.
Tread Pattern and Water Evacuation
Directional tires feature V-shaped tread patterns designed to efficiently channel water away from the tire's contact patch, enhancing hydroplaning resistance and wet traction. Non-directional tires have symmetrical tread patterns that provide uniform performance and allow for multiple rotation patterns but are generally less effective at water evacuation. Effective water evacuation in directional tires improves grip in wet conditions by maintaining consistent road contact and reducing slippage.
Rotational Restrictions and Maintenance
Directional tires require mounting in a specific rotation direction indicated by an arrow on the sidewall, ensuring optimal water evacuation and traction. Non-directional tires can be rotated in any direction, allowing for more flexible rotation patterns that extend tread life and balance wear. Proper adherence to rotational restrictions on directional tires prevents uneven wear and potential safety hazards, while non-directional tires simplify maintenance routines and improve longevity.
Ideal Applications for Directional Tires
Directional tires optimize water evacuation with their V-shaped tread patterns, making them ideal for wet and snowy conditions. They provide superior traction and handling at high speeds, benefitting performance cars and sporty driving. Best suited for vehicles frequently exposed to rain or snow, directional tires enhance safety and control on slippery surfaces.
Best Use Cases for Non-directional Tires
Non-directional tires excel in everyday driving and general all-season use due to their symmetrical tread patterns, which offer consistent performance on dry and wet roads without the need for rotation restrictions. They provide greater flexibility in tire rotation, extending tread life and maintaining balanced wear, making them ideal for passenger vehicles and light trucks in varied conditions. These tires also perform well on paved city streets and highways, ensuring reliable traction and comfort for daily commuting and long-distance travel.
Choosing the Right Tire Type for Your Vehicle
Directional tires feature a tread pattern designed to rotate in one direction, providing enhanced water evacuation and improved traction in wet conditions, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles. Non-directional tires offer versatility with symmetrical tread patterns that can be rotated in multiple ways, promoting even wear and extended tire life, suitable for everyday driving and varied road conditions. Selecting between directional and non-directional tires depends on your vehicle's performance requirements, driving environment, and maintenance preferences to maximize safety and efficiency.
Directional vs Non-directional Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com