Handicap parking spaces are specifically designed to provide easier access for individuals with disabilities, featuring wider spots and proximity to building entrances. General parking is intended for all drivers without special permits and often lacks the additional space and accessibility features required by disabled individuals. Ensuring compliance with ADA guidelines in handicap parking promotes inclusivity and convenience for those who need it most.
Table of Comparison
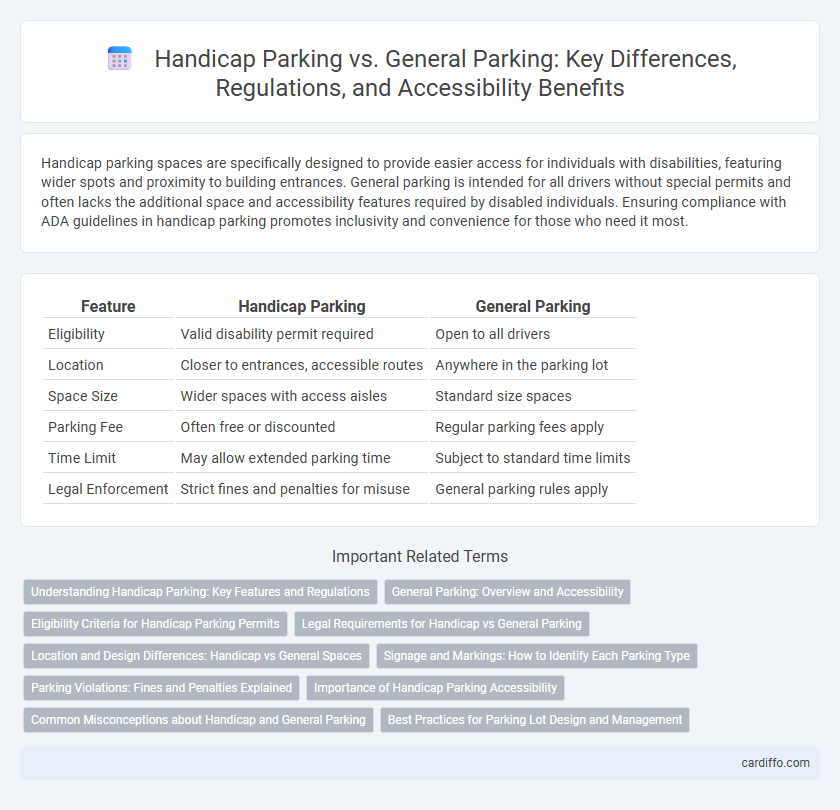
| Feature | Handicap Parking | General Parking |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | Valid disability permit required | Open to all drivers |
| Location | Closer to entrances, accessible routes | Anywhere in the parking lot |
| Space Size | Wider spaces with access aisles | Standard size spaces |
| Parking Fee | Often free or discounted | Regular parking fees apply |
| Time Limit | May allow extended parking time | Subject to standard time limits |
| Legal Enforcement | Strict fines and penalties for misuse | General parking rules apply |
Understanding Handicap Parking: Key Features and Regulations
Handicap parking spaces are designed to provide accessible, close-to-entrance parking for individuals with disabilities, featuring wider dimensions and clear signage with the International Symbol of Access. Regulations mandate specific dimensions, curb cuts, and access aisles to ensure safe and convenient use, often requiring a valid disability parking permit or placard. Compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) ensures legal standards are met, promoting equitable access in public and private parking facilities.
General Parking: Overview and Accessibility
General parking offers a wide range of accessible spaces designed to accommodate the majority of vehicles, ensuring convenience for daily commuters and visitors. These parking areas are strategically located near entrances, equipped with clear signage and smooth pathways to facilitate easy movement. While not tailored specifically for individuals with disabilities, general parking prioritizes efficiency, capacity, and straightforward access to key facilities and amenities.
Eligibility Criteria for Handicap Parking Permits
Eligibility criteria for handicap parking permits typically require applicants to have a permanent or temporary mobility impairment certified by a qualified healthcare professional. Documentation must demonstrate conditions such as limited ability to walk, use mobility aids, or other severe disabilities affecting mobility. These permits grant access to designated handicap parking spaces closer to building entrances, facilitating easier access for individuals with disabilities.
Legal Requirements for Handicap vs General Parking
Handicap parking spaces must comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) standards, including specific dimensions, signage, and access aisle requirements to ensure accessibility for individuals with disabilities. General parking spaces do not have these stringent legal requirements and can vary widely in size and design based on local regulations and property needs. Failure to meet ADA standards for handicap parking can result in legal penalties and mandated corrective actions.
Location and Design Differences: Handicap vs General Spaces
Handicap parking spaces are strategically located closer to building entrances to provide easier access for individuals with disabilities, complying with ADA regulations which mandate minimum width and adjacent access aisles for wheelchair maneuverability. These spaces feature distinct signage and pavement markings, including the International Symbol of Access, and often have a flat surface with curb cuts or ramps nearby. In contrast, general parking spaces are typically narrower, spaced uniformly without additional features, and located farther from entrances, prioritizing maximum vehicle capacity over accessibility.
Signage and Markings: How to Identify Each Parking Type
Handicap parking spaces are identified by blue-painted markings and the International Symbol of Access (wheelchair symbol) on both signage and ground markings, ensuring clear visibility and compliance with ADA standards. General parking areas lack these specialized signs and are typically marked with white or yellow lines without any accessibility symbols. Proper identification through signage and pavement markings is crucial for enforcing parking regulations and providing accessibility for individuals with disabilities.
Parking Violations: Fines and Penalties Explained
Handicap parking violations incur significantly higher fines compared to general parking offenses, often ranging from $250 to $1,000 depending on the jurisdiction. Unauthorized use of handicap parking spaces can also result in vehicle towing and additional penalties such as points on the driver's license. These strict regulations aim to ensure accessibility for individuals with disabilities and discourage misuse of designated handicap parking spots.
Importance of Handicap Parking Accessibility
Handicap parking accessibility ensures equitable access for individuals with disabilities, promoting independence and inclusion in public spaces. Designated handicap parking spots are strategically located near building entrances, minimizing physical barriers and enhancing safety for those with mobility challenges. Compliance with ADA standards in handicap parking design is crucial to meet legal requirements and support community accessibility needs.
Common Misconceptions about Handicap and General Parking
Handicap parking spaces are specifically designed to provide closer and safer access to buildings for individuals with disabilities, often marked with the International Symbol of Access. A common misconception is that anyone with a disabled parking permit can park anywhere, but regulations require using designated handicap spots unless none are available. General parking spaces lack these accommodations and are intended for all drivers without disability permits, emphasizing the importance of respecting these distinctions to ensure accessibility and compliance with ADA guidelines.
Best Practices for Parking Lot Design and Management
Handicap parking spaces must comply with the ADA requirements, including proper width, signage, and surface markings to ensure accessibility and safety for disabled users. General parking areas should prioritize efficient layout and clear traffic flow to maximize capacity and minimize congestion while incorporating durable materials for long-term maintenance. Integrating both types with adequate lighting, signage, and pedestrian pathways enhances overall parking lot usability and compliance.
Handicap Parking vs General Parking Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com