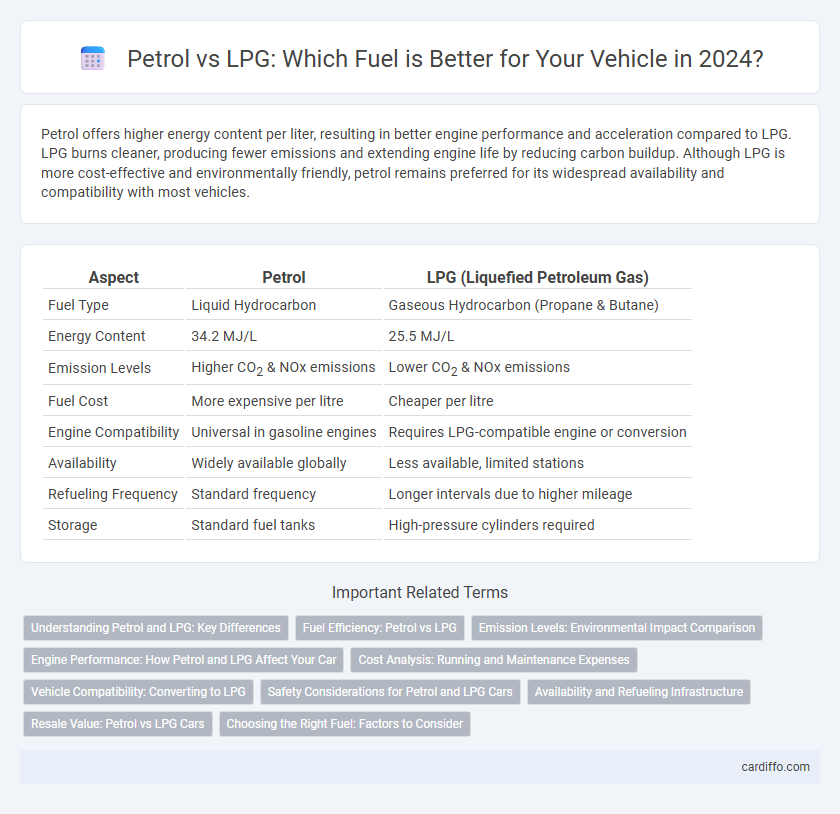
Petrol offers higher energy content per liter, resulting in better engine performance and acceleration compared to LPG. LPG burns cleaner, producing fewer emissions and extending engine life by reducing carbon buildup. Although LPG is more cost-effective and environmentally friendly, petrol remains preferred for its widespread availability and compatibility with most vehicles.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Petrol | LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Liquid Hydrocarbon | Gaseous Hydrocarbon (Propane & Butane) |
| Energy Content | 34.2 MJ/L | 25.5 MJ/L |
| Emission Levels | Higher CO2 & NOx emissions | Lower CO2 & NOx emissions |
| Fuel Cost | More expensive per litre | Cheaper per litre |
| Engine Compatibility | Universal in gasoline engines | Requires LPG-compatible engine or conversion |
| Availability | Widely available globally | Less available, limited stations |
| Refueling Frequency | Standard frequency | Longer intervals due to higher mileage |
| Storage | Standard fuel tanks | High-pressure cylinders required |
Understanding Petrol and LPG: Key Differences
Petrol and LPG are both popular fuels used in vehicles, but they differ significantly in composition, energy content, and environmental impact. Petrol, a liquid hydrocarbon, has higher energy density and faster combustion but produces more carbon emissions compared to LPG, a gaseous mixture primarily of propane and butane, known for cleaner burning and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing fuel efficiency, engine performance, and reducing environmental footprint in transportation.
Fuel Efficiency: Petrol vs LPG
LPG typically offers better fuel efficiency compared to petrol, as it has a higher octane rating allowing engines to operate at higher compression ratios. Vehicles running on LPG often achieve improved mileage and lower fuel consumption due to cleaner combustion and reduced engine knocking. However, the energy content per liter of petrol is higher, which can result in slightly longer driving ranges between refueling.
Emission Levels: Environmental Impact Comparison
Petrol engines emit higher levels of carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter compared to LPG, which produces significantly lower CO2 and nearly zero particulate emissions. LPG combustion results in reduced greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to improved air quality and decreased environmental pollution. Transitioning from petrol to LPG can effectively lower a vehicle's carbon footprint and decrease smog-forming pollutants in urban areas.
Engine Performance: How Petrol and LPG Affect Your Car
Petrol engines deliver higher power output and acceleration due to petrol's superior energy density and combustion efficiency. LPG engines run cleaner, producing fewer emissions and offering smoother operation, though they may experience a slight reduction in engine power compared to petrol. Choosing between petrol and LPG impacts overall engine performance, fuel economy, and environmental footprint.
Cost Analysis: Running and Maintenance Expenses
Petrol vehicles generally incur higher running costs due to frequent refueling and increased fuel consumption compared to LPG, which is more economical per kilometer. Maintenance expenses for LPG systems can be slightly higher initially due to installation and periodic system checks but tend to balance out with overall savings on fuel costs. LPG's lower carbon emissions also reduce engine wear, potentially decreasing long-term maintenance expenditures.
Vehicle Compatibility: Converting to LPG
Vehicles originally designed for petrol engines often require specialized conversion kits to run efficiently on LPG, involving modifications to the fuel system, ignition timing, and engine calibration. LPG-compatible engines experience different combustion characteristics, necessitating adjustments to ensure optimal performance and emissions compliance. Properly converted petrol vehicles can benefit from LPG's lower fuel costs and reduced carbon emissions without compromising drivability or engine longevity.
Safety Considerations for Petrol and LPG Cars
Petrol cars carry a higher risk of fire and explosion due to the volatile nature of gasoline vapors, requiring stringent handling and storage precautions. LPG vehicles have enhanced safety features such as automatic shut-off valves and pressure relief devices to prevent leaks and reduce the risk of combustion. Both fuels necessitate regular maintenance and proper tank inspections to ensure safe operation and minimize accident risks.
Availability and Refueling Infrastructure
Petrol benefits from an extensive global availability with a well-established refueling infrastructure, making it accessible in urban and rural areas worldwide. LPG, while offering cleaner combustion, has a more limited network of refueling stations concentrated mainly in specific regions or countries with supportive policies. The disparity in infrastructure impacts convenience and adoption rates, with petrol retaining dominance due to its widespread supply chain and rapid refueling capabilities.
Resale Value: Petrol vs LPG Cars
Petrol cars generally have a higher resale value compared to LPG vehicles due to wider market demand and more established refueling infrastructure. LPG cars often face depreciation because of limited fueling stations and concerns about engine compatibility, impacting buyer preference. However, LPG vehicles may attract niche buyers focused on fuel cost savings and environmental benefits, influencing their resale dynamics.
Choosing the Right Fuel: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right fuel between petrol and LPG depends on factors such as fuel efficiency, cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and vehicle compatibility. Petrol offers higher energy content and better performance, while LPG provides lower emissions and reduced fuel expenses. Assessing regional fuel availability and maintenance requirements ensures optimal long-term benefits for your specific vehicle and driving habits.
Petrol vs LPG Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com