Choosing between an engine swap and an engine build for your modified vehicle depends on your performance goals and budget. An engine swap offers a quick upgrade by replacing the entire engine with a more powerful or modern unit, often enhancing reliability and horsepower. In contrast, an engine build focuses on customizing and upgrading the existing engine components to increase power and efficiency while maintaining the original engine architecture.
Table of Comparison
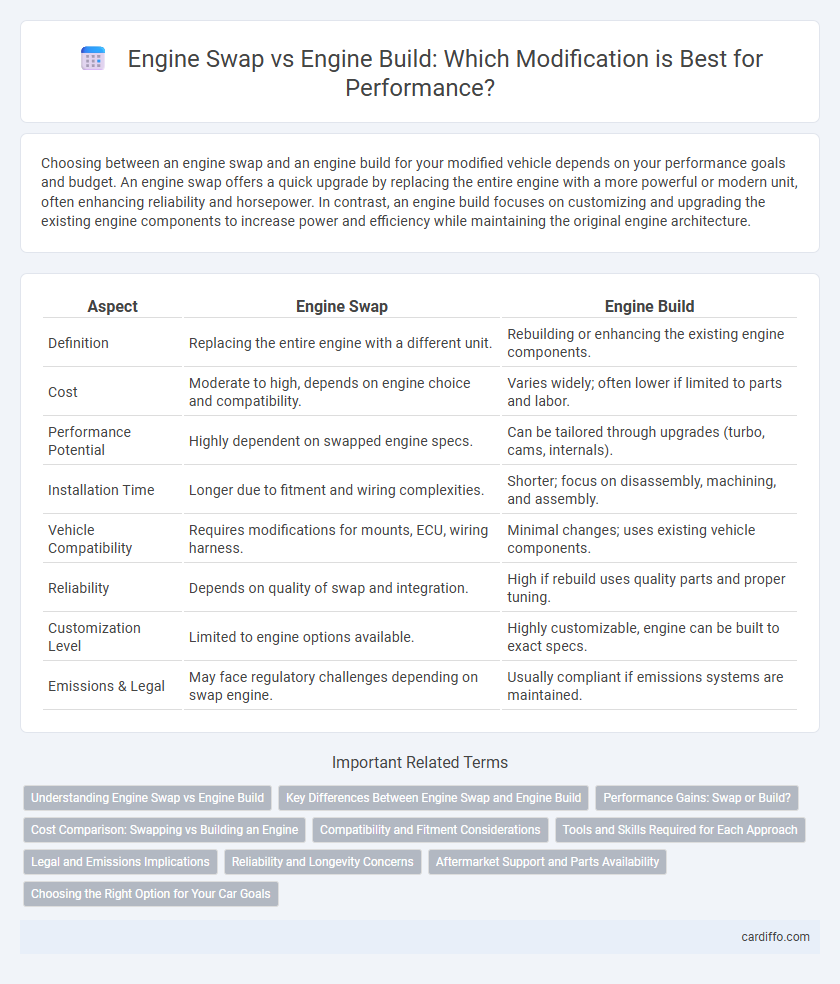
| Aspect | Engine Swap | Engine Build |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Replacing the entire engine with a different unit. | Rebuilding or enhancing the existing engine components. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depends on engine choice and compatibility. | Varies widely; often lower if limited to parts and labor. |
| Performance Potential | Highly dependent on swapped engine specs. | Can be tailored through upgrades (turbo, cams, internals). |
| Installation Time | Longer due to fitment and wiring complexities. | Shorter; focus on disassembly, machining, and assembly. |
| Vehicle Compatibility | Requires modifications for mounts, ECU, wiring harness. | Minimal changes; uses existing vehicle components. |
| Reliability | Depends on quality of swap and integration. | High if rebuild uses quality parts and proper tuning. |
| Customization Level | Limited to engine options available. | Highly customizable, engine can be built to exact specs. |
| Emissions & Legal | May face regulatory challenges depending on swap engine. | Usually compliant if emissions systems are maintained. |
Understanding Engine Swap vs Engine Build
Engine swap involves replacing an existing engine with a completely different unit, often to increase power or upgrade technology, while an engine build focuses on enhancing the original engine's components for improved performance and reliability. Swapping engines can require modifications to mounts, wiring, and the transmission system to ensure compatibility, whereas building an engine centers on upgrading pistons, camshafts, and the fuel system within the same engine block. Choosing between an engine swap and a build depends on budget, goals, and the desired balance between originality and performance enhancement.
Key Differences Between Engine Swap and Engine Build
Engine swap involves replacing the original engine with a different one, often to increase power, improve reliability, or change engine characteristics, while an engine build focuses on modifying and upgrading the existing engine components for better performance. Engine swaps require compatibility considerations such as motor mounts, wiring harnesses, and ECU tuning, whereas engine builds concentrate on internal parts like pistons, camshafts, and cylinder heads. Cost and complexity vary, with swaps potentially involving higher initial expense and custom fabrication, whereas builds allow for incremental upgrades tailored to specific power goals.
Performance Gains: Swap or Build?
Engine swaps often provide immediate and substantial performance gains by installing a more powerful or modern engine, bypassing limitations of the original powerplant. Engine builds enhance performance incrementally through precision upgrades like forged pistons, camshafts, and turbochargers, optimizing reliability and efficiency. Choosing between a swap or build depends on desired power output, budget constraints, and compatibility with the vehicle's existing systems.
Cost Comparison: Swapping vs Building an Engine
Swapping an engine typically involves higher initial costs due to purchasing a complete replacement unit and potential labor expenses for installation and calibration. Building an engine usually incurs variable costs tied to parts quality and customization, often leading to a more budget-friendly option for performance improvements. Long-term maintenance costs may be lower for a built engine, as components are new or upgraded, reducing the risk of future repairs compared to a used swapped engine.
Compatibility and Fitment Considerations
Engine swaps require thorough compatibility checks to ensure the donor engine aligns with the vehicle's existing mounts, transmission, and electronic systems, preventing fitment issues and costly modifications. Engine builds focus on internal improvements without altering the vehicle's original architecture, maintaining factory compatibility and reducing integration challenges. Proper measurement of engine bay dimensions and assessment of wiring harness adaptability are critical to successful engine swaps compared to the more straightforward fitment of engine builds.
Tools and Skills Required for Each Approach
Engine swaps require specialized mechanical tools such as hoists, engine stands, and custom wiring harnesses, along with skills in dismantling, fitting, and integrating components for compatibility. Engine builds demand precision tools including torque wrenches, bore gauges, and machining equipment, alongside advanced skills in engine assembly, balancing, and tuning for optimal performance. Mastery in diagnostic tools and software is essential for both approaches to ensure reliability and efficiency.
Legal and Emissions Implications
Engine swaps often face stricter legal scrutiny and emissions testing, as replacing the original engine may violate local regulations and emissions standards. Engine builds, which involve enhancing or rebuilding the existing engine, typically retain compliance with vehicle certification, making them less likely to trigger legal or emissions issues. Understanding regional laws and emissions requirements is essential to ensure modifications remain street-legal and avoid costly fines or vehicle impoundment.
Reliability and Longevity Concerns
Engine swaps often introduce compatibility challenges that can affect reliability, such as wiring harness integration or ECU mapping issues, potentially leading to long-term mechanical failures. In contrast, engine builds prioritize internal component upgrades and precision tuning to enhance durability and consistent performance without the risks associated with mismatched parts. Selecting quality forged internals and balanced assemblies during a build significantly improves engine longevity compared to many swap scenarios.
Aftermarket Support and Parts Availability
Engine swaps benefit from extensive aftermarket support and wide availability of compatible components, making it easier to source parts and upgrade options. Engine builds require specialized aftermarket parts tailored to specific configurations, often necessitating custom fabrication for performance enhancements. Access to a vast range of off-the-shelf parts favors engine swaps, while engine builds leverage niche aftermarket solutions for precision tuning and reliability.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Car Goals
Selecting between an engine swap and an engine build depends on your car's performance goals, budget, and long-term reliability preferences. An engine swap offers immediate power upgrades by installing a more powerful or newer engine, making it ideal for those seeking quick performance gains. In contrast, an engine build allows for customized enhancements within the existing engine, providing tailored power and durability improvements while retaining original components.
engine swap vs engine build Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com