Roadside pet services often provide minor mechanical assistance such as tire changes, fuel delivery, and battery jump-starts to help stranded drivers quickly resume their journey. Electrical assistance typically involves diagnosing and fixing small electrical faults, including battery replacements or alternator issues, ensuring that vehicles regain power efficiently. Choosing the right type of assistance depends on whether the problem is mechanical or electrical, with both services designed to minimize downtime and enhance driver safety.
Table of Comparison
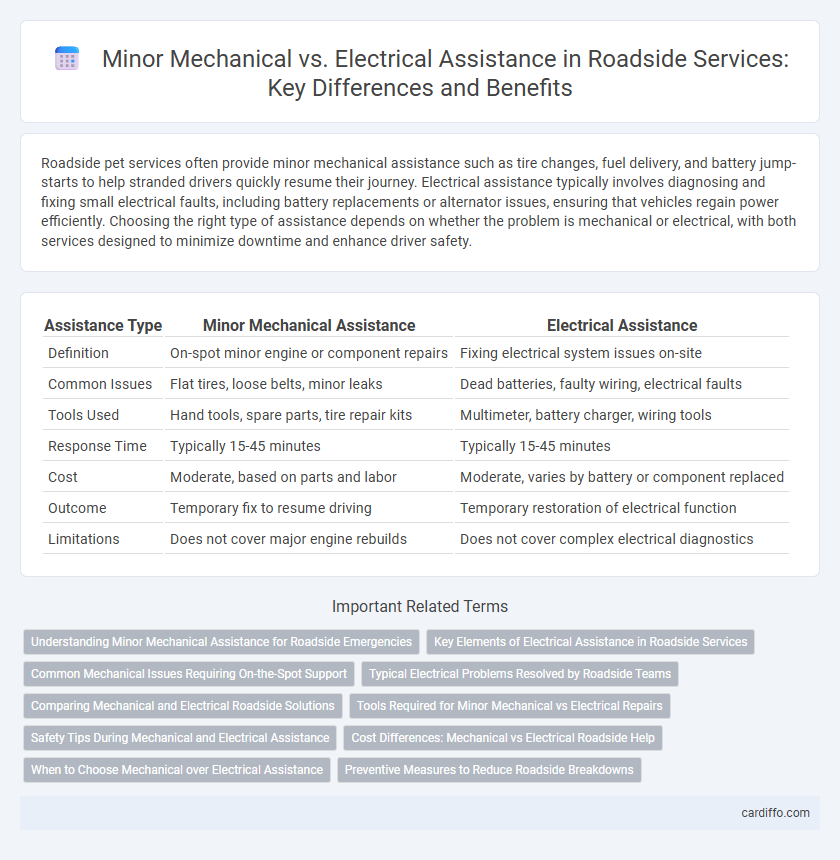
| Assistance Type | Minor Mechanical Assistance | Electrical Assistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | On-spot minor engine or component repairs | Fixing electrical system issues on-site |
| Common Issues | Flat tires, loose belts, minor leaks | Dead batteries, faulty wiring, electrical faults |
| Tools Used | Hand tools, spare parts, tire repair kits | Multimeter, battery charger, wiring tools |
| Response Time | Typically 15-45 minutes | Typically 15-45 minutes |
| Cost | Moderate, based on parts and labor | Moderate, varies by battery or component replaced |
| Outcome | Temporary fix to resume driving | Temporary restoration of electrical function |
| Limitations | Does not cover major engine rebuilds | Does not cover complex electrical diagnostics |
Understanding Minor Mechanical Assistance for Roadside Emergencies
Minor mechanical assistance for roadside emergencies involves quick, on-the-spot repairs such as tire changes, battery jump-starts, and fuel delivery to restore vehicle functionality without transporting the car to a repair shop. This type of assistance addresses common mechanical issues like flat tires, dead batteries, and overheating, enabling drivers to continue their journey safely and efficiently. Understanding these basic mechanical interventions helps drivers respond promptly to minor breakdowns, reducing downtime and enhancing roadside safety.
Key Elements of Electrical Assistance in Roadside Services
Electrical assistance in roadside services primarily involves jump-starting batteries, replacing fuses, and addressing alternator or starter motor issues to restore vehicle power. Technicians use diagnostic tools to identify electrical faults, ensuring efficient resolution of problems related to wiring, battery terminals, and lighting systems. This type of assistance is crucial for resolving common vehicle malfunctions that prevent ignition or operation without requiring extensive mechanical repairs.
Common Mechanical Issues Requiring On-the-Spot Support
Common mechanical issues requiring on-the-spot roadside assistance include flat tires, dead batteries, and engine overheating. Minor mechanical repairs such as replacing fuses, jump-starting vehicles, and tightening loose belts are frequently performed to quickly restore functionality. Roadside technicians often address fuel system problems, brake adjustments, and minor engine troubleshooting to minimize vehicle downtime.
Typical Electrical Problems Resolved by Roadside Teams
Roadside teams frequently resolve typical electrical problems such as dead batteries, faulty alternators, and malfunctioning starter motors, ensuring quick vehicle recovery. Other common issues include blown fuses, wiring faults, and problems with ignition systems that hinder vehicle operation. These electrical repairs often prevent the need for towing, providing efficient on-the-spot assistance to stranded drivers.
Comparing Mechanical and Electrical Roadside Solutions
Minor mechanical assistance typically involves addressing issues like flat tires, engine overheating, or fluid top-ups that require hands-on physical repairs. Electrical roadside solutions focus on diagnostics and repairs related to the vehicle's battery, alternator, starter motor, and electronic control units using specialized tools and software. Comparing both, mechanical assistance demands manual intervention and basic tools, while electrical solutions rely on advanced diagnostics and expertise to resolve complex vehicle system failures.
Tools Required for Minor Mechanical vs Electrical Repairs
Minor mechanical repairs on the roadside often require essential tools like wrenches, screwdrivers, pliers, and socket sets to address issues such as loose bolts, flat tires, or fluid leaks. Electrical assistance typically involves specialized tools including multimeters, wire strippers, crimpers, and test light devices to diagnose and fix battery, wiring, or fuse problems. Proper tool kits tailored to mechanical or electrical tasks ensure efficient and safe roadside repairs, minimizing vehicle downtime.
Safety Tips During Mechanical and Electrical Assistance
When providing minor mechanical or electrical assistance roadside, always prioritize safety by wearing high-visibility clothing and positioning warning triangles at a safe distance to alert oncoming traffic. Use insulated tools when handling electrical components to prevent shocks, and ensure the vehicle's engine is off before attempting any repairs to avoid injury from moving parts. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby in case of electrical sparks or fuel leaks, and never work alone to ensure immediate help in emergencies.
Cost Differences: Mechanical vs Electrical Roadside Help
Minor mechanical assistance on the roadside typically incurs lower costs due to the use of basic tools and manual labor, such as tire changes or fluid top-ups. Electrical roadside help often demands specialized diagnostic equipment and skilled technicians to address issues like battery replacement, wiring faults, or electronic system resets, resulting in higher service fees. Understanding these cost differences helps vehicle owners budget appropriately for roadside support based on the nature of their mechanical or electrical vehicle problems.
When to Choose Mechanical over Electrical Assistance
Choose minor mechanical assistance over electrical help when issues involve physical components such as flat tires, broken belts, or engine overheating. Mechanical interventions are necessary for tangible repairs like changing spark plugs or fixing fuel lines. Electrical assistance suits battery problems or electronic malfunctions but falls short in addressing mechanical breakdowns requiring hands-on repairs.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Roadside Breakdowns
Regular maintenance checks on fluid levels, tire pressure, and battery health significantly reduce the risk of minor mechanical roadside breakdowns. Inspecting electrical components such as wiring, fuses, and lighting systems helps prevent electrical failures during travel. Using quality parts and timely servicing enhances vehicle reliability and minimizes the need for emergency roadside assistance.
Minor Mechanical vs Electrical Assistance Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com