Fog lights are designed to improve visibility in foggy, rainy, or misty conditions by emitting a wide, low beam that reduces glare and illuminates the road close to the vehicle. Driving lights provide a powerful, focused beam intended to supplement high beams for enhanced long-distance visibility on open roads and highways. Choosing the right accessory depends on driving conditions and whether near-range or far-range illumination is needed.
Table of Comparison
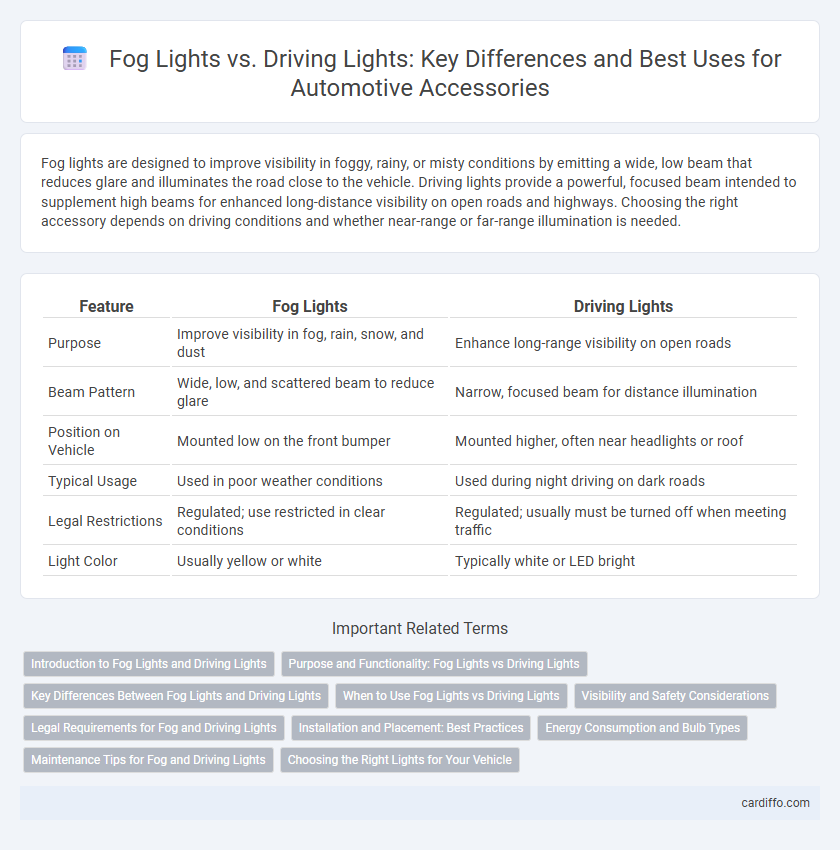
| Feature | Fog Lights | Driving Lights |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Improve visibility in fog, rain, snow, and dust | Enhance long-range visibility on open roads |
| Beam Pattern | Wide, low, and scattered beam to reduce glare | Narrow, focused beam for distance illumination |
| Position on Vehicle | Mounted low on the front bumper | Mounted higher, often near headlights or roof |
| Typical Usage | Used in poor weather conditions | Used during night driving on dark roads |
| Legal Restrictions | Regulated; use restricted in clear conditions | Regulated; usually must be turned off when meeting traffic |
| Light Color | Usually yellow or white | Typically white or LED bright |
Introduction to Fog Lights and Driving Lights
Fog lights are designed to improve visibility during fog, heavy rain, or snow by emitting a wide, low beam that reduces glare and illuminates the road close to the ground. Driving lights enhance long-range visibility by producing a focused, intense beam that complements high beams, allowing drivers to see farther in clear conditions. Both fog lights and driving lights serve distinct purposes, optimizing safety and visibility based on environmental needs.
Purpose and Functionality: Fog Lights vs Driving Lights
Fog lights are designed to emit a wide, low beam of light that minimizes glare and improves visibility in foggy, rainy, or snowy conditions by illuminating the road directly ahead. Driving lights provide a long-range, focused beam that enhances visibility at higher speeds and in clear conditions, complementing high beams for extended sight distance. Both accessories improve safety but serve distinct purposes: fog lights enhance close-range vision in poor weather, while driving lights increase long-distance visibility.
Key Differences Between Fog Lights and Driving Lights
Fog lights are designed to emit a wide, low beam pattern that cuts through fog, rain, and snow, improving visibility close to the ground. Driving lights provide a long-range, focused beam aimed at enhancing visibility at higher speeds on clear roads. The key difference lies in their beam patterns and intended use: fog lights reduce glare and illuminate road edges, while driving lights extend the driver's sight distance down the road.
When to Use Fog Lights vs Driving Lights
Fog lights are designed to improve visibility during low-visibility conditions such as fog, heavy rain, or snow by emitting a wide, bar-shaped beam that stays close to the road surface, reducing glare and illuminating the road edges. Driving lights provide a long-range, focused beam to supplement high beams when driving on dark, open roads without oncoming traffic, enhancing distance visibility and spotting hazards earlier. Use fog lights in adverse weather conditions to enhance road visibility without blinding other drivers, while driving lights are best for clear, rural roads requiring extended forward illumination.
Visibility and Safety Considerations
Fog lights improve visibility by emitting a wide, low beam that reduces glare and penetrates fog, rain, or snow, enhancing driver safety in poor weather conditions. Driving lights produce a focused, long-range beam that supplements high beams, increasing visibility on open roads without weather obstructions. Prioritizing fog lights in foggy conditions and driving lights on clear roads maximizes both visibility and safety.
Legal Requirements for Fog and Driving Lights
Fog lights are subject to strict legal requirements regarding their color, positioning, and usage to ensure they are only used in low-visibility conditions such as fog or heavy rain. Driving lights, designed to supplement high beams for improved long-range visibility, must comply with regulations limiting their brightness and aiming to prevent glare for other drivers. Both accessories require proper installation and alignment according to regional traffic laws to avoid penalties and ensure road safety.
Installation and Placement: Best Practices
Fog lights should be installed low on the vehicle's front bumper to minimize glare and illuminate the road directly under fog or heavy rain. Driving lights work best when mounted higher, near the grille or on the roof, providing long-range visibility for clear conditions. Proper alignment and secure placement are essential to maximize performance and comply with local regulations.
Energy Consumption and Bulb Types
Fog lights typically consume less energy due to lower wattage halogen or LED bulbs designed for short-range, wide-angle illumination in adverse weather conditions. Driving lights use higher wattage halogen, HID, or LED bulbs optimized for long-range, focused beams, resulting in increased power consumption. Choosing between fog lights and driving lights depends on balancing energy efficiency with the desired lighting performance and application.
Maintenance Tips for Fog and Driving Lights
Regularly inspect fog lights and driving lights for dirt buildup and moisture to maintain optimal brightness and functionality. Replace bulbs promptly when dimming or flickering occurs, using manufacturer-recommended types to prevent electrical issues. Ensure proper sealing and alignment during maintenance to avoid water damage and improve road visibility in adverse conditions.
Choosing the Right Lights for Your Vehicle
Fog lights improve visibility by cutting through fog, rain, and snow with a wide, low beam designed to reduce glare and illuminate the road surface. Driving lights provide long-range illumination with a focused, high-intensity beam, enhancing visibility on dark, open roads and highways. Selecting the right lights depends on your driving environment, prioritizing fog lights for adverse weather conditions and driving lights for extended distance visibility.
Fog lights vs driving lights Infographic
 cardiffo.com
cardiffo.com