Incident management prioritizes the rapid identification and resolution of emergencies to minimize disruption and ensure safety, while traffic control focuses on directing and regulating vehicle flow to prevent congestion and accidents. Effective roadside pet management integrates incident management strategies to quickly address accidents involving animals, alongside traffic control measures to maintain smooth and safe travel conditions. Coordinating both approaches enhances overall roadway safety and reduces the risk of secondary incidents.
Table of Comparison
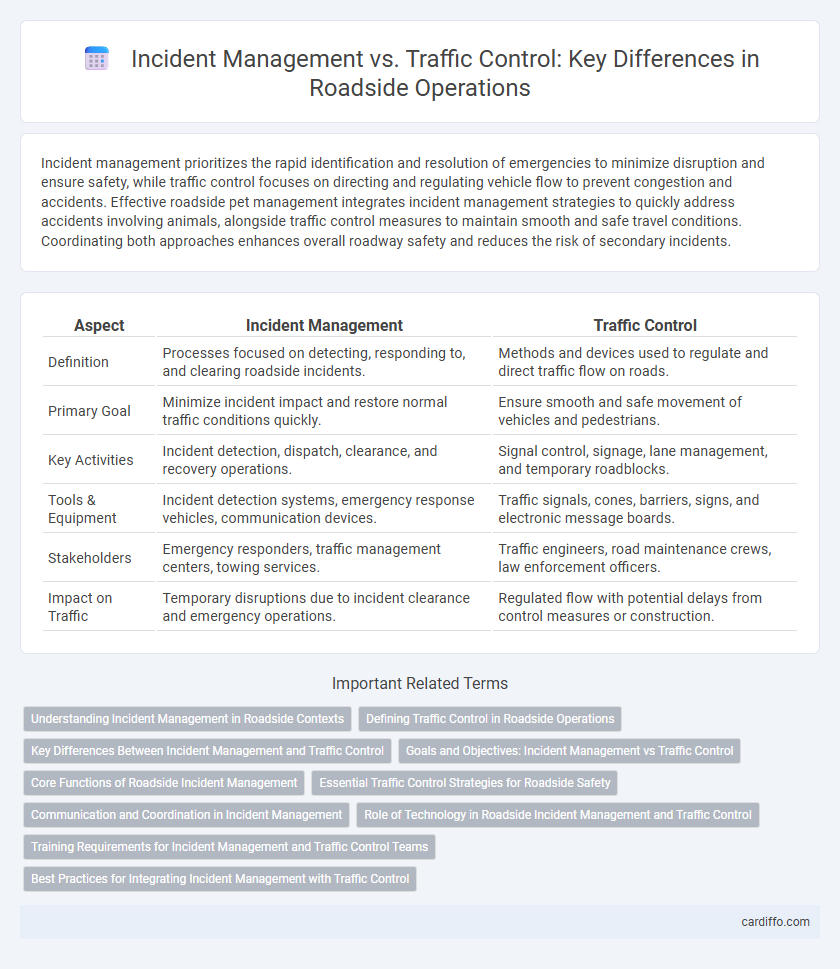
| Aspect | Incident Management | Traffic Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes focused on detecting, responding to, and clearing roadside incidents. | Methods and devices used to regulate and direct traffic flow on roads. |
| Primary Goal | Minimize incident impact and restore normal traffic conditions quickly. | Ensure smooth and safe movement of vehicles and pedestrians. |
| Key Activities | Incident detection, dispatch, clearance, and recovery operations. | Signal control, signage, lane management, and temporary roadblocks. |
| Tools & Equipment | Incident detection systems, emergency response vehicles, communication devices. | Traffic signals, cones, barriers, signs, and electronic message boards. |
| Stakeholders | Emergency responders, traffic management centers, towing services. | Traffic engineers, road maintenance crews, law enforcement officers. |
| Impact on Traffic | Temporary disruptions due to incident clearance and emergency operations. | Regulated flow with potential delays from control measures or construction. |
Understanding Incident Management in Roadside Contexts
Incident management in roadside contexts involves coordinated efforts to quickly detect, respond to, and clear traffic incidents to minimize disruptions and enhance safety. It encompasses activities such as emergency response, incident investigation, and communication with traffic control centers to facilitate timely rerouting and resource deployment. Effective incident management reduces secondary accidents and congestion, ensuring smoother traffic flow and improved roadway resilience.
Defining Traffic Control in Roadside Operations
Traffic control in roadside operations refers to the systematic regulation and guidance of vehicle and pedestrian movement to ensure safety and efficient traffic flow during incidents or roadworks. It involves the strategic placement of signs, signals, barriers, and personnel to prevent accidents and minimize disruptions. Effective traffic control integrates real-time monitoring and communication to adapt to changing roadside conditions, enhancing overall road safety and operational efficiency.
Key Differences Between Incident Management and Traffic Control
Incident management focuses on rapidly identifying, responding to, and clearing traffic incidents to restore normal traffic flow and ensure safety. Traffic control involves the strategic deployment of signs, signals, and personnel to direct vehicle movements and maintain orderly traffic operations. Key differences include that incident management is reactive and event-driven, while traffic control is proactive and continuously managed to prevent congestion and accidents.
Goals and Objectives: Incident Management vs Traffic Control
Incident management aims to quickly restore normal traffic flow and ensure safety by efficiently handling emergencies, accidents, and road hazards. Traffic control focuses on regulating and directing vehicle and pedestrian movement to prevent congestion and reduce the risk of collisions. Both share the objective of minimizing delays and enhancing roadway safety but prioritize response and prevention strategies respectively.
Core Functions of Roadside Incident Management
Roadside Incident Management focuses on rapid detection, response, and clearance of incidents to minimize traffic disruptions and enhance safety. Core functions include coordinating emergency services, ensuring efficient traffic flow around incident sites, and clearing debris or hazards swiftly. Unlike Traffic Control, which primarily directs vehicle movement, Incident Management integrates multi-agency collaboration and resource deployment to restore normal conditions promptly.
Essential Traffic Control Strategies for Roadside Safety
Incident management integrates rapid response tactics and real-time coordination to minimize roadside disruptions, while traffic control focuses on systematic deployment of signs, barriers, and personnel to guide vehicle flow safely. Essential traffic control strategies include dynamic lane closures, advance warning systems, and clear detour routes to protect both responders and motorists. Effective roadside safety hinges on synchronized communication between incident management teams and traffic control units to reduce accident risks and enhance operational efficiency.
Communication and Coordination in Incident Management
Incident management relies heavily on real-time communication and coordination among emergency responders, traffic authorities, and dispatch centers to promptly address roadway incidents. Effective communication systems facilitate rapid information exchange regarding incident location, severity, and required resources, enabling coordinated traffic control measures that minimize congestion and enhance safety. Integrated technology platforms such as computer-aided dispatch (CAD) and traffic management centers (TMCs) are critical for synchronizing operational responses in managing incidents efficiently.
Role of Technology in Roadside Incident Management and Traffic Control
Advanced technologies such as real-time traffic monitoring systems, intelligent cameras, and automated incident detection play a crucial role in enhancing roadside incident management and traffic control, enabling faster response times and minimizing traffic disruptions. Integrated platforms use data analytics and AI to coordinate emergency services, optimize traffic signal timing, and provide dynamic route guidance to drivers, improving safety and traffic flow efficiency. The deployment of connected vehicle technology and communication networks facilitates seamless information exchange between roadside units and vehicles, further enhancing proactive incident detection and effective traffic management.
Training Requirements for Incident Management and Traffic Control Teams
Incident Management teams require specialized training in emergency response, hazard assessment, and communication protocols to efficiently coordinate on-scene activities during roadside incidents. Traffic Control personnel must be trained in setting up safe work zones, deploying signage, and directing traffic flow to minimize disruption while ensuring the safety of both workers and motorists. Both teams benefit from continuous education on regulatory standards, technology advancements, and scenario-based drills to enhance operational effectiveness.
Best Practices for Integrating Incident Management with Traffic Control
Integrating incident management with traffic control enhances roadway safety and reduces congestion by ensuring rapid response and efficient vehicle flow. Best practices include deploying real-time traffic monitoring systems, establishing clear communication protocols between incident responders and traffic controllers, and using adaptive signal control technology to dynamically manage traffic around incident sites. Coordinated strategies minimize secondary accidents and improve overall incident clearance times, benefiting both emergency personnel and road users.
Incident Management vs Traffic Control Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com