Naturally aspirated engines deliver power through atmospheric pressure, offering linear throttle response and simpler maintenance. Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, increase engine power by compressing air into the combustion chamber, resulting in higher horsepower and torque. Choosing between the two depends on desired performance gains, engine durability, and driving style preferences.
Table of Comparison
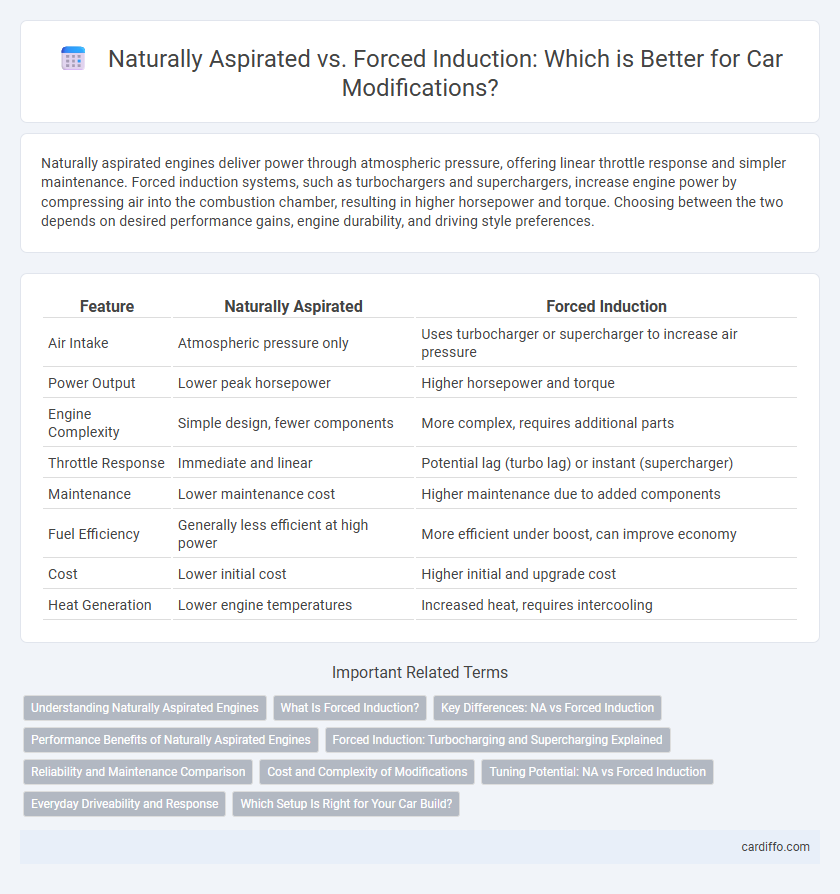
| Feature | Naturally Aspirated | Forced Induction |
|---|---|---|
| Air Intake | Atmospheric pressure only | Uses turbocharger or supercharger to increase air pressure |
| Power Output | Lower peak horsepower | Higher horsepower and torque |
| Engine Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | More complex, requires additional parts |
| Throttle Response | Immediate and linear | Potential lag (turbo lag) or instant (supercharger) |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance cost | Higher maintenance due to added components |
| Fuel Efficiency | Generally less efficient at high power | More efficient under boost, can improve economy |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial and upgrade cost |
| Heat Generation | Lower engine temperatures | Increased heat, requires intercooling |
Understanding Naturally Aspirated Engines
Naturally aspirated engines rely on atmospheric pressure to draw air into the combustion chamber, providing a linear throttle response and simpler design without the need for turbochargers or superchargers. They typically offer more predictable power delivery and smoother acceleration, making them favored for applications prioritizing reliability and drivability. Understanding their limitations in air intake efficiency explains why forced induction systems are often adopted for increased performance and power output.
What Is Forced Induction?
Forced induction is a method used to increase an engine's power output by compressing the intake air, allowing more oxygen to enter the combustion chamber. This process is commonly achieved through turbochargers or superchargers, which boost air density and improve combustion efficiency. Unlike naturally aspirated engines that rely on atmospheric pressure, forced induction engines deliver significantly higher horsepower and torque.
Key Differences: NA vs Forced Induction
Naturally aspirated engines rely solely on atmospheric pressure for air intake, resulting in linear power delivery and simpler mechanical design. Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, compress intake air to increase oxygen availability, significantly boosting horsepower and torque. Key differences include response time, complexity, thermal management, and overall efficiency, with forced induction typically offering higher performance at the cost of increased mechanical stress.
Performance Benefits of Naturally Aspirated Engines
Naturally aspirated engines deliver linear throttle response and predictable power delivery, enhancing driver control during performance driving. These engines often provide a more immediate and consistent torque curve, which can improve handling and acceleration feel without lag. The simplicity of naturally aspirated setups reduces mechanical complexity, resulting in potentially greater reliability and easier maintenance compared to forced induction systems.
Forced Induction: Turbocharging and Supercharging Explained
Forced induction enhances engine performance by increasing air intake using turbocharging or supercharging methods. Turbochargers utilize exhaust gases to spin a turbine, compressing air before entering the combustion chamber, which improves power and efficiency. Superchargers, driven mechanically by the engine, deliver instant boost and better throttle response, making them ideal for immediate power gains in performance vehicles.
Reliability and Maintenance Comparison
Naturally aspirated engines generally offer higher reliability and simpler maintenance due to fewer components like turbochargers or superchargers that can fail or require servicing. Forced induction systems deliver increased power output but often demand more frequent maintenance, such as intercooler inspections and turbo oil changes, to ensure longevity. Choosing between them involves weighing the trade-off between enhanced performance and the potential for increased mechanical complexity and upkeep costs.
Cost and Complexity of Modifications
Naturally aspirated engines typically incur lower costs and simpler modifications, as they require fewer specialized components like intercoolers, turbochargers, or superchargers. Forced induction systems involve higher complexity due to the need for upgraded fuel injectors, reinforced engine internals, and advanced tuning to manage increased pressure and heat. Maintenance expenses also rise with forced induction setups, reflecting the intricate engineering and higher failure risk of added components.
Tuning Potential: NA vs Forced Induction
Naturally aspirated engines offer linear throttle response and predictable tuning characteristics but are limited in power gains without extensive internal modifications. Forced induction systems, such as turbocharging or supercharging, provide significantly higher tuning potential by increasing air intake pressure, allowing substantial horsepower and torque improvements with proper boost management and supporting modifications. Effective tuning of forced induction engines involves optimizing fuel delivery, ignition timing, and boost control to maximize performance while maintaining reliability.
Everyday Driveability and Response
Naturally aspirated engines offer linear throttle response and smooth power delivery, making them ideal for everyday drivability with predictable acceleration. Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, provide increased power and torque but may introduce turbo lag or boost threshold delays affecting immediate throttle response. For daily driving, naturally aspirated setups often ensure consistent performance and easier maintenance, while forced induction enhances power but can require more careful driving to manage response variability.
Which Setup Is Right for Your Car Build?
Choosing between naturally aspirated and forced induction depends on your car build goals, budget, and intended performance. Naturally aspirated engines offer linear power delivery and reliability, ideal for daily driving and smooth throttle response. Forced induction setups, such as turbocharging or supercharging, provide significant power boosts and efficiency but require careful tuning and stronger internals to handle increased stress.
Naturally Aspirated vs Forced Induction Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com