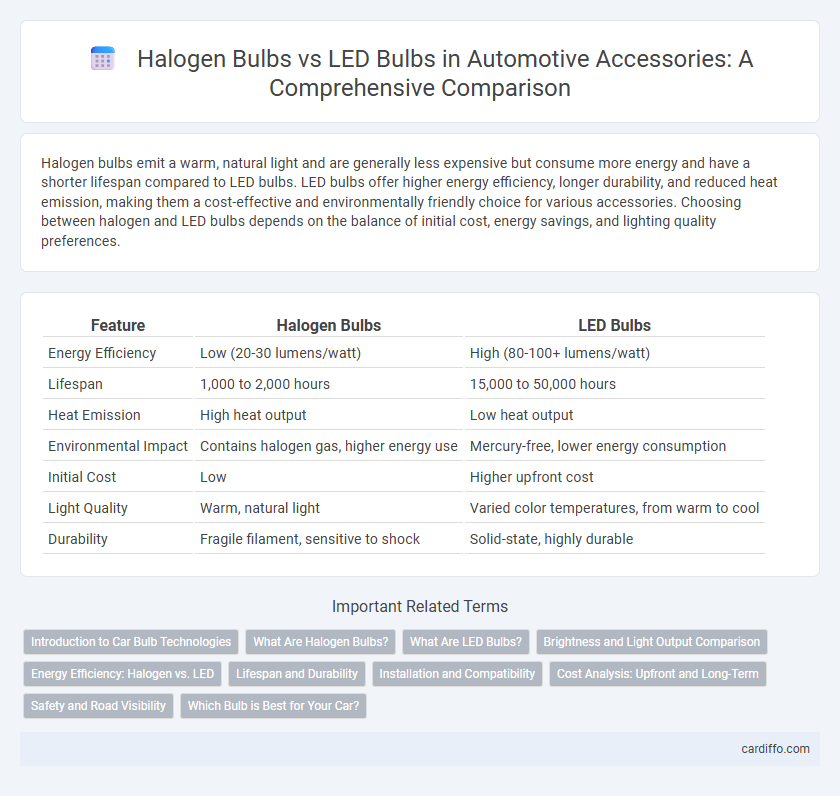
Halogen bulbs emit a warm, natural light and are generally less expensive but consume more energy and have a shorter lifespan compared to LED bulbs. LED bulbs offer higher energy efficiency, longer durability, and reduced heat emission, making them a cost-effective and environmentally friendly choice for various accessories. Choosing between halogen and LED bulbs depends on the balance of initial cost, energy savings, and lighting quality preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Halogen Bulbs | LED Bulbs |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Low (20-30 lumens/watt) | High (80-100+ lumens/watt) |
| Lifespan | 1,000 to 2,000 hours | 15,000 to 50,000 hours |
| Heat Emission | High heat output | Low heat output |
| Environmental Impact | Contains halogen gas, higher energy use | Mercury-free, lower energy consumption |
| Initial Cost | Low | Higher upfront cost |
| Light Quality | Warm, natural light | Varied color temperatures, from warm to cool |
| Durability | Fragile filament, sensitive to shock | Solid-state, highly durable |
Introduction to Car Bulb Technologies
Halogen bulbs operate by heating a tungsten filament inside a halogen gas-filled capsule, producing bright, warm-colored light with a relatively short lifespan and higher energy consumption. LED bulbs use semiconductor technology to emit light efficiently, offering longer durability, lower power usage, and cooler operation compared to halogen bulbs. Advances in LED technology have enabled improved brightness, color accuracy, and compatibility with modern vehicle electrical systems, making them increasingly popular in automotive lighting.
What Are Halogen Bulbs?
Halogen bulbs are a type of incandescent lighting that uses halogen gas to increase brightness and lifespan compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. They produce light by heating a tungsten filament, offering a warm color temperature and high color rendering index (CRI). Halogen bulbs consume more energy and generate more heat than LED bulbs, making them less energy-efficient for modern lighting needs.
What Are LED Bulbs?
LED bulbs are energy-efficient light sources that use light-emitting diodes to produce illumination. They consume significantly less power compared to halogen bulbs and offer longer lifespan, reducing replacement frequency in accessories like lamps and automotive lighting. LED technology also emits less heat, enhancing safety and durability in various accessory applications.
Brightness and Light Output Comparison
Halogen bulbs typically emit a warm, bright light with a luminous efficacy around 16-24 lumens per watt, resulting in a lower light output compared to LED bulbs. LED bulbs provide superior brightness, producing up to 80-100 lumens per watt, making them more energy-efficient with higher luminous intensity. When comparing light output, LED bulbs offer better illumination and longer lifespan, ideal for accessory lighting needing consistent, powerful brightness.
Energy Efficiency: Halogen vs. LED
LED bulbs consume up to 85% less energy than halogen bulbs while producing the same amount of light, making them significantly more energy-efficient. Halogen bulbs convert most of their energy into heat rather than light, resulting in higher electricity costs and shorter lifespan. Choosing LED bulbs reduces power consumption and lowers utility bills, offering sustainable lighting solutions for both residential and commercial use.
Lifespan and Durability
Halogen bulbs typically have a lifespan of around 2,000 hours, whereas LED bulbs last significantly longer, often exceeding 25,000 hours. The durability of LED bulbs is superior due to their solid-state construction, making them more resistant to shocks and vibrations compared to the fragile filament inside halogen bulbs. This extended lifespan and enhanced durability make LED bulbs a more cost-effective and reliable accessory choice for long-term use.
Installation and Compatibility
Halogen bulbs typically require standard fixtures and simple installation, making them compatible with most existing lighting systems without modification. LED bulbs often need compatible drivers or transformers, especially for dimmable setups, which may require additional installation steps or fixture updates. Compatibility issues arise primarily when replacing halogen bulbs with LED alternatives, necessitating careful selection to ensure proper fit and voltage matching.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Halogen bulbs typically have a lower upfront cost but consume more energy and have a shorter lifespan, leading to higher long-term expenses. LED bulbs, while more expensive initially, offer significant savings through lower energy consumption and durability, often lasting up to 25,000 hours compared to halogen's 2,000 hours. Evaluating the total cost of ownership reveals that LED bulbs provide better economic value over time despite the higher initial investment.
Safety and Road Visibility
Halogen bulbs emit a warm, bright light that provides decent road visibility but generate more heat, increasing the risk of bulb damage or fire hazards. LED bulbs offer superior brightness with a whiter, more intense light, enhancing road visibility and reaction times while operating at lower temperatures for improved safety. The longer lifespan and lower energy consumption of LED bulbs also reduce maintenance needs and electrical strain on vehicle systems.
Which Bulb is Best for Your Car?
LED bulbs offer superior energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and brighter, more focused light compared to halogen bulbs, making them an excellent choice for car headlights. Halogen bulbs are generally less expensive and easier to replace, but they produce more heat and consume more power, which can affect overall vehicle performance. For optimal visibility and durability, LED bulbs are often the best option for modern vehicles, especially for drivers seeking enhanced safety and reduced maintenance.
Halogen bulbs vs LED bulbs Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com