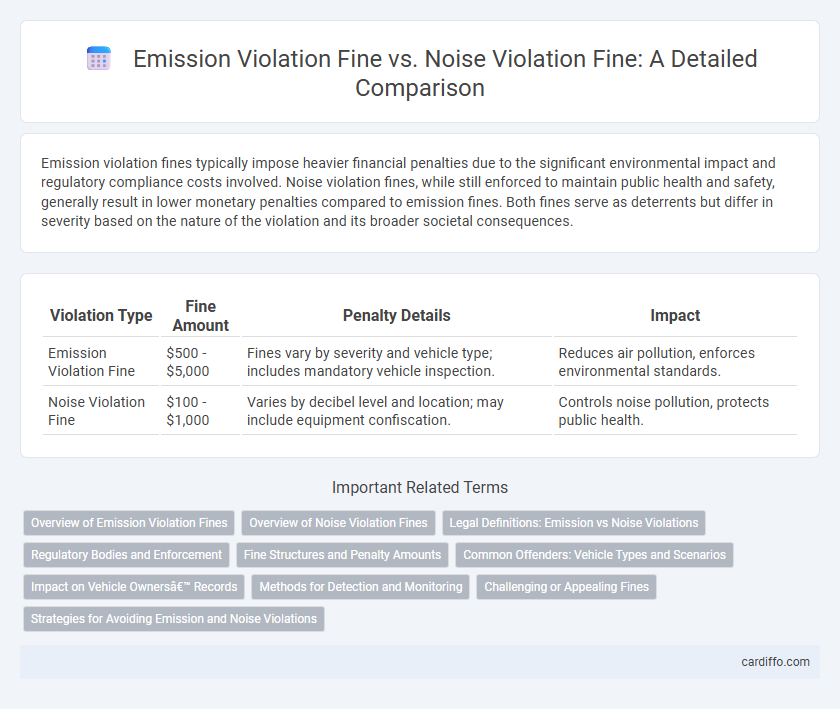
Emission violation fines typically impose heavier financial penalties due to the significant environmental impact and regulatory compliance costs involved. Noise violation fines, while still enforced to maintain public health and safety, generally result in lower monetary penalties compared to emission fines. Both fines serve as deterrents but differ in severity based on the nature of the violation and its broader societal consequences.
Table of Comparison
| Violation Type | Fine Amount | Penalty Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emission Violation Fine | $500 - $5,000 | Fines vary by severity and vehicle type; includes mandatory vehicle inspection. | Reduces air pollution, enforces environmental standards. |
| Noise Violation Fine | $100 - $1,000 | Varies by decibel level and location; may include equipment confiscation. | Controls noise pollution, protects public health. |
Overview of Emission Violation Fines
Emission violation fines are monetary penalties imposed for exceeding permissible levels of pollutants released into the environment, primarily targeting vehicles and industrial sources. These fines aim to enforce compliance with environmental regulations such as the Clean Air Act in the United States and similar frameworks worldwide. The amount of the fine typically depends on the severity of the violation, type of pollutant emitted, and whether the offense is a repeat occurrence.
Overview of Noise Violation Fines
Noise violation fines vary widely by jurisdiction, typically imposed for exceeding decibel limits in residential, commercial, or industrial areas. Penalties often include monetary fines ranging from $50 to over $1,000, with repeat offenders facing increased charges or legal action. Enforcement relies on measurements using decibel meters and complaints from residents or authorities to maintain community noise standards.
Legal Definitions: Emission vs Noise Violations
Emission violation fines are imposed for exceeding legally established limits on pollutants released into the air, typically regulated under environmental protection laws such as the Clean Air Act in the United States. Noise violation fines address breaches of permissible sound levels in residential, commercial, or industrial zones, governed by local noise control ordinances and regulations. Legal definitions distinguish emission violations by the measurable concentration of pollutants like carbon monoxide or nitrogen oxides, while noise violations are defined by decibel thresholds and time restrictions to prevent excessive sound disturbances.
Regulatory Bodies and Enforcement
Emission violation fines are primarily enforced by environmental regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, which monitor air quality standards and impose penalties for non-compliance with emission limits. Noise violation fines fall under the jurisdiction of local government agencies or municipal noise control boards that regulate sound levels in residential and commercial areas, often applying specific decibel limits. Both enforcement mechanisms rely on regular inspections, reports from monitoring devices, and public complaints to ensure adherence to environmental and public health regulations.
Fine Structures and Penalty Amounts
Emission violation fines typically involve a tiered penalty structure based on the severity of the offense, with initial fines ranging from $100 to $1,000 and escalating to thousands for repeat violations or excessive emissions. Noise violation fines are often fixed or scaled according to decibel levels and time of day, generally starting around $50 and increasing to several hundred dollars for persistent disturbances or violations during restricted hours. Both fine structures emphasize deterrence, but emission fines tend to incur higher financial penalties reflecting their environmental impact.
Common Offenders: Vehicle Types and Scenarios
Emission violation fines most frequently target diesel trucks, older gasoline cars, and vehicles with tampered or faulty catalytic converters, especially in urban areas with strict air quality regulations. Noise violation fines are commonly issued to motorcycles, modified cars with aftermarket exhausts, and commercial vehicles operating after-hours near residential zones. Both fines often arise from scenarios involving repeated offenses in densely populated or environmentally sensitive regions.
Impact on Vehicle Owners’ Records
Emission violation fines often lead to mandatory vehicle inspections and recorded penalties that can affect a vehicle owner's compliance history, potentially increasing insurance premiums. Noise violation fines usually result in less severe record implications but may still be documented by local enforcement agencies, impacting the owner's standing in community enforcement databases. Both fines can influence future legal scrutiny, but emission violations typically carry longer-lasting effects on a vehicle owner's official records.
Methods for Detection and Monitoring
Emission violation fines are primarily enforced through continuous air quality monitoring systems and remote sensing technologies like infrared cameras and gas analyzers that detect pollutant levels exceeding regulatory limits. Noise violation fines rely on sound level meters and automated noise monitoring stations strategically placed in urban areas to measure decibel levels and record time-stamped data for compliance assessment. Both methods employ real-time data acquisition and analysis, enabling authorities to identify violations promptly and impose fines based on documented evidence.
Challenging or Appealing Fines
Challenging an emission violation fine often requires presenting evidence of proper vehicle maintenance, valid emission test results, or errors in testing procedures. Appealing a noise violation fine typically involves demonstrating compliance with local noise ordinances, providing proof of permitted activity, or disputing the accuracy of noise measurements. Both violations demand thorough documentation and understanding of specific regulatory frameworks to increase the likelihood of a successful appeal.
Strategies for Avoiding Emission and Noise Violations
Implementing regular vehicle maintenance and adhering to local emission standards significantly reduces the risk of emission violation fines. Utilizing noise-dampening technologies and observing prescribed quiet hours mitigate noise violation penalties effectively. Consistent monitoring through onboard diagnostic tools and sound level meters ensures compliance with environmental regulations.
Emission Violation Fine vs Noise Violation Fine Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com