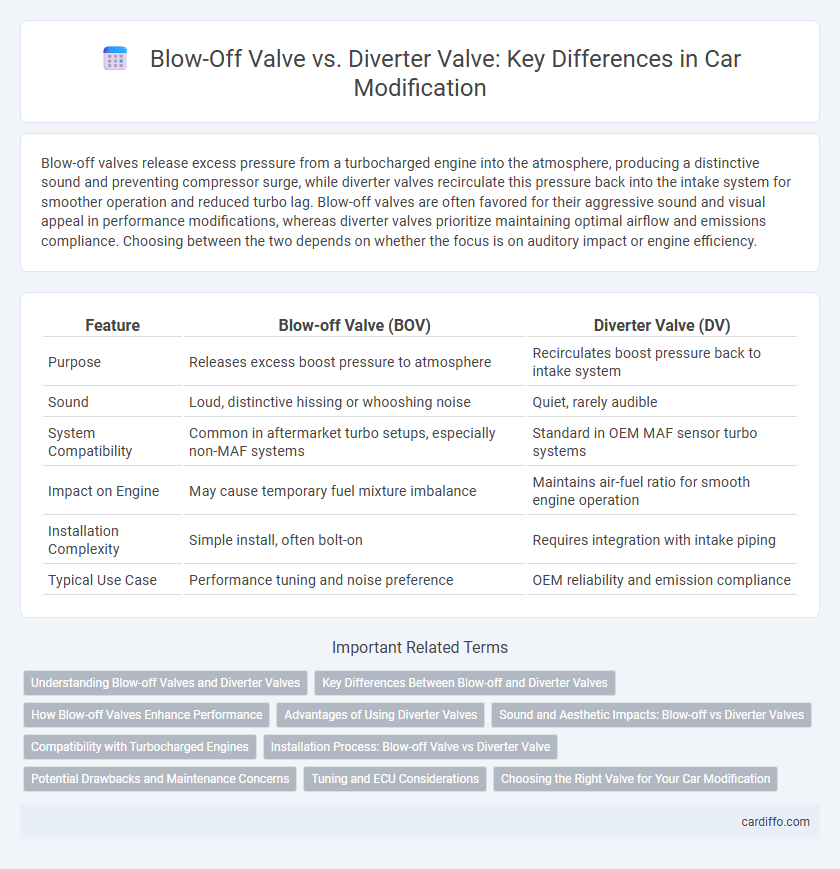
Blow-off valves release excess pressure from a turbocharged engine into the atmosphere, producing a distinctive sound and preventing compressor surge, while diverter valves recirculate this pressure back into the intake system for smoother operation and reduced turbo lag. Blow-off valves are often favored for their aggressive sound and visual appeal in performance modifications, whereas diverter valves prioritize maintaining optimal airflow and emissions compliance. Choosing between the two depends on whether the focus is on auditory impact or engine efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Blow-off Valve (BOV) | Diverter Valve (DV) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Releases excess boost pressure to atmosphere | Recirculates boost pressure back to intake system |
| Sound | Loud, distinctive hissing or whooshing noise | Quiet, rarely audible |
| System Compatibility | Common in aftermarket turbo setups, especially non-MAF systems | Standard in OEM MAF sensor turbo systems |
| Impact on Engine | May cause temporary fuel mixture imbalance | Maintains air-fuel ratio for smooth engine operation |
| Installation Complexity | Simple install, often bolt-on | Requires integration with intake piping |
| Typical Use Case | Performance tuning and noise preference | OEM reliability and emission compliance |
Understanding Blow-off Valves and Diverter Valves
Blow-off valves (BOVs) and diverter valves (DVs) both manage excess boost pressure in turbocharged engines, preventing compressor surge and protecting the turbocharger. A blow-off valve releases excess pressure into the atmosphere, producing a distinct hissing sound and reducing stress on the intake system, while a diverter valve reroutes the pressure back into the intake system for smoother operation and emissions compliance. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate valve based on performance goals, sound preference, and engine configuration.
Key Differences Between Blow-off and Diverter Valves
Blow-off valves release excess pressure from the turbocharger system into the atmosphere, producing an audible whoosh sound, while diverter valves recirculate the excess pressure back into the intake system to reduce turbo lag and improve efficiency. Blow-off valves are commonly used in aftermarket modifications for aggressive sound and aesthetics, whereas diverter valves are typically OEM components designed to protect the turbo and maintain emissions compliance. The main difference lies in pressure release location and impact on engine performance, with blow-off valves venting outside and diverter valves rerouting internally.
How Blow-off Valves Enhance Performance
Blow-off valves enhance performance by quickly releasing excess turbo boost pressure, preventing compressor surge and protecting the turbocharger from damage. This rapid pressure relief improves turbo spool time, resulting in faster throttle response and reduced turbo lag. Compared to diverter valves that recirculate air back into the intake, blow-off valves provide audible feedback and more effective pressure management for high-performance turbocharged engines.
Advantages of Using Diverter Valves
Diverter valves improve turbocharger efficiency by redirecting excess boost pressure back into the intake system, reducing turbo lag and enhancing throttle response. They maintain optimal boost levels and prevent compressor surge, leading to increased engine longevity compared to blow-off valves. Their design helps preserve engine performance during gear changes and rapid deceleration, making them ideal for turbocharged vehicles seeking smoother power delivery and better drivability.
Sound and Aesthetic Impacts: Blow-off vs Diverter Valves
Blow-off valves produce a distinct, sharp hissing sound during boost release, enhancing the aggressive audio signature preferred by many car enthusiasts, while diverter valves operate quietly, maintaining a stock-like appearance and sound that appeals to those seeking subtle modifications. Visually, blow-off valves are often exposed on the intake piping, adding an aggressive, aftermarket aesthetic, whereas diverter valves are integrated into the turbo system, resulting in a cleaner under-hood look. The choice between blow-off and diverter valves significantly influences both the acoustic and visual character of a turbocharged vehicle.
Compatibility with Turbocharged Engines
Blow-off valves and diverter valves both serve to release excess pressure in turbocharged engines, but their compatibility varies based on engine design and turbo system configuration. Blow-off valves are typically compatible with engines that vent to the atmosphere, providing audible pressure release, while diverter valves recirculate excess boost back into the intake system, making them ideal for modern turbocharged engines with mass airflow sensors to prevent check engine lights. Selecting the appropriate valve ensures optimal turbocharger performance, pressure management, and engine reliability across various turbocharged platforms.
Installation Process: Blow-off Valve vs Diverter Valve
Installing a blow-off valve (BOV) requires cutting or replacing a section of the turbocharger wastegate or boost control line, often involving welding or precise fitting to ensure proper boost release. Diverter valves (DV) generally offer a simpler installation process, as they are designed to fit directly into the factory recirculation system without requiring extensive modifications, often utilizing OEM mounting points and connectors. Choosing between a BOV and DV installation hinges on compatibility with the vehicle's intake system and the desired ease of retrofit.
Potential Drawbacks and Maintenance Concerns
Blow-off valves (BOVs) can cause issues with modern turbocharged engines by disrupting the mass airflow sensor readings, leading to potential engine stalling and decreased fuel efficiency. Diverter valves (DVs) generally minimize this problem by recirculating the excess boost air back into the intake, but they are often more complex and may require frequent inspections to ensure proper diaphragm function. Both valves demand regular maintenance to prevent leaks, diaphragm wear, and degraded performance, with BOVs typically needing more attention due to their exposure to atmospheric conditions.
Tuning and ECU Considerations
Blow-off valves (BOVs) and diverter valves (DVs) serve distinct functions in turbocharged engine tuning, with BOVs venting excess boost pressure to the atmosphere, creating a distinctive sound, while DVs recirculate pressure back into the intake system to maintain boost levels and protect the turbo. ECU tuning must accommodate the chosen valve type to prevent issues such as check engine lights or lean conditions, with some factory ECUs programmed specifically for the stock diverter valve operation. Proper calibration ensures optimal boost control, throttle response, and overall engine reliability when integrating either a blow-off or diverter valve in modified turbo setups.
Choosing the Right Valve for Your Car Modification
Choosing the right valve for your car modification hinges on understanding their distinct functions: blow-off valves release excess turbo pressure to prevent compressor surge, while diverter valves reroute this pressure back into the intake system to maintain turbo speed. Blow-off valves are ideal for vehicles with atmospheric intake systems, offering audible turbo sound enhancements, whereas diverter valves suit cars with recirculating systems, ensuring smoother performance and improved efficiency. Selecting the appropriate valve depends on your turbo setup, driving style, and desired balance between sound and performance in your modification project.
Blow-off Valve vs Diverter Valve Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com